Frontend development focuses on creating the user interface and experience by using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to ensure responsive and visually appealing designs. Backend development involves server-side logic, database management, and application functionality using languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js to handle data processing and API integrations. Effective software engineering requires seamless coordination between frontend and backend to deliver robust, scalable, and user-centric applications.
Table of Comparison
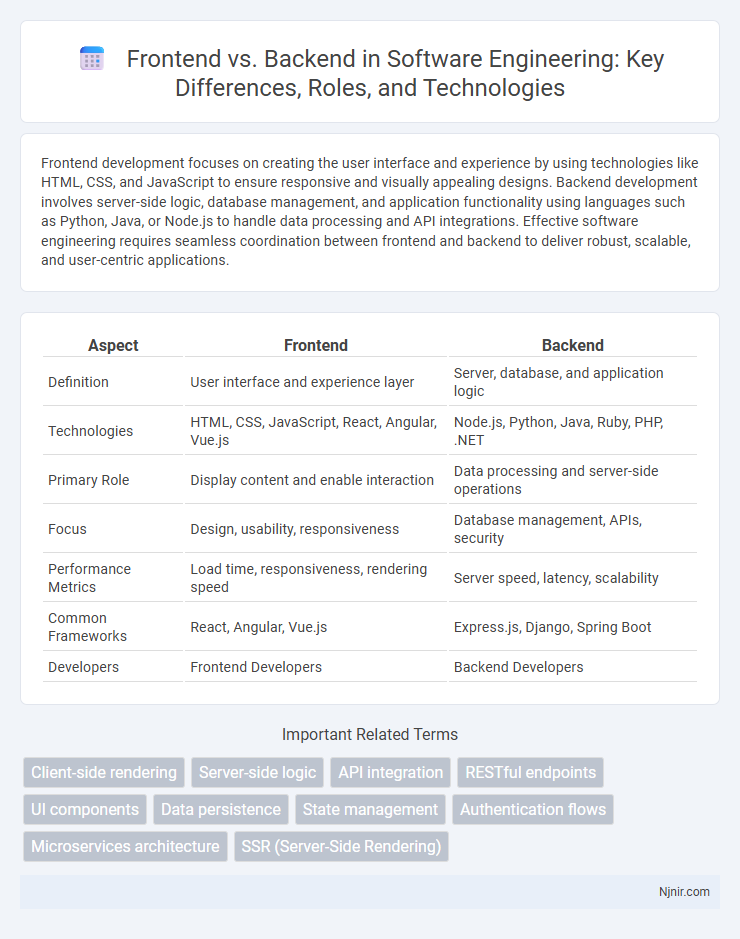
| Aspect | Frontend | Backend |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | User interface and experience layer | Server, database, and application logic |
| Technologies | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Angular, Vue.js | Node.js, Python, Java, Ruby, PHP, .NET |
| Primary Role | Display content and enable interaction | Data processing and server-side operations |
| Focus | Design, usability, responsiveness | Database management, APIs, security |
| Performance Metrics | Load time, responsiveness, rendering speed | Server speed, latency, scalability |
| Common Frameworks | React, Angular, Vue.js | Express.js, Django, Spring Boot |
| Developers | Frontend Developers | Backend Developers |
Overview of Frontend and Backend
Frontend development involves designing the user interface and experience using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to ensure responsive and interactive web applications. Backend development manages server-side logic, databases, and application functionality through languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js, enabling data processing and secure communication between the server and client. Both frontend and backend work together to create seamless, dynamic web experiences by handling user interaction and data management respectively.
Key Responsibilities of Frontend Development
Frontend development primarily involves designing and implementing the user interface to ensure seamless user experience through responsive layouts, interactive elements, and visual aesthetics. Developers utilize technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks such as React or Angular to create dynamic, accessible, and performant web pages. Key responsibilities also include optimizing cross-browser compatibility, enhancing website accessibility compliance (WCAG), and integrating APIs to connect frontend components with backend services.
Core Functions of Backend Development
Backend development focuses on server-side logic, database management, and API integration to ensure seamless data processing and storage. It handles user authentication, server configuration, and business logic implementation essential for application functionality. Core backend technologies include Node.js, Python, Ruby on Rails, and databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB.
Essential Technologies for Frontend
Essential frontend technologies include HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which form the foundation for building user interfaces and improving website interactivity. Frameworks and libraries like React, Angular, and Vue.js enable developers to create dynamic and responsive web applications efficiently. Tools such as Webpack, Babel, and NPM streamline the development process by optimizing code, managing dependencies, and facilitating modular design.
Popular Tools and Frameworks for Backend
Backend development relies heavily on robust tools and frameworks such as Node.js, which enables JavaScript runtime for server-side scripts, and Django, a high-level Python framework known for its security features and rapid development capabilities. Other popular backend tools include Ruby on Rails, valued for its convention over configuration philosophy, and Laravel, a PHP framework that offers elegant syntax and powerful features for scalable web applications. Database management systems like MySQL and MongoDB are integral to backend processes, providing structured and unstructured data handling for efficient information retrieval and storage.
User Experience in Frontend Engineering
Frontend engineering directly shapes user experience by designing intuitive interfaces, seamless navigation, and responsive layouts that enhance user satisfaction across devices. It employs technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks such as React or Angular to ensure fast loading times and interactive elements. Backend engineering supports this experience by managing databases, server logic, and APIs, enabling dynamic content and personalized user interactions.
Data Management in Backend Systems
Backend systems specialize in robust data management, handling storage, retrieval, and processing through databases like SQL, NoSQL, and data warehousing solutions. These systems ensure data integrity, security, and scalability by leveraging technologies such as server-side scripting, APIs, and cloud services. Efficient backend data management supports seamless interaction with frontend interfaces, enabling dynamic content delivery and personalized user experiences.
Collaboration Between Frontend and Backend
Effective collaboration between frontend and backend teams enhances website performance and user experience by ensuring seamless data flow and consistent design implementation. Utilizing APIs and clear communication protocols allows frontend developers to access backend services efficiently, reducing integration issues and streamlining updates. Shared version control systems like Git further facilitate coordinated development and quicker troubleshooting, bridging the gap between UI design and server-side logic.
Career Paths: Frontend vs Backend Engineers
Frontend engineers specialize in designing intuitive user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on visual aesthetics and user experience. Backend engineers develop server-side logic, databases, and APIs with languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js to ensure data processing and system functionality. Career paths diverge as frontend roles emphasize creativity and design skills, whereas backend roles require strong programming and problem-solving expertise in server environments.
Future Trends in Frontend and Backend Development
Front-end development is rapidly evolving with frameworks like React, Vue.js, and Svelte prioritizing performance, accessibility, and enhanced user experience through component-based architectures and server-side rendering techniques. Backend development is shifting towards microservices, containerization with Docker and Kubernetes, and adopting serverless architectures to improve scalability, security, and deployment speed. Emerging trends like AI-driven development, edge computing, and WebAssembly are expected to blur the lines between front-end and backend, enabling more seamless, intelligent, and efficient application ecosystems.
Client-side rendering
Client-side rendering improves user experience by dynamically generating web pages in the browser using JavaScript frameworks like React, reducing server load compared to traditional backend server-side rendering.
Server-side logic
Backend development handles server-side logic, managing databases, authentication, and application functionality, while frontend focuses on user interface and client-side interactions.
API integration
Effective API integration requires seamless collaboration between frontend interfaces for user interaction and backend systems for data processing and business logic.
RESTful endpoints
Frontend interfaces consume RESTful endpoints to dynamically render user experiences, while backend services manage data processing and business logic through those RESTful APIs.
UI components
Frontend development focuses on creating and optimizing UI components that enhance user interaction, while backend development manages data processing and server-side logic supporting those components.
Data persistence
Backend enables robust data persistence through databases and server-side logic, while frontend primarily handles user interface and presentation without directly managing data storage.
State management
Frontend state management optimizes user interface responsiveness by handling dynamic data locally, while backend state management ensures data consistency and persistence across distributed systems and user sessions.
Authentication flows
Authentication flows in frontend manage user interface and input validation, while backend handles secure data processing, token generation, and session management.
Microservices architecture
Microservices architecture separates frontend services, which handle user interface and experience, from backend services that manage business logic, data storage, and API integration, enabling scalable, independent development and deployment.
SSR (Server-Side Rendering)
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) enhances frontend performance by pre-rendering web pages on the backend server, improving SEO and load times compared to client-side rendering.
frontend vs backend Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com