Livestock automation enhances productivity by integrating advanced technologies like automated feeding, health monitoring, and environmental control systems, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error. Manual livestock management relies heavily on human skills and physical labor, which can be less efficient and more prone to inconsistencies in animal care. Automated systems optimize animal welfare and farm profitability by enabling precise data-driven decisions and continuous monitoring.
Table of Comparison
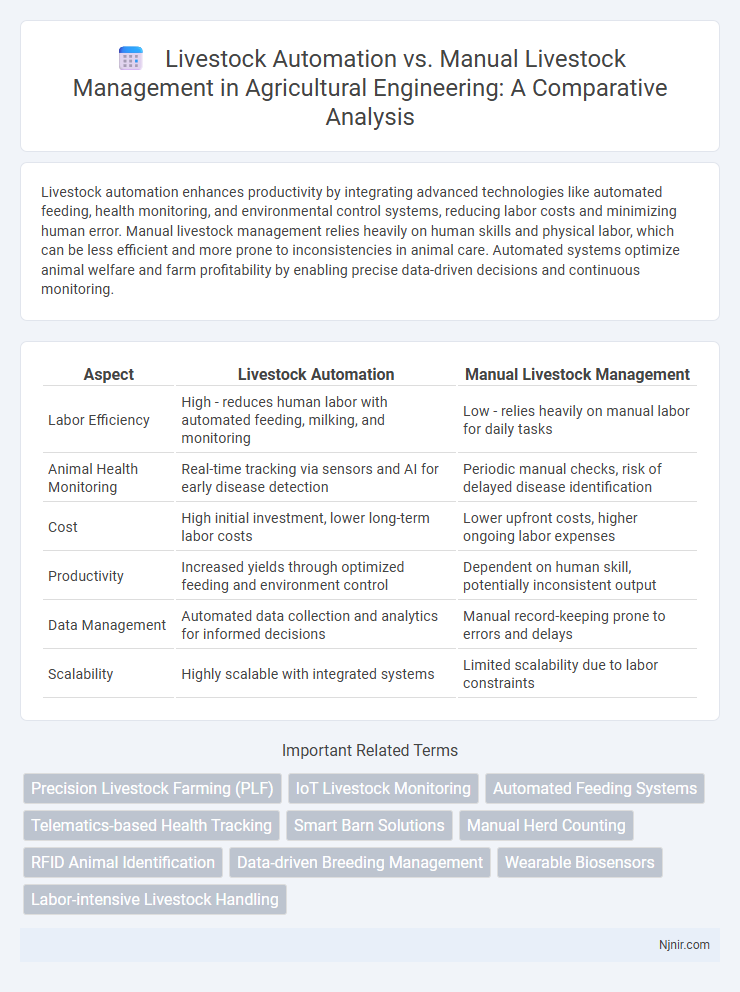
| Aspect | Livestock Automation | Manual Livestock Management |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Efficiency | High - reduces human labor with automated feeding, milking, and monitoring | Low - relies heavily on manual labor for daily tasks |
| Animal Health Monitoring | Real-time tracking via sensors and AI for early disease detection | Periodic manual checks, risk of delayed disease identification |
| Cost | High initial investment, lower long-term labor costs | Lower upfront costs, higher ongoing labor expenses |
| Productivity | Increased yields through optimized feeding and environment control | Dependent on human skill, potentially inconsistent output |
| Data Management | Automated data collection and analytics for informed decisions | Manual record-keeping prone to errors and delays |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with integrated systems | Limited scalability due to labor constraints |
Overview of Livestock Automation Technologies
Livestock automation technologies include precision feeding systems, automated milking machines, and environmental monitoring sensors that improve efficiency and animal welfare. These technologies leverage IoT devices, AI-driven data analytics, and robotics to streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and enhance productivity compared to manual livestock management. Adoption of automated solutions enables real-time monitoring and faster decision-making, driving sustainable farming practices and optimizing resource utilization.
Traditional Manual Livestock Management Practices
Traditional manual livestock management practices rely on hands-on monitoring of animal health, feeding, and breeding, often requiring skilled labor and daily physical inspections. These methods can be labor-intensive and prone to human error, leading to inconsistent productivity and challenges in timely disease detection. Manual approaches typically lack the precision and data analytics provided by livestock automation systems, impacting overall farm efficiency and scalability.
Key Differences Between Automated and Manual Systems
Automated livestock management systems use sensors, IoT devices, and AI algorithms to monitor animal health, optimize feeding schedules, and manage environmental conditions, significantly reducing labor costs and human error. Manual livestock management relies heavily on human observation and intervention, which can result in slower response times and less precise data collection. Automated systems provide real-time analytics and operational efficiency, whereas manual methods depend on experience and are often limited in scalability and accuracy.
Labor Efficiency: Automation vs Manual Operations
Livestock automation significantly enhances labor efficiency by streamlining tasks such as feeding, monitoring, and cleaning through automated systems, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing human error. Manual livestock management demands extensive time and physical effort from workers, often leading to inconsistencies and slower response times in animal care. Automated solutions enable continuous monitoring and precise data collection, optimizing labor allocation and improving overall productivity on farms.
Impact on Animal Health and Welfare
Livestock automation enhances animal health and welfare by providing consistent monitoring through sensors and real-time data analytics, enabling early disease detection and timely interventions. Manual livestock management often relies on routine human observation, which can be less precise and slower, potentially leading to delayed treatment and stress in animals. Automated systems reduce human error and stress by minimizing invasive handling, promoting a more stable and humane environment for livestock.
Data Collection and Decision Making in Livestock Management
Livestock automation enhances data collection with real-time monitoring through IoT sensors, RFID tags, and automated weighing systems, providing precise and continuous insights into animal health, behavior, and environment. Manual livestock management relies on periodic human observations and manual record-keeping, leading to less accurate and slower data acquisition. Automated systems enable data-driven decision making by analyzing large datasets for optimizing feeding, breeding, and health interventions, whereas manual management depends heavily on subjective experience and delayed responses.
Economic Considerations: Costs and Returns
Livestock automation significantly reduces labor costs by streamlining feeding, monitoring, and health management through technology such as robotic milking and automated feeders. Initial investment in automated systems is high, but increased efficiency and improved animal health contribute to higher returns over time compared to manual management. Manual livestock management incurs lower upfront expenses but often results in higher ongoing labor costs and less precise resource utilization, potentially reducing overall profitability.
Environmental Sustainability in Automated and Manual Systems
Automated livestock management systems significantly reduce environmental impact by optimizing feed efficiency, minimizing waste, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to manual methods. Precision technologies in automated systems enable real-time monitoring of animal health and resource use, contributing to sustainable water and energy consumption. Manual livestock management often results in higher resource wastage and less accurate environmental control, leading to greater soil degradation and pollution.
Challenges and Limitations of Livestock Automation
Livestock automation faces challenges such as high initial capital investment and complex integration with existing farm infrastructures. Limited adaptability to diverse animal behaviors and environmental conditions can lead to inconsistencies in monitoring and care. Data privacy concerns and reliance on technology infrastructure contribute to operational risks compared to manual livestock management.
Future Trends in Livestock Management Technologies
Livestock automation is transforming animal husbandry by integrating advanced sensors, AI-driven monitoring systems, and automated feeding and cleaning processes, significantly improving efficiency and data accuracy compared to manual management. Emerging trends include the use of IoT devices for real-time health tracking, blockchain for supply chain transparency, and robotics for labor-intensive tasks, promising enhanced productivity and sustainability. The future of livestock management technologies emphasizes precision agriculture, minimizing human error, reducing labor costs, and enabling predictive analytics for disease prevention and optimized resource use.
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF)
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) enhances productivity and animal welfare by automating monitoring and management processes, offering real-time data and analytics compared to traditional manual livestock management.
IoT Livestock Monitoring
IoT livestock monitoring enhances automation by providing real-time data on animal health, location, and behavior, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy compared to manual livestock management methods.
Automated Feeding Systems
Automated feeding systems in livestock automation enhance feed efficiency and reduce labor costs compared to manual livestock management.
Telematics-based Health Tracking
Telematics-based health tracking in livestock automation enhances real-time monitoring accuracy, reduces labor costs, and improves early disease detection compared to manual livestock management.
Smart Barn Solutions
Smart Barn Solutions revolutionize livestock management by automating feeding, climate control, and health monitoring, significantly improving efficiency and animal welfare compared to manual livestock management methods.
Manual Herd Counting
Manual herd counting in livestock management is time-consuming and prone to human error compared to automated systems that enhance accuracy and efficiency.
RFID Animal Identification
RFID animal identification in livestock automation enhances real-time tracking accuracy, reduces labor costs, and improves data management compared to traditional manual livestock management methods.
Data-driven Breeding Management
Data-driven breeding management in livestock automation enhances genetic selection accuracy and reproductive efficiency compared to traditional manual livestock management methods.
Wearable Biosensors
Wearable biosensors in livestock automation enhance real-time health monitoring, improve disease detection accuracy by 40%, and reduce labor costs by 30% compared to manual livestock management.
Labor-intensive Livestock Handling
Automated livestock management reduces labor-intensive tasks by using advanced technologies like RFID tracking, automated feeders, and robotic milking systems, significantly improving efficiency compared to manual livestock handling.
Livestock automation vs Manual livestock management Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com