Smart tractors integrate GPS technology, automated steering, and real-time data analysis to optimize field operations, significantly enhancing efficiency and precision compared to traditional tractors. These advanced machines reduce fuel consumption, minimize soil compaction, and enable targeted application of inputs like fertilizers and pesticides, promoting sustainable farming practices. In contrast, traditional tractors lack these capabilities, often resulting in higher resource usage and lower productivity on the farm.
Table of Comparison
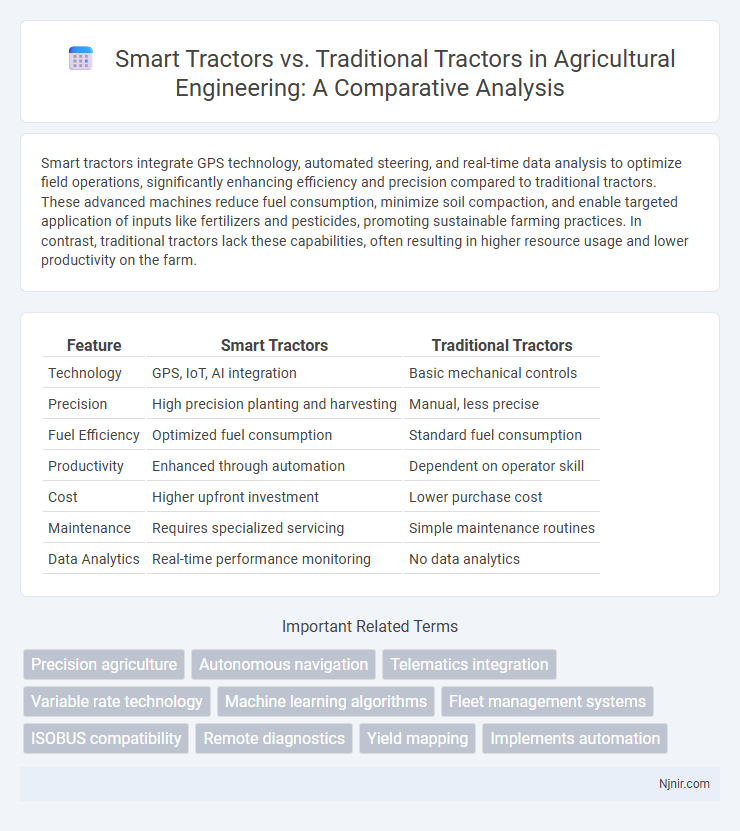
| Feature | Smart Tractors | Traditional Tractors |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | GPS, IoT, AI integration | Basic mechanical controls |
| Precision | High precision planting and harvesting | Manual, less precise |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimized fuel consumption | Standard fuel consumption |
| Productivity | Enhanced through automation | Dependent on operator skill |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment | Lower purchase cost |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized servicing | Simple maintenance routines |
| Data Analytics | Real-time performance monitoring | No data analytics |
Introduction to Smart Tractors and Traditional Tractors
Smart tractors integrate advanced technologies such as GPS, IoT sensors, and AI for precision farming, enabling real-time data monitoring and automated operations. Traditional tractors rely on manual controls and mechanical power, offering reliable performance but limited efficiency and data collection. The shift toward smart tractors enhances productivity, reduces fuel consumption, and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
Key Technological Differences
Smart tractors integrate advanced GPS technology, real-time data analytics, and autonomous driving capabilities, enhancing precision in planting, fertilizing, and harvesting compared to traditional tractors. They feature IoT connectivity for remote monitoring and maintenance, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Traditional tractors rely more on manual controls and mechanical systems, lacking the sensor-driven automation and intelligent decision-making found in smart tractor models.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
Smart tractors integrate GPS technology, automated steering, and real-time data analysis, significantly enhancing operational precision and fuel efficiency compared to traditional tractors. These advancements reduce overlap in fieldwork, optimize input use, and increase acreage covered per hour, resulting in higher overall productivity. Traditional tractors, lacking these technologies, rely heavily on manual operation and often experience greater fuel consumption and time inefficiencies.
Fuel and Energy Consumption
Smart tractors utilize advanced GPS-guided systems and precision farming technology to optimize fuel consumption, reducing energy use by up to 20% compared to traditional tractors. Traditional tractors often rely on manual operation with less efficient fuel usage, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Integration of real-time data in smart tractors allows for adaptive engine performance, minimizing fuel wastage and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Smart tractors significantly reduce maintenance requirements and costs compared to traditional tractors through advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance technologies. These tractors utilize real-time sensors to monitor engine performance, tire pressure, and fluid levels, allowing early detection of potential issues before they escalate. Traditional tractors often incur higher repair costs and downtime due to reactive maintenance and lack of automated monitoring systems.
Impact on Precision Farming
Smart tractors significantly enhance precision farming by integrating GPS technology, sensors, and real-time data analytics, enabling accurate seed planting, fertilization, and irrigation. These advancements reduce resource waste, increase crop yields, and minimize environmental impact compared to traditional tractors that rely on manual operation and limited technology. The ability of smart tractors to optimize field operations through automated guidance and variable rate application transforms agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Environmental Considerations
Smart tractors significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing GPS-guided precision farming techniques that minimize fuel consumption and limit soil compaction. Traditional tractors often run less efficiently, leading to higher carbon emissions and increased use of chemical inputs due to imprecise application. Advanced sensors and real-time data analytics in smart tractors enable optimized resource management, promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing pollution.
Initial Investment and Return on Investment
Smart tractors require a higher initial investment, often ranging from $100,000 to $300,000 due to advanced technologies like GPS guidance, sensors, and data analytics, compared to traditional tractors costing between $20,000 and $70,000. Despite the upfront costs, smart tractors improve operational efficiency by up to 20%, reducing fuel, labor, and maintenance expenses, which accelerates the return on investment within 3 to 5 years. Traditional tractors have lower entry costs but typically yield slower ROI due to increased manual labor and less precision, impacting overall farm productivity and profitability.
Challenges and Limitations
Smart tractors face challenges including high initial costs and the need for specialized technical skills for operation and maintenance, unlike traditional tractors which have simpler mechanics. Connectivity issues and dependence on GPS signals can limit the effectiveness of smart tractors in remote or signal-poor areas. Data security and privacy concerns also pose limitations to the widespread adoption of smart tractors in modern agriculture.
Future Trends in Tractor Technology
Smart tractors are revolutionizing agriculture by integrating GPS, IoT sensors, and AI-driven automation, improving precision and efficiency compared to traditional tractors. Future trends in tractor technology emphasize autonomous operation, real-time data analytics for soil and crop monitoring, and seamless connectivity with farm management systems. These advancements are set to reduce labor costs, enhance sustainability, and optimize yield through predictive maintenance and adaptive machine learning algorithms.
Precision agriculture
Smart tractors equipped with GPS-guided systems and real-time data analytics significantly enhance precision agriculture by optimizing planting, fertilizing, and irrigation compared to traditional tractors.
Autonomous navigation
Smart tractors utilize advanced autonomous navigation systems enabling precise, efficient field operations without human intervention, whereas traditional tractors rely entirely on manual control for navigation and operation.
Telematics integration
Smart tractors equipped with advanced telematics systems enable real-time data monitoring and remote diagnostics, significantly enhancing operational efficiency compared to traditional tractors lacking such integration.
Variable rate technology
Smart tractors equipped with Variable Rate Technology optimize input usage by precisely adjusting seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides in real-time, significantly enhancing efficiency and crop yields compared to traditional tractors.
Machine learning algorithms
Smart tractors utilize advanced machine learning algorithms to optimize field operations, improve precision, and increase crop yield compared to traditional tractors.
Fleet management systems
Smart tractors equipped with advanced Fleet Management Systems enable real-time monitoring, optimized route planning, and predictive maintenance, significantly enhancing operational efficiency compared to traditional tractors.
ISOBUS compatibility
Smart tractors equipped with ISOBUS compatibility enable seamless communication and control of implements, significantly improving efficiency and precision compared to traditional tractors lacking this standardized technology.
Remote diagnostics
Smart tractors leverage remote diagnostics to enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, significantly reducing downtime compared to traditional tractors.
Yield mapping
Smart tractors equipped with advanced GPS and yield mapping technology enable precise field data collection and real-time crop management, significantly enhancing productivity compared to traditional tractors.
Implements automation
Smart tractors equipped with automated implements drastically improve agricultural efficiency by precisely controlling planting, fertilizing, and harvesting processes compared to traditional tractors that rely on manual operation.
smart tractors vs traditional tractors Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com