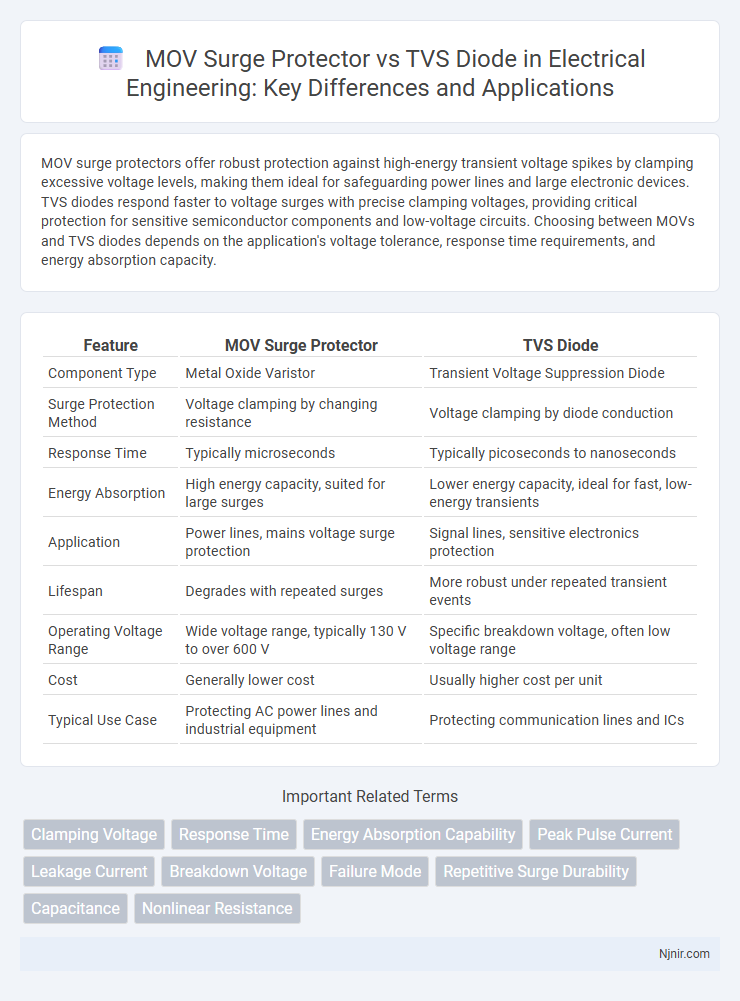
MOV surge protectors offer robust protection against high-energy transient voltage spikes by clamping excessive voltage levels, making them ideal for safeguarding power lines and large electronic devices. TVS diodes respond faster to voltage surges with precise clamping voltages, providing critical protection for sensitive semiconductor components and low-voltage circuits. Choosing between MOVs and TVS diodes depends on the application's voltage tolerance, response time requirements, and energy absorption capacity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MOV Surge Protector | TVS Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Component Type | Metal Oxide Varistor | Transient Voltage Suppression Diode |
| Surge Protection Method | Voltage clamping by changing resistance | Voltage clamping by diode conduction |
| Response Time | Typically microseconds | Typically picoseconds to nanoseconds |
| Energy Absorption | High energy capacity, suited for large surges | Lower energy capacity, ideal for fast, low-energy transients |
| Application | Power lines, mains voltage surge protection | Signal lines, sensitive electronics protection |
| Lifespan | Degrades with repeated surges | More robust under repeated transient events |
| Operating Voltage Range | Wide voltage range, typically 130 V to over 600 V | Specific breakdown voltage, often low voltage range |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost per unit |
| Typical Use Case | Protecting AC power lines and industrial equipment | Protecting communication lines and ICs |
Introduction to Surge Protection in Electrical Engineering
Surge protection in electrical engineering involves safeguarding circuits from transient voltage spikes caused by lightning, switching operations, or fault conditions. Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs) absorb high-energy surges by changing resistance during voltage spikes, making them ideal for protecting power lines and household appliances. Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes respond faster to voltage transients, clamping the voltage instantly to prevent damage in sensitive electronic components and communication devices.
Overview of MOV Surge Protectors
MOV surge protectors use metal oxide varistors to absorb and dissipate voltage spikes, providing robust protection against transient surges in electrical circuits. They are commonly employed in power strips, surge protectors, and electrical panels where high energy absorption and rapid response are critical. MOVs effectively clamp voltage surges by changing resistance, making them ideal for safeguarding sensitive electronics from lightning strikes and switching transients.
Overview of TVS Diodes
TVS diodes are semiconductor devices designed to protect sensitive electronic circuits from transient voltage spikes by clamping voltage to safe levels. Unlike MOV surge protectors that rely on metal oxide varistor materials, TVS diodes have faster response times and precise voltage clamping characteristics, making them ideal for high-speed digital circuit protection. Their low leakage current and high surge current capability provide reliable safeguarding against electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and other transient overvoltages.
Working Principle: MOV vs TVS Diode
MOV surge protectors operate by clamping high voltage spikes through a material with variable resistance, which decreases sharply during surges to divert excess current and protect connected devices. TVS diodes function by rapidly switching from a high-impedance to a low-impedance state when voltage exceeds a threshold, thereby shunting transient voltage spikes safely to ground. Both devices protect circuits from transient overvoltages but differ in response speed and energy handling; TVS diodes react faster, while MOVs handle higher energy surges.
Response Time Comparison
MOV surge protectors typically have slower response times ranging from nanoseconds to microseconds, which can result in brief exposure to high voltage spikes before clamping occurs. TVS diodes offer significantly faster response times, often in the picosecond to nanosecond range, providing near-instantaneous voltage suppression and superior protection for sensitive electronic components. This rapid reaction capability makes TVS diodes more effective in guarding against transient voltage surges caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD) and fast switching events.
Voltage and Current Handling Capabilities
MOV surge protectors excel in high voltage and current handling capabilities, typically managing surges up to several thousand volts and thousands of amperes, making them ideal for protecting power lines in industrial environments. TVS diodes offer faster response times and precise voltage clamping, usually handling lower energy surges with peak pulse currents ranging from a few amperes to several hundred amperes, suitable for sensitive electronic circuits. The superior energy absorption capacity of MOVs contrasts with the low capacitance and rapid response of TVS diodes, influencing their application based on surge intensity and circuit sensitivity.
Energy Absorption and Clamping Effectiveness
MOV surge protectors offer superior energy absorption capacity, handling high surge currents typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of joules, making them ideal for protecting against large, high-energy transients. TVS diodes excel in clamping effectiveness with rapid response times and low breakdown voltage, providing precise voltage clamping suitable for sensitive electronic components in low-energy scenarios. The choice between MOVs and TVS diodes depends on balancing energy absorption needs with clamping voltage accuracy to optimize transient voltage suppression performance.
Lifespan and Reliability Assessment
MOV surge protectors exhibit limited lifespan due to material degradation from repeated surge events, typically lasting for a few years under moderate electrical stress. TVS diodes offer higher reliability with rapid response times and a long operational lifespan, as they clamp voltage spikes without significant wear during normal operation. For critical applications, TVS diodes provide superior durability and consistent protection compared to MOVs, which require periodic replacement to maintain effectiveness.
Application Scenarios: MOV vs TVS Diode
MOV surge protectors are ideal for protecting power lines and home appliances from high-energy, low-frequency surges such as lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations due to their ability to absorb large surge currents. TVS diodes are better suited for sensitive electronic circuits and data lines where fast response times and low clamping voltages are critical, effectively guarding against transient voltage spikes from electrostatic discharge (ESD) or switching events. MOVs excel in industrial and residential power surge scenarios, while TVS diodes are preferred in telecommunications, automotive electronics, and semiconductor protection.
Selection Criteria and Practical Recommendations
MOV surge protectors offer high energy absorption capacity, making them ideal for protecting against large voltage spikes in power lines, while TVS diodes provide fast response times suitable for sensitive electronic circuits with low energy transients. Selection criteria should consider the maximum clamping voltage, energy rating, response time, and application environment; MOVs excel in AC power applications, whereas TVS diodes are preferred in DC signal or data lines due to precision and speed. Practical recommendations include using MOVs for mains surge protection with adequate thermal protection to prevent failure, and deploying TVS diodes near semiconductor devices for localized transient suppression without impacting signal integrity.
Clamping Voltage
MOV surge protectors typically have a higher clamping voltage ranging from 330V to 600V, whereas TVS diodes offer lower clamping voltages often between 5V to 40V, providing faster response and better protection for sensitive electronics.
Response Time
MOV surge protectors typically have slower response times ranging from microseconds to milliseconds, whereas TVS diodes offer ultra-fast response times in the picosecond to nanosecond range, making TVS diodes more effective for protecting sensitive electronic components from transient voltage spikes.
Energy Absorption Capability
MOV surge protectors absorb higher surge energy levels, typically up to thousands of joules, providing superior protection compared to TVS diodes, which handle lower energy pulses usually in the range of tens to hundreds of joules.
Peak Pulse Current
MOV surge protectors typically handle higher Peak Pulse Currents ranging from hundreds to thousands of amperes, whereas TVS diodes are designed for lower Peak Pulse Currents typically up to a few hundred amperes.
Leakage Current
MOV surge protectors typically exhibit higher leakage current compared to TVS diodes, making TVS diodes more suitable for low-leakage applications requiring precise protection.
Breakdown Voltage
MOV surge protectors typically have higher breakdown voltages ranging from 10V to several hundred volts, whereas TVS diodes offer precise and lower breakdown voltages between 5V and 500V for faster, more accurate transient voltage suppression.
Failure Mode
MOV surge protectors typically fail by degradation and short-circuiting after repeated high-energy surges, while TVS diodes fail by catastrophic open-circuit breakdown or thermal runaway under excessive transient voltage stress.
Repetitive Surge Durability
MOV surge protectors typically offer higher repetitive surge durability than TVS diodes, making them more suitable for absorbing multiple high-energy transient surges.
Capacitance
MOV surge protectors typically have higher capacitance than TVS diodes, which can affect high-frequency signal integrity in sensitive electronic circuits.
Nonlinear Resistance
MOV surge protectors exhibit significantly lower nonlinear resistance compared to TVS diodes, enabling superior energy absorption during transient voltage spikes.
MOV surge protector vs TVS diode Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com