API Gateways manage and route client requests to backend services, offering features like authentication, rate limiting, and caching to simplify communication between external users and microservices. Service Meshes provide a dedicated infrastructure layer for service-to-service communication, handling load balancing, service discovery, and observability within complex microservice architectures. While API Gateways optimize external traffic management, Service Meshes enhance internal microservice interactions with fine-grained control and security.
Table of Comparison
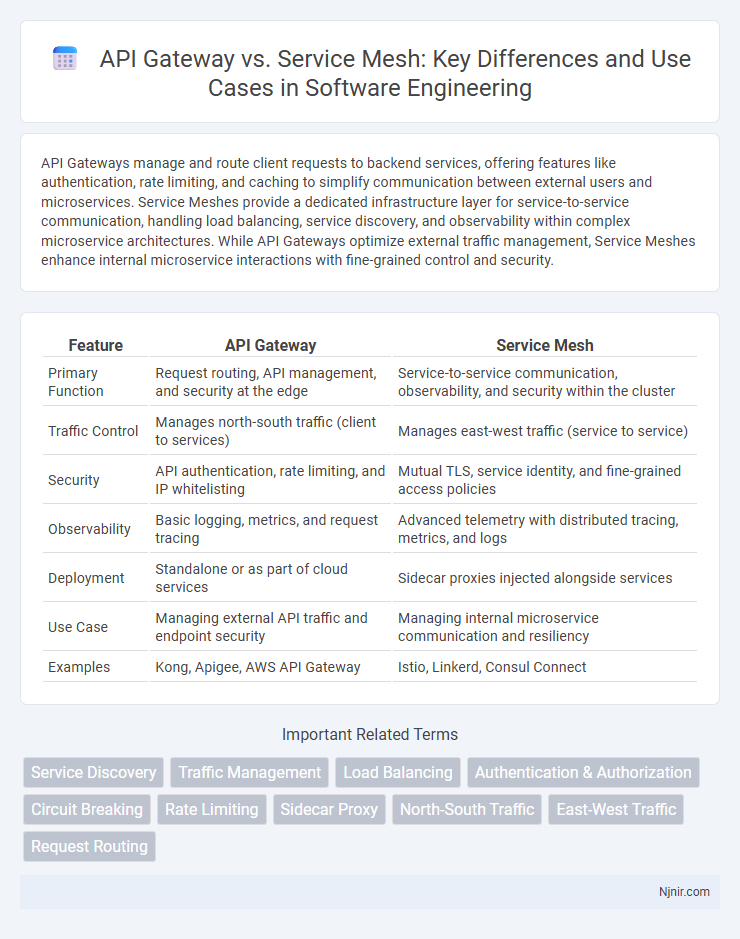
| Feature | API Gateway | Service Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Request routing, API management, and security at the edge | Service-to-service communication, observability, and security within the cluster |
| Traffic Control | Manages north-south traffic (client to services) | Manages east-west traffic (service to service) |
| Security | API authentication, rate limiting, and IP whitelisting | Mutual TLS, service identity, and fine-grained access policies |
| Observability | Basic logging, metrics, and request tracing | Advanced telemetry with distributed tracing, metrics, and logs |
| Deployment | Standalone or as part of cloud services | Sidecar proxies injected alongside services |
| Use Case | Managing external API traffic and endpoint security | Managing internal microservice communication and resiliency |
| Examples | Kong, Apigee, AWS API Gateway | Istio, Linkerd, Consul Connect |
Introduction to API Gateway and Service Mesh
API Gateway serves as a centralized entry point that manages client requests, performs authentication, rate-limiting, and request routing to backend services, enhancing API security and performance. Service Mesh provides a dedicated infrastructure layer for managing service-to-service communication within microservices architectures, handling load balancing, service discovery, and policy enforcement without modifying application code. While API Gateway focuses on external traffic management, Service Mesh optimizes internal service interactions and observability.
Core Functions and Responsibilities
API Gateway manages client requests by routing, authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation between external users and backend services. Service Mesh handles inter-service communication within a microservices architecture, providing load balancing, service discovery, security policies, and observability. Both play crucial roles in modern cloud-native applications, with API Gateway focusing on ingress traffic and Service Mesh optimizing internal service-to-service interactions.
Architectural Differences
API Gateway acts as a centralized entry point managing client-to-service communications, handling tasks like request routing, rate limiting, and authentication at the edge of the network. Service Mesh operates as a dedicated infrastructure layer for managing service-to-service communication within microservices, providing features such as load balancing, service discovery, and secure inter-service communication through sidecar proxies. The architectural difference lies in API Gateway's focus on north-south traffic control between clients and services, while Service Mesh addresses east-west traffic by orchestrating internal service interactions.
Deployment Models
API Gateway typically follows a centralized deployment model, acting as a single entry point that manages and routes client requests to backend services, improving security and request handling. Service Mesh employs a decentralized deployment model by injecting lightweight proxies (sidecars) alongside each microservice instance, enabling fine-grained traffic management, service discovery, and observability within the service-to-service communication. While API Gateway focuses on north-south traffic management, Service Mesh optimizes east-west traffic, making them complementary in complex microservices architectures.
Traffic Management and Routing
API Gateway centralizes traffic management by handling request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation at the edge of the network, efficiently directing client requests to backend services. Service Mesh operates within the microservices environment, providing fine-grained routing control, load balancing, and service-to-service traffic encryption through sidecar proxies that manage internal communication. While API Gateway focuses on north-south traffic (client-to-service), Service Mesh excels at east-west traffic (service-to-service), enabling advanced traffic shaping, traffic splitting, and observability at the microservice level.
Security Features and Policies
API Gateway enforces security through centralized authentication, rate limiting, and IP filtering, ensuring robust access control at the entry point of microservices. Service Mesh provides fine-grained security with mutual TLS encryption, workload identity, and policy-driven traffic management between services for secure service-to-service communication. Both strengthen security posture, but API Gateway focuses on external threat protection while Service Mesh secures internal service interactions.
Observability and Monitoring Capabilities
API Gateway centralizes observability by providing detailed metrics, logging, and tracing for incoming API requests, enabling streamlined monitoring of traffic patterns and error rates at the front door of microservices. Service Mesh offers granular observability within the service-to-service communication layer, capturing telemetry data like service latency, retries, and circuit breaker status, which facilitates deep insight into internal microservice interactions. Combining an API Gateway with a Service Mesh results in comprehensive monitoring coverage, from external API calls to internal service communication, enhancing overall system reliability and performance tracking.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
API Gateway centralizes request routing and rate limiting, improving scalability by efficiently managing client connections and reducing overhead for backend services. Service Mesh enhances performance through fine-grained traffic control, load balancing, and resilient service-to-service communication, optimizing resource utilization across microservices. Combining both enables scalable API management with robust inter-service reliability, delivering high throughput and low latency in distributed applications.
When to Use API Gateway vs Service Mesh
API Gateway is ideal for managing external client requests, providing features like request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and API composition, making it essential for exposing services to the outside world. Service Mesh excels in managing internal service-to-service communications, offering traffic management, security, observability, and resilience within microservices architectures. Use an API Gateway when controlling, securing, and monitoring client-facing APIs, and implement a Service Mesh to handle complex inter-service communication and reliability within distributed systems.
Conclusion and Best Practices
API Gateway centralizes entry point management, simplifying client interaction with microservices by handling routing, authentication, and rate limiting, while Service Mesh excels in managing inter-service communication, security, and observability within the microservices ecosystem. Combining both technologies yields a robust infrastructure: API Gateways optimize external traffic and security, whereas Service Meshes enhance internal service reliability and monitoring. Best practices recommend deploying API Gateways to expose services externally and adopting Service Meshes to manage internal service-to-service communication for scalability and resilience.
Service Discovery
Service Mesh enhances service discovery by providing dynamic, decentralized routing and real-time health monitoring across microservices, whereas API Gateway relies on static service registration and centralized routing configurations.
Traffic Management
API Gateway centralizes traffic management at the edge for routing, rate limiting, and security, while Service Mesh provides fine-grained, service-to-service traffic control and observability within microservices environments.
Load Balancing
API Gateway primarily handles load balancing at the edge for API traffic routing, while Service Mesh provides fine-grained, internal load balancing across microservices within a distributed system.
Authentication & Authorization
API Gateways centralize authentication and authorization at the edge, managing client access and enforcing security policies, while Service Meshes provide fine-grained, service-to-service authentication and authorization within the microservices network using mutual TLS and role-based access control.
Circuit Breaking
API Gateway manages circuit breaking at the edge for client requests, while a Service Mesh implements circuit breaking internally between microservices to enhance fault tolerance and resilience.
Rate Limiting
API Gateway enforces centralized rate limiting for traffic management at the edge, while Service Mesh applies fine-grained rate limiting within microservices communication for enhanced internal traffic control.
Sidecar Proxy
A sidecar proxy in a service mesh handles inter-service communication, security, and observability at the microservice level, while an API Gateway manages external client requests, routing, and API transformations at the application edge.
North-South Traffic
API Gateway efficiently manages North-South traffic by routing external client requests to backend services, while Service Mesh primarily handles East-West traffic within the cluster and offers limited North-South traffic control.
East-West Traffic
Service Mesh optimizes East-West traffic by providing granular service-to-service communication, security, and observability, whereas API Gateway primarily manages North-South traffic by handling client-to-service requests.
Request Routing
API Gateways handle request routing by managing external client traffic through a single entry point with path-based rules, while Service Meshes provide granular, internal service-to-service request routing using sidecar proxies for dynamic routing and load balancing.
API Gateway vs Service Mesh Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com