Jupyter and Zeppelin are popular open-source notebooks widely used in software engineering for interactive data analysis and visualization. Jupyter supports multiple programming languages, including Python, R, and Julia, with extensive community support and numerous extensions, making it ideal for diverse data science workflows. Zeppelin offers strong integration with big data tools like Apache Spark and supports collaborative notebook sharing, which is beneficial for distributed teams working on large-scale data processing.
Table of Comparison
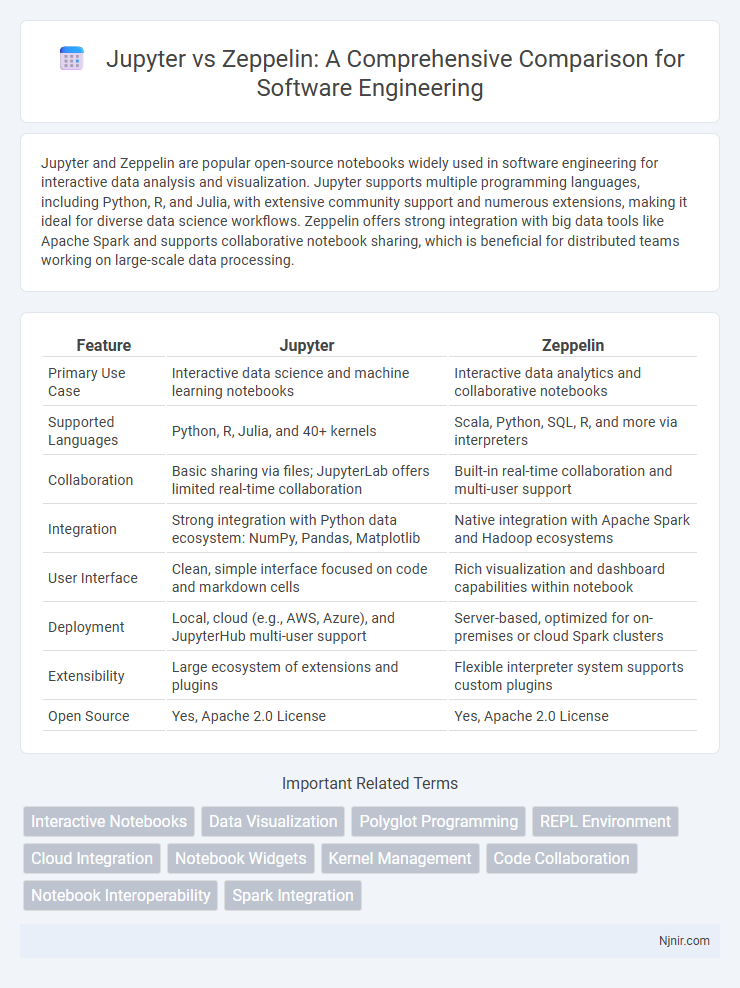
| Feature | Jupyter | Zeppelin |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Interactive data science and machine learning notebooks | Interactive data analytics and collaborative notebooks |
| Supported Languages | Python, R, Julia, and 40+ kernels | Scala, Python, SQL, R, and more via interpreters |
| Collaboration | Basic sharing via files; JupyterLab offers limited real-time collaboration | Built-in real-time collaboration and multi-user support |
| Integration | Strong integration with Python data ecosystem: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib | Native integration with Apache Spark and Hadoop ecosystems |
| User Interface | Clean, simple interface focused on code and markdown cells | Rich visualization and dashboard capabilities within notebook |
| Deployment | Local, cloud (e.g., AWS, Azure), and JupyterHub multi-user support | Server-based, optimized for on-premises or cloud Spark clusters |
| Extensibility | Large ecosystem of extensions and plugins | Flexible interpreter system supports custom plugins |
| Open Source | Yes, Apache 2.0 License | Yes, Apache 2.0 License |
Overview of Jupyter and Zeppelin
Jupyter is an open-source interactive computing environment that supports over 40 programming languages, including Python, R, and Julia, enabling users to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. Apache Zeppelin is a web-based notebook designed for data-driven, interactive data analytics and collaborative documents, offering built-in support for multiple backend systems like Apache Spark, Flink, and Hive. Both platforms facilitate data science workflows, but Jupyter emphasizes language versatility and extensive extensions, while Zeppelin integrates tightly with big data ecosystems.
Key Features Comparison
Jupyter offers extensive language support, including Python, R, and Julia, with a vast ecosystem of extensions and interactive widgets, making it ideal for diverse data science workflows. Zeppelin emphasizes native support for multiple interpreters such as Apache Spark, SQL, and Markdown, providing seamless integration for big data analytics and collaborative notebook sharing. Both platforms deliver real-time visualization and code execution, but Jupyter excels in community-driven development while Zeppelin prioritizes native multi-backend connectivity.
Supported Languages and Integrations
Jupyter supports over 40 programming languages, including Python, R, and Julia, through various kernels, making it highly versatile for data science and machine learning workflows. Zeppelin primarily supports Apache Spark with native integration for Scala, Python, and SQL, offering strong capabilities for big data analytics within Hadoop ecosystems. Both platforms integrate with numerous data sources and tools, but Jupyter's compatibility with cloud services and libraries like TensorFlow and Pandas provides broader flexibility for diverse development environments.
User Interface and Experience
Jupyter offers a clean, minimalistic user interface with straightforward notebook navigation, emphasizing ease of use for data scientists and educators. Zeppelin provides a richer, more interactive experience with native support for multiple languages and integrated visualization tools, appealing to collaborative data environments. Both platforms enable code execution and visualization, but Jupyter excels in simplicity, while Zeppelin prioritizes multi-user workflows and real-time collaboration features.
Collaboration Capabilities
Jupyter and Zeppelin both support collaborative work but differ in their approaches. Jupyter offers real-time collaboration through JupyterHub and JupyterLab, enabling multiple users to work simultaneously on notebooks with integrated version control via Git. Apache Zeppelin facilitates collaboration by allowing multiple users to share and run interactive notebooks with built-in support for multi-user access and interpreter isolation, making it suitable for enterprise environments requiring concurrent data exploration.
Data Visualization Support
Jupyter offers extensive data visualization support through integration with libraries such as Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly, and Bokeh, enabling interactive and static visualizations within notebooks. Apache Zeppelin provides built-in visualization tools with native support for dynamic charts, graphs, and dashboards, particularly strong in supporting multiple languages like Scala, Python, and SQL for big data contexts. Both platforms facilitate rich data visualization but Jupyter's ecosystem has a broader range of customizable and third-party visualization plugins.
Performance and Scalability
Jupyter offers robust performance with efficient kernel management and supports a wide range of programming languages, making it scalable for diverse data science workflows. Apache Zeppelin excels in handling large-scale distributed data processing through native integration with Apache Spark, enhancing scalability in big data environments. While Jupyter is preferred for interactive analysis and prototyping, Zeppelin's architecture optimizes execution speed in cluster computing scenarios, providing superior performance in scalable analytics.
Security and Authentication
Jupyter supports token-based authentication and integrates with LDAP, PAM, and OAuth for secure user access, but its default setup requires careful configuration to avoid exposing notebooks to unauthorized users. Apache Zeppelin offers robust authentication options including LDAP, Kerberos, OAuth, and SAML, enabling enterprise-grade access control tailored for multi-user environments. Both platforms emphasize secure communication through SSL/TLS encryption, yet Zeppelin's built-in support for fine-grained permission management provides enhanced control for collaborative analytics.
Community and Ecosystem
Jupyter boasts a vast, active community with extensive support from major organizations like Project Jupyter and a rich ecosystem of over 100 programming languages and countless extensions. Apache Zeppelin features a robust open-source community primarily focused on big data and Apache Spark integration, offering native support for multiple interpreters and collaborative notebooks. Jupyter's widespread adoption in data science and academia results in more frequent updates, diverse plugins, and comprehensive documentation compared to Zeppelin's niche but strong presence in enterprise environments.
Best Use Cases for Each Platform
Jupyter excels in interactive data science workflows, supporting over 40 programming languages with strong integration for Python, R, and Julia, making it ideal for machine learning, statistical analysis, and research prototyping. Zeppelin offers native support for multi-language interpreters such as Scala, Python, and SQL, with built-in integration with Apache Spark, making it best suited for big data analytics and collaborative data engineering projects on distributed computing platforms. Organizations focused on data exploration and interactive visualization often prefer Jupyter, while enterprises handling large-scale data processing and real-time analytics frequently adopt Zeppelin.
Interactive Notebooks
Jupyter and Zeppelin both provide interactive notebooks for data analysis, with Jupyter offering extensive language support and a vast ecosystem, while Zeppelin excels in multi-language integration and seamless Apache Spark connectivity.
Data Visualization
Jupyter offers extensive data visualization support through libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly, while Zeppelin provides built-in interactive visualization features and seamless integration with big data tools such as Apache Spark.
Polyglot Programming
Jupyter supports polyglot programming with over 100 language kernels including Python, R, and Julia, while Zeppelin offers strong multi-language support and seamless integration for SQL, Scala, Python, and more within a single notebook environment.
REPL Environment
Jupyter offers a versatile REPL environment with language-specific kernels and rich multimedia support, while Zeppelin provides a collaborative REPL experience with integrated data visualization and multi-language notebook capabilities.
Cloud Integration
Jupyter offers extensive cloud integration through platforms like Google Colab and Azure Notebooks, while Zeppelin provides robust cloud support with native integrations for Apache Spark on AWS EMR and Azure HDInsight.
Notebook Widgets
Jupyter Notebook offers a broader range of interactive widgets like ipywidgets for enhanced user interactivity compared to Apache Zeppelin's more limited and less integrated widget support.
Kernel Management
Jupyter supports multiple kernels with dynamic switching for diverse languages, while Zeppelin offers interpreter-based kernel management tailored for data integration and simultaneous multi-language execution.
Code Collaboration
Jupyter supports real-time code collaboration through extensions like JupyterLab and Google Colab, while Zeppelin offers native multi-user collaboration with shared notebooks and integrated version control.
Notebook Interoperability
Jupyter offers broader notebook interoperability with support for over 40 languages and native integration with various data science tools, whereas Zeppelin specializes in multi-language notebooks primarily for Spark but has limited compatibility with Jupyter formats.
Spark Integration
Jupyter supports Spark integration through PySpark and Apache Toree kernels enabling interactive big data analysis, while Zeppelin offers native multi-language Spark interpreter support with dynamic visualizations and collaborative notebooks.
Jupyter vs Zeppelin Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com