AWS Lambda offers serverless computing with automatic scaling and event-driven execution, ideal for short-lived, stateless functions. AWS Fargate provides container-based compute resources, enabling the deployment of long-running applications with more control over the underlying infrastructure. Choosing between Lambda and Fargate depends on workload characteristics, such as execution duration, scalability needs, and application complexity.
Table of Comparison
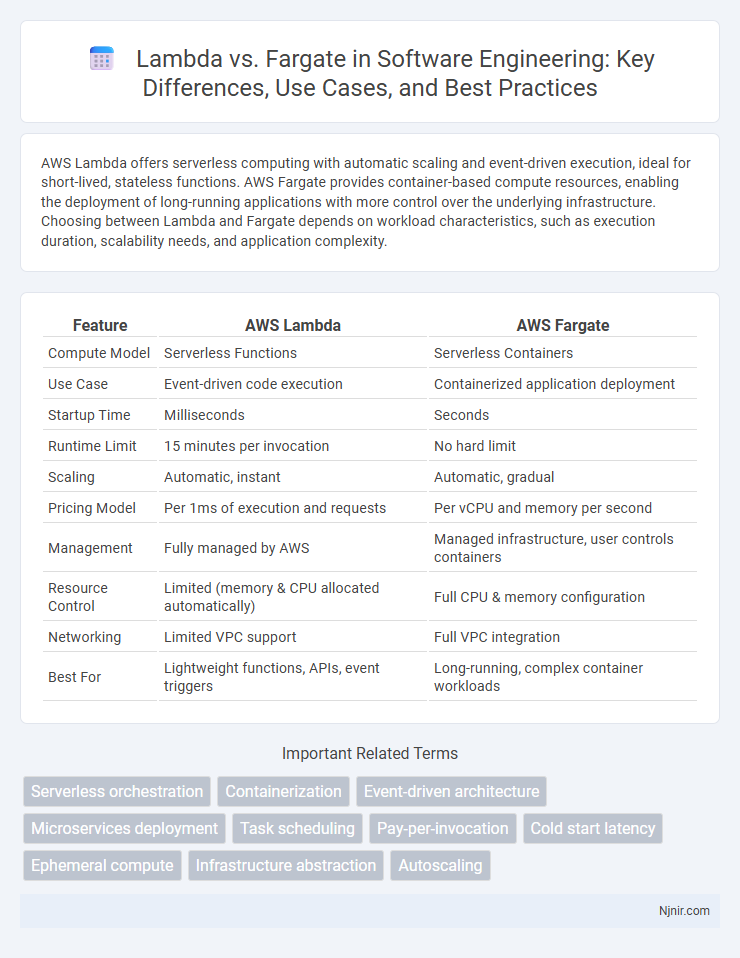
| Feature | AWS Lambda | AWS Fargate |
|---|---|---|
| Compute Model | Serverless Functions | Serverless Containers |
| Use Case | Event-driven code execution | Containerized application deployment |
| Startup Time | Milliseconds | Seconds |
| Runtime Limit | 15 minutes per invocation | No hard limit |
| Scaling | Automatic, instant | Automatic, gradual |
| Pricing Model | Per 1ms of execution and requests | Per vCPU and memory per second |
| Management | Fully managed by AWS | Managed infrastructure, user controls containers |
| Resource Control | Limited (memory & CPU allocated automatically) | Full CPU & memory configuration |
| Networking | Limited VPC support | Full VPC integration |
| Best For | Lightweight functions, APIs, event triggers | Long-running, complex container workloads |
Introduction to AWS Lambda and Fargate
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying infrastructure, enabling developers to build scalable applications without provisioning servers. AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that works with Amazon ECS and EKS, allowing users to run containers without managing servers or clusters. Both services enable automatic scaling and pay-as-you-go pricing, but Lambda focuses on event-driven functions while Fargate provides container orchestration for long-running applications.
Core Concepts: Serverless vs Containerized Computing
Lambda provides a serverless computing model where code runs in response to events without managing servers, enabling automatic scaling and precise resource allocation based on execution time. Fargate offers containerized computing by running Docker containers without server management, allowing more control over container orchestration with seamless integration into Amazon ECS or EKS. The primary distinction lies in Lambda's event-driven function execution versus Fargate's flexible container deployment for long-running and complex applications.
Architecture Overview: Lambda vs Fargate
AWS Lambda operates on a serverless architecture that automatically provisions and manages compute resources, enabling event-driven execution without server management. AWS Fargate utilizes a container-based architecture that abstracts server infrastructure, allowing users to run and scale containerized applications with precise control over CPU and memory allocation. Lambda is optimized for short-lived, stateless functions triggered by events, while Fargate supports long-running, stateful container workloads requiring persistent storage and networking configuration.
Use Cases: When to Choose Lambda or Fargate
AWS Lambda excels in event-driven, short-duration workloads like real-time file processing, API backends, or automated triggers where rapid scaling and minimal management are crucial. AWS Fargate suits containerized applications requiring long-running or complex workflows, such as microservices with persistent connections, batch jobs, or legacy application migrations demanding granular resource control. Choose Lambda for stateless, highly scalable tasks, and Fargate for stateful, container-based scenarios needing fine-tuned environment and resource customization.
Performance Comparison: Scaling and Latency
AWS Lambda offers rapid, event-driven scaling with near-instantaneous start times, making it ideal for low-latency workloads and unpredictable traffic patterns. AWS Fargate provides sustained performance with fine-grained control over container resources, suitable for applications requiring consistent CPU and memory allocation at scale. Lambda's cold start latency can impact performance under sudden load spikes, whereas Fargate delivers stable latency by maintaining containers in a running state, optimizing throughput for long-running or high-demand tasks.
Pricing Models and Cost Efficiency
AWS Lambda follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model based on the number of requests and compute duration, making it cost-effective for sporadic, short-lived tasks. AWS Fargate charges per vCPU and memory resources allocated, billed by the second, which suits steady or long-running workloads requiring dedicated infrastructure. Cost efficiency depends on workload patterns: Lambda excels with intermittent, event-driven executions, while Fargate is more economical for consistent, containerized applications with predictable demand.
Deployment and Management Differences
AWS Lambda offers serverless computing with automatic scaling and no server management, enabling developers to deploy code as individual functions triggered by events. AWS Fargate provides container orchestration without managing underlying servers, allowing deployment of Docker containers with full control over application lifecycle and configuration. Lambda emphasizes event-driven execution with minimal operational overhead, while Fargate focuses on managing containerized applications with greater customization in deployment and scaling policies.
Security Considerations in Lambda and Fargate
Lambda enforces strict execution isolation at the function level, reducing attack surfaces by limiting permissions through IAM roles and automatically patching the underlying infrastructure. Fargate enhances security by running containers in dedicated, kernel-isolated environments, enabling granular control over networking and resource policies via AWS Security Groups and IAM roles. Both services support encryption of data at rest and in transit, but Fargate offers greater customization for container security configurations and compliance requirements.
Integration with AWS Ecosystem
AWS Lambda seamlessly integrates with a wide range of AWS services including API Gateway, DynamoDB, S3, and CloudWatch, enabling event-driven architectures with automatic scaling and built-in monitoring. AWS Fargate also integrates deeply with AWS services such as Amazon ECS, ECR, CloudWatch, and IAM, providing container orchestration with flexible compute options without managing servers. Both services support IAM roles for secure access and integrate with VPC for network isolation, but Lambda excels in serverless event-driven use cases while Fargate is optimized for containerized workloads requiring more control over runtime environment.
Decision Matrix: Selecting the Right Solution
Choosing between AWS Lambda and Fargate depends on workload characteristics, cost considerations, and scalability requirements. Lambda excels in event-driven, short-duration tasks with automatic scaling and minimal management, while Fargate handles long-running, containerized applications with precise resource control and flexible scaling. Evaluate factors such as invocation frequency, execution time, container orchestration needs, and operational complexity to optimize performance and cost efficiency.
Serverless orchestration
AWS Lambda offers fully managed serverless compute for event-driven functions, while AWS Fargate provides serverless orchestration for containerized applications with seamless scalability and infrastructure management.
Containerization
AWS Fargate provides serverless container orchestration allowing users to run containers without managing servers, while AWS Lambda offers event-driven, short-duration function execution ideal for lightweight containerized microservices with automatic scaling.
Event-driven architecture
AWS Lambda enables efficient event-driven architecture with seamless automatic scaling and cost-based execution, while AWS Fargate offers flexible container management for event-driven applications requiring longer processing times and custom runtime environments.
Microservices deployment
AWS Lambda offers rapid, event-driven microservices deployment with automatic scaling and no server management, while AWS Fargate provides greater control over containerized microservices with flexible resource allocation and seamless integration with Amazon ECS or EKS.
Task scheduling
AWS Fargate provides granular task scheduling control with support for ECS and EKS clusters, enabling customizable resource allocation and persistent container management, while AWS Lambda offers automatic scaling and event-driven execution without explicit task scheduling configurations.
Pay-per-invocation
AWS Lambda charges strictly on a pay-per-invocation basis with precise billing per 100 milliseconds of execution, while AWS Fargate bills based on the allocated vCPU and memory resources per second during container runtime.
Cold start latency
AWS Lambda exhibits higher cold start latency ranging from 100ms to several seconds compared to AWS Fargate's minimal cold start delays typically under 100ms for containerized workloads.
Ephemeral compute
AWS Lambda provides fully managed ephemeral compute with automatic scaling for short-lived, event-driven tasks, while AWS Fargate offers ephemeral container-based compute designed for long-running, containerized workloads without server management.
Infrastructure abstraction
AWS Lambda offers complete infrastructure abstraction with automatic scaling and no server management, while AWS Fargate abstracts server infrastructure by managing containers without requiring provisioning or managing underlying servers.
Autoscaling
AWS Lambda automatically scales based on incoming request volume without user intervention, while AWS Fargate requires configuring its autoscaling policies using ECS Service Auto Scaling for workload-driven resource adjustments.
Lambda vs Fargate Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com