No-code platforms enable users to build applications through visual interfaces without writing any code, making software development accessible to non-technical users. Low-code solutions require minimal coding, allowing professional developers to accelerate development while maintaining some customization and control. Both approaches reduce time-to-market and development costs, but low-code offers greater flexibility for complex applications.
Table of Comparison
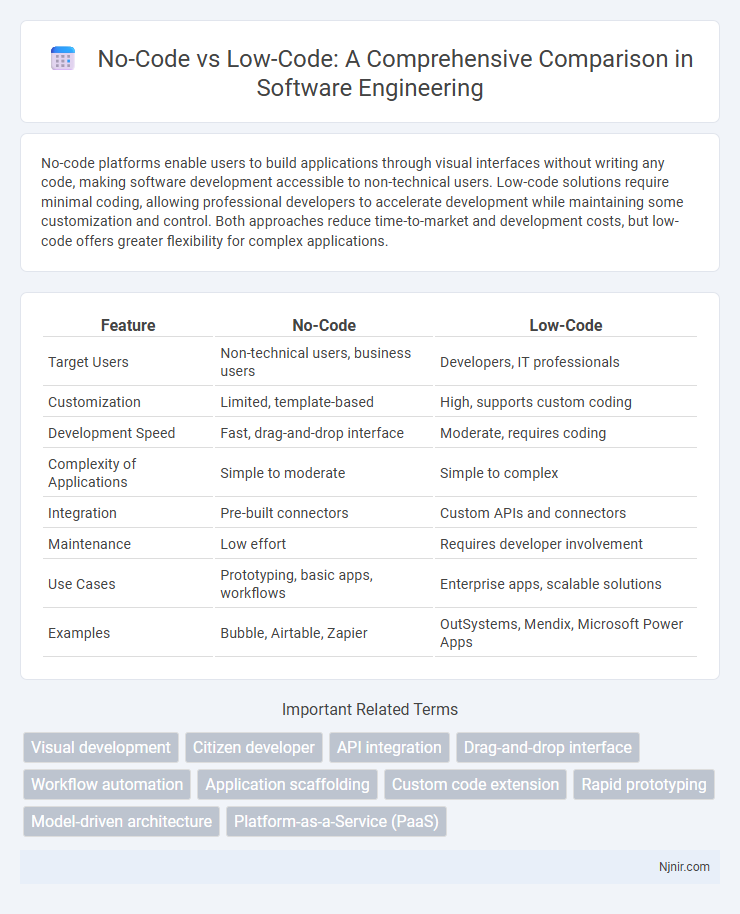
| Feature | No-Code | Low-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | Non-technical users, business users | Developers, IT professionals |
| Customization | Limited, template-based | High, supports custom coding |
| Development Speed | Fast, drag-and-drop interface | Moderate, requires coding |
| Complexity of Applications | Simple to moderate | Simple to complex |
| Integration | Pre-built connectors | Custom APIs and connectors |
| Maintenance | Low effort | Requires developer involvement |
| Use Cases | Prototyping, basic apps, workflows | Enterprise apps, scalable solutions |
| Examples | Bubble, Airtable, Zapier | OutSystems, Mendix, Microsoft Power Apps |
Introduction to No-Code and Low-Code in Software Engineering
No-code platforms empower users to create applications through visual interfaces and pre-built templates without writing any code, enabling rapid development and democratizing software creation. Low-code platforms combine visual development with minimal coding, offering greater flexibility for professional developers to customize and extend applications efficiently. Both approaches accelerate software delivery, reduce dependency on specialized programming skills, and support digital transformation initiatives across industries.
Key Differences Between No-Code and Low-Code Platforms
No-code platforms enable users with no programming skills to build applications through drag-and-drop interfaces, prioritizing ease of use and rapid development. Low-code platforms provide more customization options by allowing developers to write minimal code, offering greater flexibility for complex application needs. Key differences include target users, development complexity, and extensibility, with no-code focusing on business users and low-code catering to professional developers seeking to accelerate project delivery.
Benefits of No-Code Development for Businesses
No-code development empowers businesses to accelerate application delivery by enabling non-technical users to create software without extensive coding knowledge, reducing reliance on IT departments and lowering development costs. This approach enhances agility by allowing rapid iteration and customization, facilitating quicker responses to market changes and customer demands. Moreover, no-code platforms improve collaboration between business and technical teams, driving innovation and efficiency across the organization.
Advantages of Low-Code Solutions for Developers
Low-code solutions enable developers to accelerate application development through pre-built components and visual interfaces, reducing the need for extensive manual coding. These platforms enhance collaboration by allowing both professional developers and business users to contribute, fostering innovation and faster problem-solving. Integration capabilities with existing systems and scalability further empower developers to deliver robust, enterprise-grade applications efficiently.
Common Use Cases: No-Code vs. Low-Code
No-code platforms excel in creating simple applications, automating routine tasks, and enabling non-technical users to build websites or workflows without coding knowledge. Low-code solutions are preferred for developing more complex enterprise-grade applications, integrating multiple systems, and customizing functionalities with minimal hand-coding. Businesses often choose no-code for rapid prototyping and citizen development, while low-code supports scalable application development and IT-driven projects.
Limitations and Challenges of No-Code Platforms
No-code platforms often face limitations in customization and scalability, restricting complex application development and integration with legacy systems. They may also pose challenges related to security vulnerabilities and insufficient control over data management, impacting enterprise-grade solutions. Furthermore, reliance on pre-built templates and components can lead to reduced flexibility and difficulties in meeting unique business requirements.
Scalability and Customization: Low-Code’s Edge
Low-code platforms offer greater scalability by enabling complex application development with reusable components and integration capabilities, accommodating enterprise-level demands more effectively than no-code solutions. Customization in low-code environments is significantly enhanced through access to underlying code and advanced scripting, allowing tailored functionality that no-code platforms cannot achieve. Enterprises seeking robust, scalable applications with specific requirements benefit from low-code's superior flexibility and extensibility.
Security Considerations in No-Code and Low-Code
Security considerations in no-code and low-code platforms revolve around data protection, user access controls, and compliance with industry standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. No-code solutions, often designed for business users, may have limited customization options for security configurations, whereas low-code platforms provide greater flexibility to implement advanced security measures like encryption, role-based access, and audit trails. Evaluating the security features and integration capabilities of each platform is crucial to mitigate risks associated with application vulnerabilities and unauthorized data exposure.
Choosing the Right Platform: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right platform between no-code and low-code depends on factors such as project complexity, development speed, and user expertise. No-code platforms excel in enabling non-technical users to build simple applications quickly, while low-code platforms offer more customization and scalability for professional developers. Evaluating integration capabilities, maintenance needs, and long-term flexibility is essential to align the platform with business goals and technical requirements.
Future Trends in No-Code and Low-Code Development
Future trends in no-code and low-code development emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence to automate complex workflows and enhance user experiences. The rise of citizen developers driving innovation within enterprises accelerates digital transformation and reduces reliance on traditional IT teams. Platform scalability and robust security features are becoming critical as these tools support mission-critical applications across various industries.
Visual development
Visual development in no-code platforms enables non-technical users to create applications through intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, while low-code platforms combine visual development with minimal hand-coding to accelerate complex enterprise software creation.
Citizen developer
Citizen developers accelerate digital transformation by using no-code platforms for rapid app creation, while low-code solutions offer them customizable options with minimal coding to address complex business needs.
API integration
No-code platforms simplify API integration for non-developers using visual tools, while low-code platforms offer advanced API customization and flexibility for developers with minimal coding.
Drag-and-drop interface
Low-code platforms offer drag-and-drop interfaces with customizable coding options, while no-code platforms provide purely drag-and-drop tools designed for users without programming skills.
Workflow automation
Low-code platforms accelerate workflow automation by combining visual development with customizable code options, while no-code solutions enable non-technical users to automate workflows through fully graphical interfaces.
Application scaffolding
No-code platforms enable rapid application scaffolding through visual interfaces with minimal technical expertise, while low-code platforms offer more customizable scaffolding options by combining drag-and-drop tools with traditional coding.
Custom code extension
Low-code platforms offer flexible custom code extension options for advanced functionality, while no-code tools primarily rely on built-in features with limited customization capabilities.
Rapid prototyping
No-code platforms enable rapid prototyping for non-developers by providing visual interfaces, while low-code tools offer developers greater customization and scalability with minimal coding.
Model-driven architecture
Model-driven architecture in no-code platforms enables rapid application development through visual modeling without coding, while low-code platforms combine model-driven design with minimal hand-coding to offer greater customization and flexibility.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
No-code platforms enable non-developers to build applications through intuitive interfaces on PaaS environments, while low-code platforms provide developers with pre-built components and customizable code to accelerate complex app development within the same PaaS framework.
no-code vs low-code Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com