Kubernetes excels in managing complex containerized applications with robust features for scaling, networking, and self-healing, making it ideal for large-scale deployments. Nomad offers a lightweight, flexible scheduler that supports diverse workloads beyond containers, such as virtual machines and batch jobs, simplifying infrastructure management. Choosing between Kubernetes and Nomad depends on specific project requirements like ecosystem integration, operational complexity, and workload diversity.
Table of Comparison
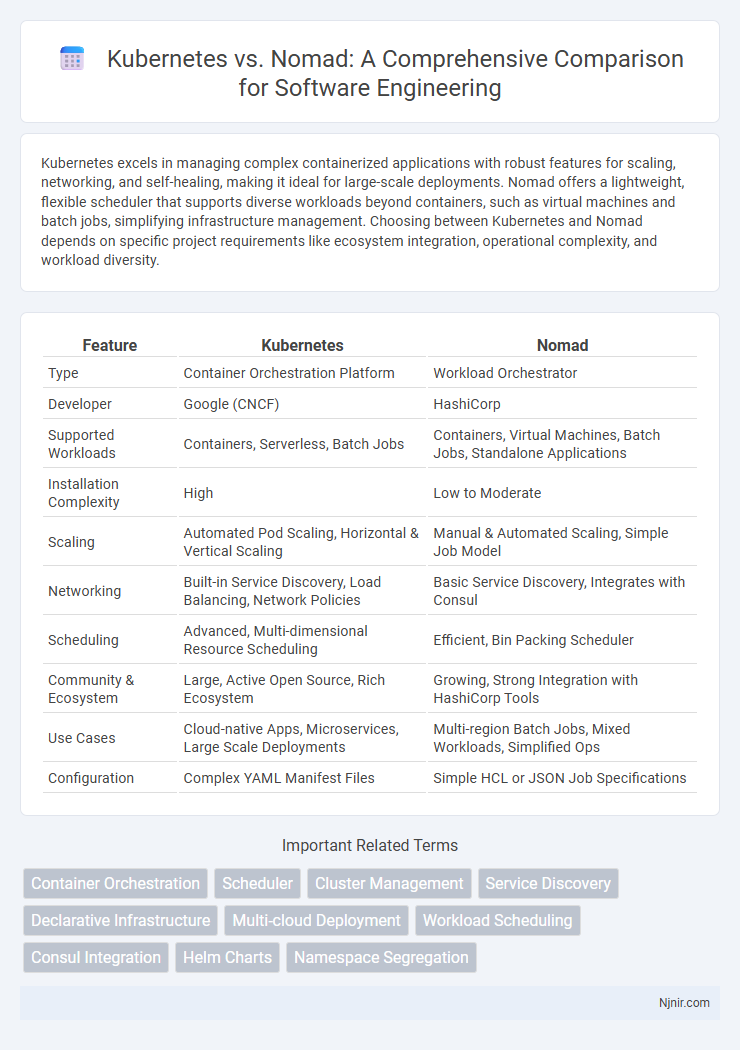
| Feature | Kubernetes | Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Container Orchestration Platform | Workload Orchestrator |
| Developer | Google (CNCF) | HashiCorp |
| Supported Workloads | Containers, Serverless, Batch Jobs | Containers, Virtual Machines, Batch Jobs, Standalone Applications |
| Installation Complexity | High | Low to Moderate |
| Scaling | Automated Pod Scaling, Horizontal & Vertical Scaling | Manual & Automated Scaling, Simple Job Model |
| Networking | Built-in Service Discovery, Load Balancing, Network Policies | Basic Service Discovery, Integrates with Consul |
| Scheduling | Advanced, Multi-dimensional Resource Scheduling | Efficient, Bin Packing Scheduler |
| Community & Ecosystem | Large, Active Open Source, Rich Ecosystem | Growing, Strong Integration with HashiCorp Tools |
| Use Cases | Cloud-native Apps, Microservices, Large Scale Deployments | Multi-region Batch Jobs, Mixed Workloads, Simplified Ops |
| Configuration | Complex YAML Manifest Files | Simple HCL or JSON Job Specifications |
Overview of Kubernetes and Nomad
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across clustered environments. Nomad, developed by HashiCorp, is a flexible and lightweight workload orchestrator that supports containerized, virtualized, and standalone applications with a simplified architecture. Both platforms emphasize scalability and resource efficiency but differ in complexity, ecosystem, and integration capabilities.
Architecture Comparison
Kubernetes architecture is based on a master-worker node model with a control plane that manages scheduling, API interactions, and cluster state through components like etcd, kube-apiserver, kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager, while worker nodes run the kubelet and container runtime. Nomad's architecture features a simpler design using a client-server model with a single leader in the server cluster managing job scheduling and allocation, supported by agents on client nodes that handle task execution and resource monitoring. Kubernetes emphasizes extensibility and rich ecosystem integrations, whereas Nomad prioritizes lightweight deployment and multi-datacenter scalability with native support for heterogeneous workloads beyond containers.
Deployment and Setup
Kubernetes offers a robust deployment model with declarative configurations using YAML files, enabling complex multi-container applications to be orchestrated efficiently across clusters. Nomad simplifies setup with a single binary and supports diverse workloads, providing flexible deployment options with minimal overhead. Kubernetes requires more initial setup and configuration, while Nomad emphasizes ease of use and rapid deployment in diverse environments.
Scalability and Performance
Kubernetes excels in scalability by managing thousands of containers across multiple nodes using its robust API and scheduler, ensuring efficient resource allocation and auto-scaling capabilities. Nomad offers high performance with a lightweight and simple architecture, providing fast job scheduling and lower latency in workload orchestration, particularly suited for diverse workloads beyond containers. Both platforms support horizontal scaling, but Kubernetes' extensive ecosystem and native support for complex microservices contribute to superior scalability, while Nomad maintains consistent performance with minimal overhead in large, heterogeneous environments.
Scheduling and Resource Management
Kubernetes excels in scheduling by using a sophisticated scheduler that assigns pods based on resource requirements, node affinity, and custom policies, ensuring efficient workload distribution across clusters. Nomad employs a lightweight, highly scalable scheduler that supports bin packing and priority-based scheduling, optimizing resource utilization with minimal overhead. Both systems offer robust resource management, but Kubernetes provides more extensive features for managing containerized applications, while Nomad supports multi-region, multi-cloud deployments with diverse workload types beyond containers.
Ecosystem and Integrations
Kubernetes offers a vast ecosystem with extensive native integrations, supporting a wide array of cloud providers, storage solutions, and networking plugins, making it highly adaptable for complex, multi-cloud environments. Nomad excels with a lightweight, flexible architecture that integrates seamlessly with HashiCorp tools like Consul and Vault, providing streamlined service discovery and secure secret management. The Kubernetes ecosystem is more mature, offering a broader range of third-party tools and community-driven add-ons, while Nomad focuses on simplicity and interoperability within the HashiCorp stack.
Security Features
Kubernetes offers robust security features such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), network policies for pod communication restrictions, and built-in secrets management to safeguard sensitive data. Nomad emphasizes simplicity with ACLs (Access Control Lists) for fine-grained permissions, integrated TLS encryption for secure communication, and isolation through job constraints to minimize attack surfaces. Both platforms support audit logging to monitor access and changes, though Kubernetes provides more extensive native security integrations and a larger ecosystem for compliance tools.
Community and Support
Kubernetes boasts a vast and active global community, supported by major cloud providers and a rich ecosystem of open-source tools, ensuring comprehensive documentation and frequent updates. Nomad, developed by HashiCorp, benefits from a dedicated user base and strong integration within the HashiCorp ecosystem but has a smaller, more specialized community compared to Kubernetes. Enterprise users often choose Kubernetes for its extensive third-party support and robust community-driven development, while Nomad appeals to organizations seeking streamlined infrastructure orchestration with HashiCorp's consistent support and commercial backing.
Use Cases and Suitability
Kubernetes excels in managing complex containerized applications at scale, making it ideal for large enterprises requiring robust orchestration, automatic scaling, and extensive ecosystem integration. Nomad is well-suited for simpler, lightweight deployments and heterogeneous workloads, offering flexibility to run containerized, non-containerized, and legacy applications with minimal operational overhead. Organizations prioritizing multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud strategies often favor Kubernetes, while those seeking simplicity and ease of use in smaller environments frequently choose Nomad.
Pros, Cons, and Recommendations
Kubernetes excels in container orchestration with a vast ecosystem, strong community support, and built-in autoscaling, but its complexity and steep learning curve can challenge small teams. Nomad offers a lightweight, easy-to-use scheduler with multi-datacenter support and simpler operational overhead, though it lacks Kubernetes' extensive native features and ecosystem integrations. For large-scale, feature-rich deployments requiring extensive customization, Kubernetes is recommended, while Nomad suits organizations seeking simplicity, speed, and multi-cloud flexibility in smaller environments.
Container Orchestration
Kubernetes offers a comprehensive container orchestration platform with advanced features like automated scaling, self-healing, and extensive ecosystem support, while Nomad provides a lightweight, flexible scheduler optimized for multi-cloud and multi-region workloads with simpler architecture and faster deployment.
Scheduler
Kubernetes uses a sophisticated, pluggable scheduler optimized for complex container orchestration with automated bin packing, while Nomad offers a lightweight, flexible scheduler designed for multi-datacenter deployments and diverse workload types.
Cluster Management
Kubernetes excels in complex cluster management with automated scaling, self-healing, and extensive ecosystem integrations, while Nomad offers a lightweight, flexible cluster management solution optimized for multi-datacenter and heterogeneous workloads.
Service Discovery
Kubernetes leverages built-in DNS-based service discovery and native integrations with CoreDNS for dynamic service endpoint resolution, while Nomad relies on Consul for robust service discovery and health checking across distributed clusters.
Declarative Infrastructure
Kubernetes and Nomad both support declarative infrastructure, with Kubernetes using YAML manifests for resource definitions and Nomad leveraging HCL for job specifications to enable automated, consistent application deployment.
Multi-cloud Deployment
Kubernetes offers robust multi-cloud deployment with native support for complex container orchestration across diverse cloud environments, while Nomad provides a lightweight, flexible scheduler optimized for seamless multi-cloud and hybrid cloud workload management.
Workload Scheduling
Kubernetes excels in workload scheduling with advanced features like custom resource definitions and pod affinity, while Nomad offers simpler, lightweight scheduling optimized for multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
Consul Integration
Kubernetes integrates with Consul primarily through service mesh solutions like Consul Connect for service discovery and network segmentation, while Nomad offers native Consul integration for dynamic service registration and health checking, enabling seamless multi-datacenter orchestration and workload scheduling.
Helm Charts
Helm Charts streamline application deployment and management on Kubernetes, whereas Nomad lacks native Helm support, making Kubernetes the preferred choice for users leveraging Helm's package management capabilities.
Namespace Segregation
Kubernetes enforces strict namespace segregation within clusters for resource isolation, while Nomad uses job-based namespaces that provide simpler yet effective multi-tenancy and access control.
Kubernetes vs Nomad Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com