End-to-end testing validates the complete flow of an application, ensuring all integrated components work together as expected, while unit testing isolates individual functions or methods to verify their correctness in isolation. End-to-end tests catch issues that arise from component interactions and real-world user scenarios, whereas unit tests provide fast, detailed feedback during development. Combining both testing strategies improves software reliability by covering both granular logic and system-wide functionality.
Table of Comparison
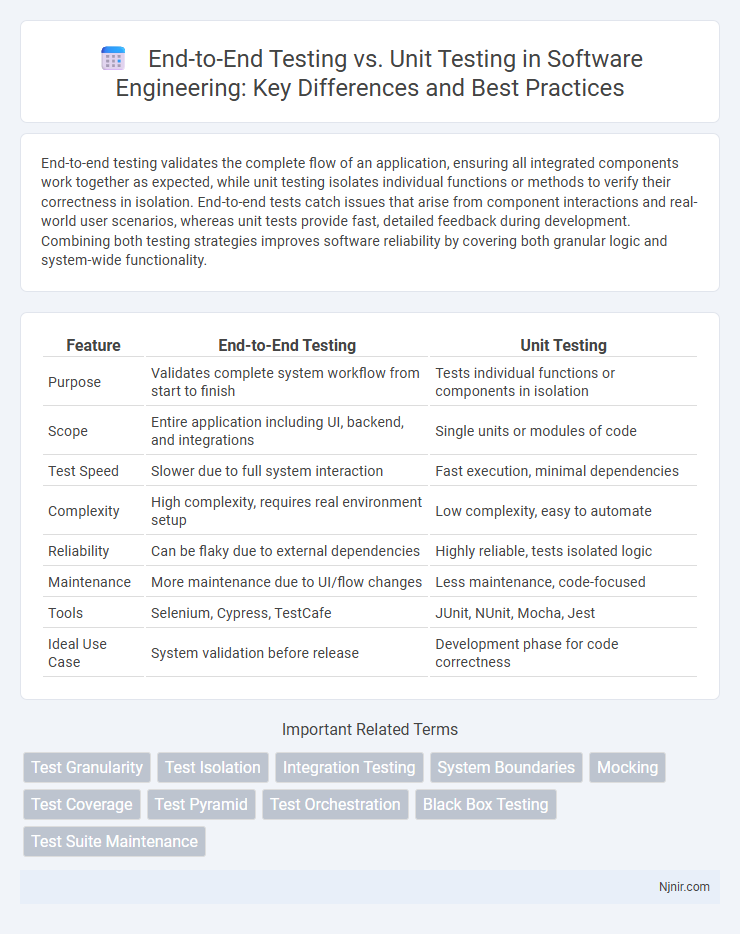
| Feature | End-to-End Testing | Unit Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validates complete system workflow from start to finish | Tests individual functions or components in isolation |
| Scope | Entire application including UI, backend, and integrations | Single units or modules of code |
| Test Speed | Slower due to full system interaction | Fast execution, minimal dependencies |
| Complexity | High complexity, requires real environment setup | Low complexity, easy to automate |
| Reliability | Can be flaky due to external dependencies | Highly reliable, tests isolated logic |
| Maintenance | More maintenance due to UI/flow changes | Less maintenance, code-focused |
| Tools | Selenium, Cypress, TestCafe | JUnit, NUnit, Mocha, Jest |
| Ideal Use Case | System validation before release | Development phase for code correctness |
Overview of End-to-End Testing and Unit Testing
End-to-end testing validates the entire software application flow from start to finish, ensuring integrated systems and components work together as expected in real-world scenarios. Unit testing targets individual functions or components in isolation to verify their correctness and reliability during development. Comprehensive test strategies combine both methods to enhance software quality by detecting issues early and confirming overall system functionality.
Key Differences Between End-to-End and Unit Testing
End-to-end testing evaluates the entire application flow to validate system integration and user experience, covering multiple components, while unit testing isolates and verifies individual functions or methods for correctness. End-to-end tests are typically slower and more complex, requiring real or simulated environments, whereas unit tests are faster and simpler to automate with mock dependencies. The scope, speed, and purpose distinguish these testing types, with end-to-end focusing on behavior and unit testing emphasizing code accuracy.
Core Objectives of Each Testing Approach
End-to-end testing primarily verifies the functionality and performance of the entire application workflow, ensuring all integrated components interact correctly to meet user requirements. Unit testing focuses on validating individual functions or methods within code modules, aiming to catch bugs early by testing small, isolated units for correctness. The core objective of end-to-end testing is to simulate real user scenarios, while unit testing targets code reliability and maintainability at a granular level.
Components Covered by Unit vs. End-to-End Tests
Unit testing targets individual components or functions in isolation, ensuring that each part performs as expected without external dependencies. End-to-end testing, conversely, covers the entire application workflow, validating the integration and interaction between multiple components through simulated real user scenarios. This comprehensive coverage detects issues that arise from component integration, which unit tests alone cannot identify.
Advantages and Limitations of Unit Testing
Unit testing offers precise validation of individual components, enabling early detection of bugs and simplifying debugging by isolating test failures. It improves code quality through immediate feedback and supports refactoring by ensuring component stability but may miss integration issues or overall system behavior errors. Limited scope and maintenance overhead can reduce effectiveness if unit tests do not evolve with changing codebases or are poorly implemented.
Benefits and Drawbacks of End-to-End Testing
End-to-end testing provides comprehensive validation of the entire application flow, ensuring all integrated components work together as expected, which significantly reduces the risk of system failures in production. However, it is time-consuming and resource-intensive compared to unit testing, as it requires a fully operational environment and complex test scenarios. The main drawback is slower feedback on defects, making it less efficient for catching issues early in the development cycle compared to faster, isolated unit tests.
Common Tools for Unit and End-to-End Testing
Common tools for unit testing include Jest, Mocha, and Jasmine, which focus on testing individual functions or components in isolation. For end-to-end testing, popular tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright simulate real user interactions across entire application flows to validate integrated functionality. Some frameworks like Cypress and Playwright offer capabilities for both unit and end-to-end testing, providing a unified testing environment for developers.
When to Use Unit Testing vs. End-to-End Testing
Unit testing is essential during the development phase to validate individual components or functions for accuracy and reliability, enabling faster identification of bugs at a granular level. End-to-end testing is best utilized after integration to ensure that the entire application workflow, including user interfaces, APIs, and databases, functions seamlessly across real-world scenarios. Prioritizing unit tests for core logic and end-to-end tests for critical user journeys optimizes test coverage and reduces debugging time.
Best Practices for Combining Both Testing Methods
Combining end-to-end testing and unit testing enhances software quality by covering both integration points and individual components. Best practices include running unit tests early and frequently during development to catch bugs at the source, while using end-to-end tests to validate user flows and system interactions in realistic environments. Prioritizing a balanced testing pyramid ensures efficient test coverage, faster feedback cycles, and more reliable releases.
Impact on Software Quality and Development Workflow
End-to-end testing ensures comprehensive validation of software functionality by simulating real user scenarios, significantly improving software quality through early detection of integration issues and overall system reliability. Unit testing focuses on verifying individual components in isolation, promoting faster development cycles and easier debugging by catching defects at the code level. Combining both testing approaches creates a robust development workflow, balancing detailed code accuracy with holistic system performance validation.
Test Granularity
End-to-end testing evaluates the entire application workflow at a coarse granularity, while unit testing focuses on fine-grained verification of individual components or functions.
Test Isolation
End-to-end testing evaluates entire application workflows with limited test isolation, while unit testing ensures high test isolation by independently verifying individual components or functions.
Integration Testing
Integration testing bridges unit testing and end-to-end testing by validating combined components' interactions and data flow within a software system.
System Boundaries
End-to-end testing evaluates the entire system's functionality across all system boundaries, ensuring integrated components work together, while unit testing isolates individual units within system boundaries to validate their correctness independently.
Mocking
Unit testing uses mocking to isolate components by simulating dependencies, while end-to-end testing validates entire workflows without mocks to ensure real-world system integration.
Test Coverage
End-to-end testing provides broader test coverage by validating complete user flows across integrated systems, while unit testing offers granular coverage by verifying individual components or functions in isolation.
Test Pyramid
The Test Pyramid prioritizes numerous fast, isolated unit tests at the base, fewer integration tests in the middle, and minimal end-to-end tests at the top to ensure efficient, reliable software quality assurance.
Test Orchestration
Test orchestration in end-to-end testing manages comprehensive workflows across multiple system components, whereas unit testing focuses on isolated code validation without orchestration complexity.
Black Box Testing
End-to-end testing verifies complete system workflows from a user's perspective without internal code knowledge, while unit testing isolates individual components, both employing black box testing to validate functionality based on inputs and expected outputs.
Test Suite Maintenance
End-to-end testing requires more complex test suite maintenance due to broader system interactions and higher dependencies, while unit testing offers easier maintenance with isolated, smaller test cases targeting individual components.
end-to-end testing vs unit testing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com