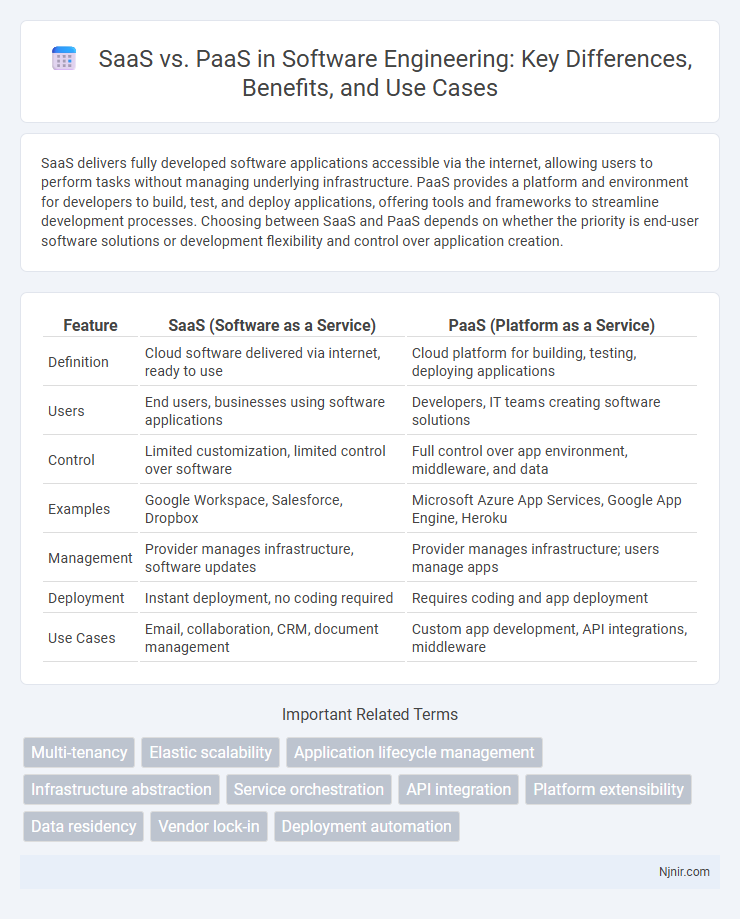
SaaS delivers fully developed software applications accessible via the internet, allowing users to perform tasks without managing underlying infrastructure. PaaS provides a platform and environment for developers to build, test, and deploy applications, offering tools and frameworks to streamline development processes. Choosing between SaaS and PaaS depends on whether the priority is end-user software solutions or development flexibility and control over application creation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SaaS (Software as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud software delivered via internet, ready to use | Cloud platform for building, testing, deploying applications |
| Users | End users, businesses using software applications | Developers, IT teams creating software solutions |
| Control | Limited customization, limited control over software | Full control over app environment, middleware, and data |
| Examples | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox | Microsoft Azure App Services, Google App Engine, Heroku |
| Management | Provider manages infrastructure, software updates | Provider manages infrastructure; users manage apps |
| Deployment | Instant deployment, no coding required | Requires coding and app deployment |
| Use Cases | Email, collaboration, CRM, document management | Custom app development, API integrations, middleware |
Understanding SaaS and PaaS: Key Definitions
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers fully functional software applications over the internet, allowing users to access programs like CRM, email, or collaboration tools without managing infrastructure. PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a development environment and tools for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without handling underlying hardware or operating systems. Understanding the distinction highlights that SaaS focuses on end-user software consumption, while PaaS centers on creating and managing custom applications.
Core Differences Between SaaS and PaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers fully functional software applications over the internet, allowing users to access and use software without managing underlying infrastructure or platforms. PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a cloud-based environment with tools and frameworks for developers to build, deploy, and manage custom applications without worrying about server or network management. The core difference lies in SaaS offering ready-to-use software solutions for end-users, while PaaS offers a development platform for creating and hosting applications.
Typical Use Cases for SaaS in Software Engineering
SaaS typical use cases in software engineering include project management tools like Jira and Trello, which facilitate collaboration and workflow automation without requiring local installation. Developer productivity applications such as GitHub and Bitbucket offer version control and code repositories accessible via the cloud, streamlining team development processes. Additionally, continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) platforms like CircleCI provide automated testing and delivery services, enhancing software release efficiency.
Typical Use Cases for PaaS in Software Engineering
PaaS platforms are ideal for software engineering projects requiring rapid development, testing, and deployment of applications without managing underlying infrastructure. Common use cases include developing web and mobile applications, creating APIs, and enabling continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. PaaS solutions like Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine, and Heroku streamline collaboration among development teams and support scalability during application lifecycle management.
Benefits of SaaS for Development Teams
SaaS offers development teams immediate access to fully managed applications, reducing the need for infrastructure maintenance and enabling rapid deployment. It provides seamless scalability and automatic updates, ensuring teams always work with the latest features and security patches. SaaS solutions enhance collaboration by allowing easy integration with various tools and enabling remote access from any device.
Advantages of PaaS for Software Projects
PaaS offers scalable infrastructure and pre-built development tools that accelerate software project delivery and reduce time-to-market. It enables seamless collaboration among distributed developer teams through integrated version control, automated testing, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. The platform's managed services handle underlying hardware and software maintenance, allowing developers to focus exclusively on coding and innovation without worrying about infrastructure management.
Limitations and Challenges: SaaS vs PaaS
SaaS platforms often face limitations in customization and integration flexibility, which can hinder businesses needing tailored solutions or complex workflows. PaaS offers greater development control but presents challenges in vendor lock-in, scalability management, and requires specialized technical expertise for platform maintenance. Both models demand careful evaluation of data security, compliance risks, and total cost of ownership before adoption.
Security Considerations in SaaS and PaaS Solutions
SaaS solutions typically require customers to rely on the provider's security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications such as SOC 2 and ISO 27001. PaaS platforms offer greater security flexibility by allowing developers to implement custom security protocols, secure APIs, and identity management within their applications, but this places more responsibility on users to manage vulnerabilities. Ensuring secure data transmission, regular patching, and robust authentication processes are critical in both SaaS and PaaS environments to protect against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Choosing Between SaaS and PaaS: Decision Factors
Choosing between SaaS and PaaS depends on the level of control, customization, and development resources required for your business applications. SaaS offers ready-to-use, cloud-based software solutions ideal for end-users seeking simplicity and minimal IT management, while PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy custom applications with greater flexibility and integration options. Key decision factors include the need for scalability, technical expertise, desired user experience, and long-term maintenance responsibilities.
Future Trends in SaaS and PaaS for Software Engineering
Future trends in SaaS and PaaS for software engineering emphasize increased integration of AI and machine learning to enhance automation and predictive analytics. SaaS platforms are evolving towards more customizable, industry-specific solutions that improve scalability and user experience. PaaS providers are expanding support for multi-cloud deployments and low-code development environments to accelerate app innovation and reduce time-to-market.
Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy in SaaS enables multiple users to share a single application instance with isolated data, while PaaS provides a multi-tenant platform for developers to build and deploy applications with shared infrastructure.
Elastic scalability
SaaS offers elastic scalability by automatically adjusting software resources for users, while PaaS provides developers with scalable infrastructure and tools to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently.
Application lifecycle management
SaaS simplifies application lifecycle management by delivering ready-to-use software with automatic updates, while PaaS provides a flexible development environment for building, testing, and deploying applications throughout their entire lifecycle.
Infrastructure abstraction
SaaS abstracts end-user applications on fully managed software platforms, while PaaS provides developers with a higher level of infrastructure abstraction by delivering managed runtime environments and development tools.
Service orchestration
SaaS provides ready-to-use software applications managed by providers, while PaaS offers a platform for developers to orchestrate and deploy custom services with integrated tools and scalable infrastructure.
API integration
SaaS platforms offer ready-to-use software with pre-built API integrations for seamless functionality, while PaaS provides developers with customizable environments and robust APIs to build, deploy, and integrate applications flexibly.
Platform extensibility
PaaS offers greater platform extensibility by enabling developers to build, customize, and deploy applications on scalable infrastructure, while SaaS provides limited extensibility with pre-built software solutions.
Data residency
SaaS solutions typically manage data residency through provider-controlled data centers, while PaaS platforms offer greater flexibility for developers to select or configure data residency based on regional compliance requirements.
Vendor lock-in
SaaS solutions often increase vendor lock-in due to proprietary application dependencies, whereas PaaS platforms offer more flexibility by allowing custom application development and easier migration across cloud providers.
Deployment automation
SaaS platforms provide fully managed deployment automation for end-users, while PaaS offers developers flexible deployment automation tools and environments to build, test, and deploy applications efficiently.
SaaS vs PaaS Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com