DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the DevOps lifecycle, ensuring continuous security testing and compliance from development to deployment. This approach reduces vulnerabilities by automating security checks alongside traditional DevOps processes like CI/CD and infrastructure as code. Organizations adopting DevSecOps benefit from faster threat detection, improved risk management, and enhanced collaboration between development, operations, and security teams.
Table of Comparison
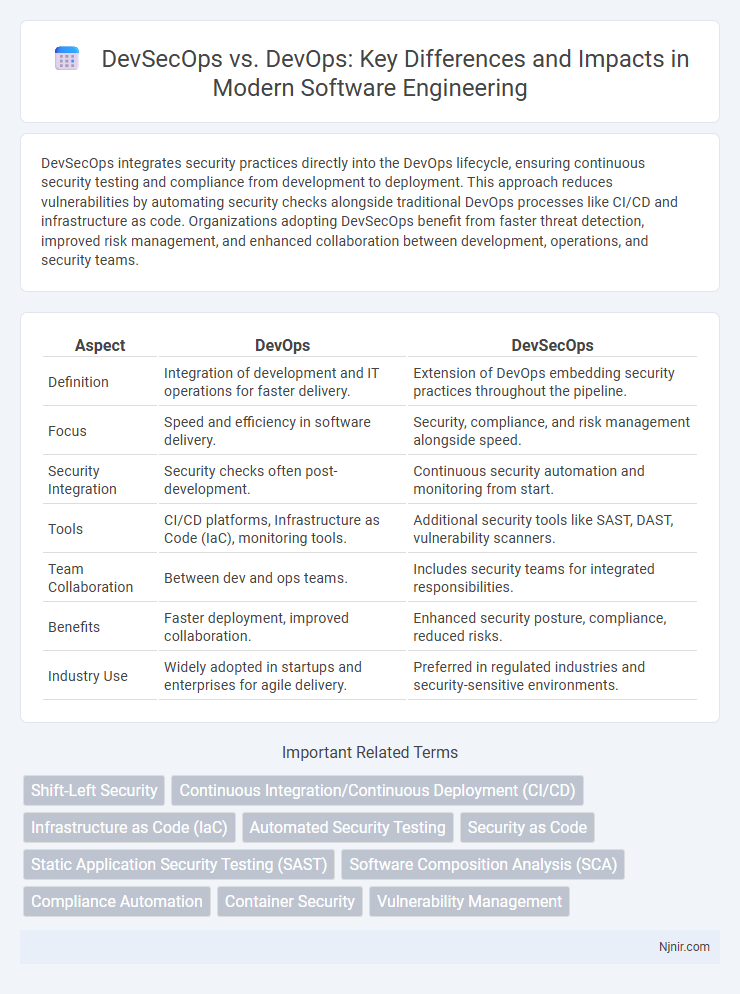
| Aspect | DevOps | DevSecOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of development and IT operations for faster delivery. | Extension of DevOps embedding security practices throughout the pipeline. |
| Focus | Speed and efficiency in software delivery. | Security, compliance, and risk management alongside speed. |
| Security Integration | Security checks often post-development. | Continuous security automation and monitoring from start. |
| Tools | CI/CD platforms, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), monitoring tools. | Additional security tools like SAST, DAST, vulnerability scanners. |
| Team Collaboration | Between dev and ops teams. | Includes security teams for integrated responsibilities. |
| Benefits | Faster deployment, improved collaboration. | Enhanced security posture, compliance, reduced risks. |
| Industry Use | Widely adopted in startups and enterprises for agile delivery. | Preferred in regulated industries and security-sensitive environments. |
Understanding DevOps: Core Principles and Practices
DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to accelerate software delivery through continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and infrastructure as code (IaC). Its core principles include automation, monitoring, and iterative feedback loops that enhance software quality and release velocity. Understanding these foundations is essential before integrating security practices to evolve into DevSecOps, which embeds security into every phase of the development lifecycle.
Introducing DevSecOps: Security Integrated Into DevOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the DevOps pipeline, ensuring continuous security throughout the software development lifecycle. Unlike traditional DevOps, which emphasizes rapid development and deployment, DevSecOps embeds automated security testing, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks early in the process. This approach reduces risks, accelerates secure delivery, and aligns development, security, and operations teams for proactive threat mitigation.
Key Differences Between DevOps and DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the DevOps workflow, emphasizing continuous security testing and automated compliance checks, unlike DevOps, which primarily focuses on collaboration between development and operations for faster delivery. Key differences include the proactive emphasis on security tools and practices in DevSecOps, such as vulnerability scanning and threat modeling, embedded early in the CI/CD pipeline. DevOps aims for rapid deployment and operational efficiency, while DevSecOps prioritizes securing the entire development lifecycle without sacrificing speed.
Why Security Matters: The Evolution from DevOps to DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the DevOps lifecycle, addressing vulnerabilities earlier in the software development process to reduce risks and enhance compliance. This shift responds to the increasing complexity of cyber threats and the need for continuous security in fast-paced development environments. Embedding security controls and automation ensures that security is a shared responsibility, fostering collaboration between development, operations, and security teams for more resilient applications.
Core Components of a DevSecOps Pipeline
Core components of a DevSecOps pipeline integrate security practices into every phase of the software development lifecycle, including automated code analysis, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) with security gates, and infrastructure as code (IaC) with embedded security policies. Key tools involve static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), software composition analysis (SCA), and runtime protection, ensuring vulnerabilities are detected and mitigated early. This approach contrasts with traditional DevOps by embedding security as a foundational element rather than an afterthought, accelerating secure software delivery without compromising agility.
Security Automation Tools in DevSecOps vs DevOps
DevSecOps integrates security automation tools such as static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), and software composition analysis (SCA) directly into the CI/CD pipeline, enabling real-time vulnerability detection and remediation. In contrast, traditional DevOps workflows prioritize speed and continuous delivery but often rely on manual security interventions or post-deployment scanning, which can delay threat identification. The proactive inclusion of automated security tools in DevSecOps reduces risks and enhances compliance, streamlining secure software development at scale.
Cultural Shifts Required for DevSecOps Adoption
DevSecOps demands a fundamental cultural shift towards integrating security as a shared responsibility across development, operations, and security teams, fostering collaboration and transparency. Embracing automated security testing and continuous monitoring within the CI/CD pipeline requires training and mindset changes to prioritize proactive risk management over reactive fixes. Organizations must cultivate a culture of accountability where security is embedded early and continuously, ensuring faster delivery without compromising compliance or quality.
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices into the DevOps pipeline, enhancing threat detection and ensuring compliance throughout the software development lifecycle. Key benefits include faster vulnerability identification, reduced security risks, and improved collaboration between development, security, and operations teams. Challenges involve the need for cultural shifts, continuous security training, and the complexity of integrating automated security tools without disrupting development velocity.
Real-World Use Cases: DevOps vs DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the DevOps pipeline, enabling real-time vulnerability detection and automated compliance checks to reduce risks in production environments. Major enterprises like Netflix and Amazon employ DevSecOps to streamline secure code deployment while maintaining rapid release cycles, contrasting with traditional DevOps which often separates security as a final stage. This unified approach enhances incident response times and ensures continuous security compliance, critical for industries handling sensitive data such as finance and healthcare.
Best Practices for Transitioning from DevOps to DevSecOps
Integrating security into the development lifecycle is essential for transitioning from DevOps to DevSecOps, emphasizing automated security testing and continuous monitoring. Implementing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with security policies embedded ensures consistency and reduces configuration drift. Collaboration between development, security, and operations teams enhances vulnerability management and accelerates secure software delivery.
Shift-Left Security
Shift-Left Security in DevSecOps integrates automated security testing early in the development lifecycle to identify vulnerabilities faster compared to traditional DevOps practices.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
DevSecOps integrates automated security testing into the Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline, enhancing DevOps by ensuring real-time vulnerability detection and compliance without slowing development cycles.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into Infrastructure as Code (IaC) workflows, enabling automated vulnerability scanning and policy enforcement, whereas traditional DevOps primarily focuses on automation and collaboration without embedding security at the IaC level.
Automated Security Testing
DevSecOps integrates Automated Security Testing into the DevOps pipeline to identify vulnerabilities early, ensuring continuous security assessment and faster remediation compared to traditional DevOps practices.
Security as Code
DevSecOps integrates Security as Code into continuous development pipelines, embedding automated security testing and compliance checks directly into DevOps workflows to enhance vulnerability detection and risk mitigation.
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) in DevSecOps integrates automated security analysis into the development pipeline, enabling early detection of vulnerabilities compared to traditional DevOps practices.
Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
DevSecOps integrates Software Composition Analysis (SCA) to automate vulnerability detection and license compliance in open-source components, enhancing security beyond traditional DevOps practices.
Compliance Automation
DevSecOps integrates compliance automation directly into the development pipeline, ensuring continuous security and regulatory adherence, whereas DevOps primarily focuses on rapid software delivery without inherent compliance controls.
Container Security
DevSecOps integrates automated container security measures such as vulnerability scanning and runtime protection into the DevOps workflow, enhancing continuous delivery pipelines by proactively identifying and mitigating container-related risks.
Vulnerability Management
DevSecOps integrates continuous vulnerability management within the development pipeline, enhancing security by automating threat detection and remediation unlike traditional DevOps which primarily focuses on deployment speed and operational efficiency.
DevSecOps vs DevOps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com