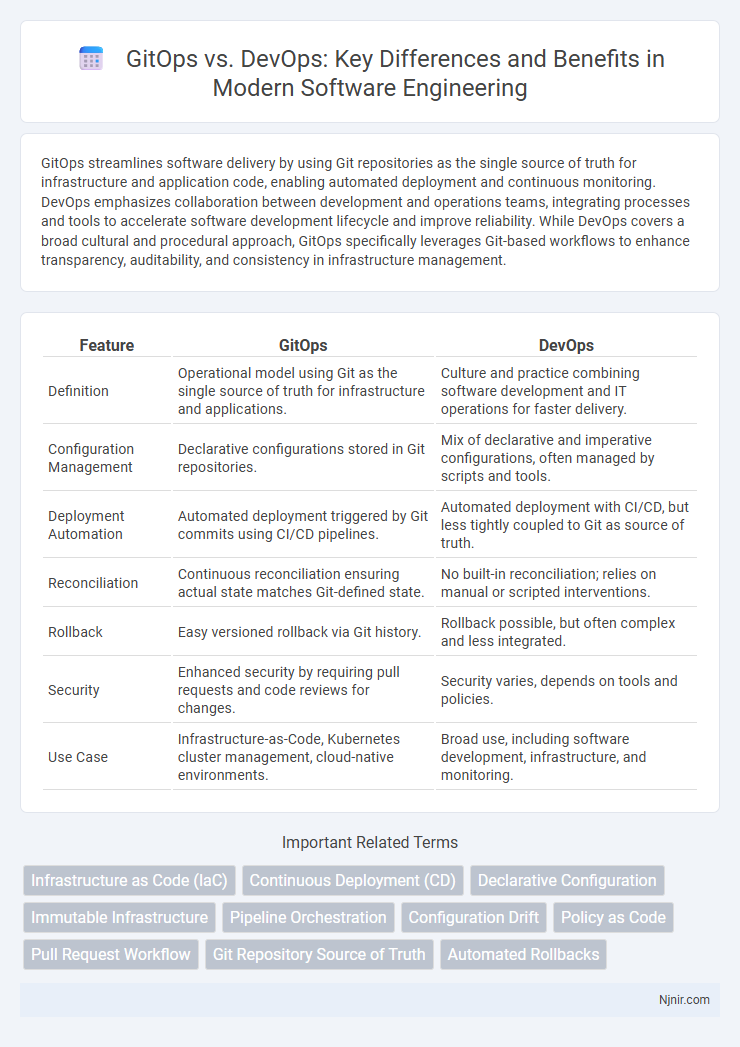
GitOps streamlines software delivery by using Git repositories as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application code, enabling automated deployment and continuous monitoring. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams, integrating processes and tools to accelerate software development lifecycle and improve reliability. While DevOps covers a broad cultural and procedural approach, GitOps specifically leverages Git-based workflows to enhance transparency, auditability, and consistency in infrastructure management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | GitOps | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Operational model using Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and applications. | Culture and practice combining software development and IT operations for faster delivery. |
| Configuration Management | Declarative configurations stored in Git repositories. | Mix of declarative and imperative configurations, often managed by scripts and tools. |
| Deployment Automation | Automated deployment triggered by Git commits using CI/CD pipelines. | Automated deployment with CI/CD, but less tightly coupled to Git as source of truth. |
| Reconciliation | Continuous reconciliation ensuring actual state matches Git-defined state. | No built-in reconciliation; relies on manual or scripted interventions. |
| Rollback | Easy versioned rollback via Git history. | Rollback possible, but often complex and less integrated. |
| Security | Enhanced security by requiring pull requests and code reviews for changes. | Security varies, depends on tools and policies. |
| Use Case | Infrastructure-as-Code, Kubernetes cluster management, cloud-native environments. | Broad use, including software development, infrastructure, and monitoring. |
Introduction to GitOps and DevOps
DevOps is a cultural and operational framework that integrates software development and IT operations to enhance collaboration, accelerate delivery cycles, and improve system reliability through continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). GitOps extends DevOps principles by using Git repositories as a single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application configurations, enabling automated deployment and management via Kubernetes. This approach leverages version control, automation, and pull request workflows to ensure transparency, traceability, and faster recovery in cloud-native environments.
Core Principles of GitOps
GitOps centers on using Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment, ensuring version control and auditability of all changes. Automation and continuous reconciliation are core principles, enabling systems to self-heal by automatically aligning the live state with the desired state defined in Git repositories. This approach leverages pull requests for change management, enhancing collaboration and operational consistency compared to traditional DevOps practices.
Fundamental Concepts of DevOps
DevOps fundamentally emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to automate the software delivery pipeline, ensuring continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) for faster and reliable releases. It relies on practices such as infrastructure as code (IaC), automated testing, and monitoring to improve efficiency and reduce errors. These core principles enable organizations to achieve agility, scalability, and enhanced system stability throughout the software development lifecycle.
Key Differences Between GitOps and DevOps
GitOps centers on using Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application deployment, automating operations through declarative configurations managed via version control. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams, integrating continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to streamline software delivery and infrastructure changes. The core difference lies in GitOps' reliance on Git-driven automation for operational tasks, whereas DevOps encompasses a broader cultural framework promoting collaboration and automation across the software lifecycle.
Advantages of GitOps in Modern Software Delivery
GitOps enhances modern software delivery by enabling fully automated and declarative infrastructure management through Git repositories as the single source of truth. This approach improves deployment consistency, reduces human error, and accelerates rollback capabilities, leading to increased reliability and faster recovery in production environments. Leveraging native Git workflows also fosters better collaboration between development and operations teams, streamlining continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
DevOps Benefits for Continuous Integration and Deployment
DevOps enhances Continuous Integration and Deployment by automating the software delivery pipeline, enabling faster and more reliable code integration and release cycles. It promotes collaboration between development and operations teams, reducing errors and improving deployment frequency through streamlined workflows and continuous feedback loops. These benefits lead to accelerated product delivery, higher software quality, and increased operational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations of GitOps
GitOps faces challenges such as complex initial setup and steep learning curves for teams unfamiliar with declarative infrastructure and Kubernetes. Limitations include dependency on Git as a single source of truth, which can lead to bottlenecks during merge conflicts or large-scale changes. Security risks arise if Git repositories are not properly managed, potentially exposing infrastructure configurations to unauthorized access.
When to Choose GitOps Over DevOps
GitOps should be chosen over DevOps when infrastructure automation and continuous deployment pipelines demand version control as a single source of truth, enhancing system reliability and auditability. Organizations managing complex Kubernetes environments benefit from GitOps' declarative configuration and automated reconciliation processes. Enterprises seeking faster rollback capabilities and improved collaboration between development and operations teams find GitOps an effective strategy for streamlining cloud-native application management.
Real-World Use Cases: GitOps vs DevOps
GitOps streamlines Kubernetes cluster management by leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling automated deployments and real-time observability, which enhances consistency and rollback capabilities in production environments. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams, utilizing CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure as code to accelerate software delivery across diverse platforms, including cloud and on-premises infrastructures. Organizations adopting GitOps benefit from improved deployment reliability in containerized applications, while DevOps remains crucial for end-to-end software lifecycle management across various environments.
Future Trends in Software Engineering: GitOps and DevOps
Future trends in software engineering emphasize the integration of GitOps and DevOps methodologies to enhance automation, scalability, and continuous delivery. GitOps leverages Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling declarative infrastructure management and faster rollback capabilities, which complement DevOps practices such as CI/CD pipelines and collaborative workflows. Emerging innovations focus on AI-driven automation, increased security through policy-as-code, and seamless cloud-native deployments, positioning GitOps as a scalable evolution of traditional DevOps frameworks.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
GitOps enhances Infrastructure as Code (IaC) by leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth for automated infrastructure deployment and continuous reconciliation, while DevOps encompasses a broader cultural and procedural framework for collaboration and automation beyond IaC.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
GitOps enhances Continuous Deployment (CD) by automating application delivery through Git-based version control and declarative infrastructure, while DevOps emphasizes collaboration and integration of development and operations teams to streamline CD pipelines.
Declarative Configuration
GitOps leverages declarative configuration stored in Git repositories to automate infrastructure and application deployments, enhancing version control and rollback capabilities compared to traditional DevOps approaches.
Immutable Infrastructure
GitOps enhances DevOps by leveraging immutable infrastructure to ensure consistent, automated deployments through declarative Git repository configurations.
Pipeline Orchestration
GitOps automates pipeline orchestration through declarative, version-controlled configurations enabling continuous deployment, while DevOps relies on manual or scripted pipeline management integrating diverse tools for continuous integration and delivery.
Configuration Drift
GitOps minimizes configuration drift by using declarative configurations stored in Git repositories as the single source of truth, ensuring continuous synchronization between desired and actual system states, whereas DevOps requires manual or scripted interventions that increase the risk of drift over time.
Policy as Code
GitOps leverages Policy as Code to automate and enforce infrastructure compliance through declarative version-controlled policies, enhancing the security and reliability of DevOps workflows.
Pull Request Workflow
GitOps enhances DevOps by using Pull Request workflows to automate infrastructure changes with version-controlled, auditable, and rollback-friendly deployments.
Git Repository Source of Truth
GitOps uses the Git repository as the single source of truth to automate infrastructure and application deployment, while DevOps encompasses broader practices without mandating Git as the exclusive source of truth.
Automated Rollbacks
GitOps ensures automated rollbacks by continuously monitoring cluster states and reverting to the last known good configuration, enhancing deployment reliability compared to traditional DevOps rollback methods.
GitOps vs DevOps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com