Agile emphasizes iterative development and customer collaboration to deliver software in small, manageable increments, fostering flexibility and continuous improvement. DevOps integrates development and operations teams to automate and streamline the software delivery pipeline, enhancing deployment frequency and reliability. Combining Agile and DevOps practices accelerates value delivery while maintaining high quality and rapid feedback cycles.
Table of Comparison
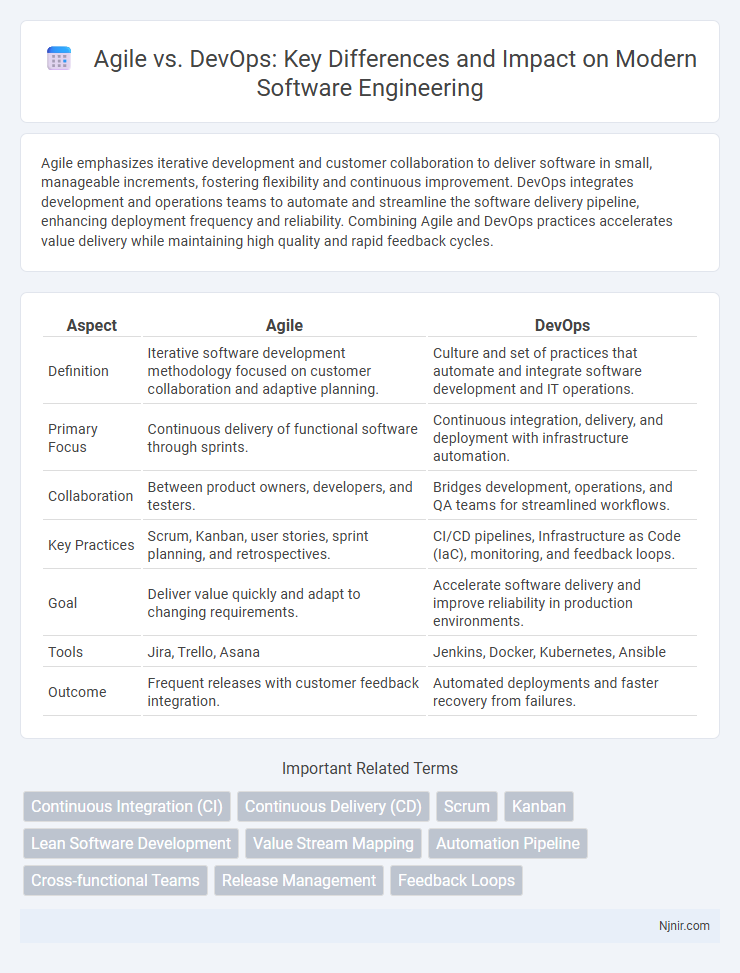
| Aspect | Agile | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Iterative software development methodology focused on customer collaboration and adaptive planning. | Culture and set of practices that automate and integrate software development and IT operations. |
| Primary Focus | Continuous delivery of functional software through sprints. | Continuous integration, delivery, and deployment with infrastructure automation. |
| Collaboration | Between product owners, developers, and testers. | Bridges development, operations, and QA teams for streamlined workflows. |
| Key Practices | Scrum, Kanban, user stories, sprint planning, and retrospectives. | CI/CD pipelines, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), monitoring, and feedback loops. |
| Goal | Deliver value quickly and adapt to changing requirements. | Accelerate software delivery and improve reliability in production environments. |
| Tools | Jira, Trello, Asana | Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible |
| Outcome | Frequent releases with customer feedback integration. | Automated deployments and faster recovery from failures. |
Introduction: Understanding Agile and DevOps
Agile is a project management methodology centered on iterative development, collaboration, and customer feedback to enhance software delivery speed and quality. DevOps combines cultural philosophies, practices, and tools to automate and integrate software development and IT operations, aiming to shorten the development lifecycle and deliver high-quality software continuously. Understanding the distinct goals and practices of Agile and DevOps is essential for optimizing software development and deployment processes.
Core Principles of Agile
Agile core principles emphasize iterative development, customer collaboration, and adaptive planning to deliver high-quality software swiftly. Teams embrace continuous feedback, self-organization, and prioritize working software over comprehensive documentation. These principles drive flexibility and responsiveness, setting the foundation for efficient project management and value delivery in dynamic environments.
Key Concepts of DevOps
DevOps emphasizes continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and automated testing to accelerate software development and deployment cycles. It fosters collaboration between development and operations teams through shared responsibilities and real-time monitoring, ensuring faster feedback and reliability. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and cloud-native technologies are foundational to DevOps, enabling scalable and consistent environments.
Agile vs DevOps: Fundamental Differences
Agile focuses on iterative software development and collaboration within cross-functional teams to enhance flexibility and customer feedback integration, while DevOps emphasizes continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and automation to streamline deployment and operations. Agile primarily addresses development processes, promoting adaptive planning, whereas DevOps bridges development and IT operations to improve deployment frequency and system reliability. The fundamental difference lies in Agile's focus on development methodology versus DevOps' goal of fostering collaboration between development and operations for faster, more reliable software delivery.
Collaboration and Team Structure
Agile emphasizes cross-functional teams that collaborate continuously through iterative development cycles, promoting transparency and flexibility within project management. DevOps integrates development and operations teams to enhance collaboration, automate workflows, and shorten release cycles, fostering a culture of shared responsibility for software delivery. Both methodologies prioritize breaking down silos, but Agile focuses on adaptive planning with customer feedback, while DevOps drives seamless end-to-end automation and continuous integration.
Workflow and Process Optimization
Agile emphasizes iterative development and continuous customer feedback, optimizing workflows through sprints and adaptive planning to enhance team collaboration and responsiveness. DevOps focuses on automating deployment pipelines, integrating development and operations teams to streamline continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) processes, reducing cycle times and improving product stability. Combining Agile and DevOps practices accelerates software delivery by refining workflows and optimizing end-to-end processes from code development to production release.
Tools and Technologies Comparison
Agile emphasizes collaboration and iterative development using tools like Jira, Trello, and Confluence for project management and communication, while DevOps integrates continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines with technologies such as Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Git for automation and infrastructure management. Agile tools streamline sprint planning and backlog grooming, whereas DevOps tools focus on automated testing, monitoring, and deployment to ensure rapid and reliable software delivery. Both methodologies rely on version control systems like Git, but DevOps extends toolchains to include configuration management with Ansible, Puppet, or Chef for scalable environment provisioning.
Benefits and Challenges of Agile
Agile enhances project flexibility through iterative development, promoting faster delivery and improved collaboration among cross-functional teams. Key benefits include increased customer satisfaction, adaptability to changing requirements, and higher product quality due to continuous feedback loops. Challenges involve managing scope creep, ensuring consistent team communication, and aligning Agile practices with organizational culture and legacy systems.
Advantages and Limitations of DevOps
DevOps enhances software delivery speed, quality, and collaboration by integrating development and operations teams, leading to continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) efficiencies. Its advantages include faster time-to-market, improved reliability through automated testing, and increased scalability in cloud environments. Limitations involve cultural resistance, complexity in toolchain integration, and challenges in maintaining security during rapid deployment cycles.
Choosing Between Agile and DevOps for Your Project
Choosing between Agile and DevOps depends on your project's focus: Agile optimizes iterative development and customer feedback cycles, ideal for dynamic requirement adjustments, while DevOps emphasizes continuous integration, delivery, and infrastructure automation to accelerate deployment and improve collaboration between development and operations. Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban prioritize flexible planning and team communication, whereas DevOps integrates tools such as Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes to streamline operational workflows. Evaluating your team's experience, project complexity, and desired release frequency will determine the best methodology or the need to combine both for a streamlined software development lifecycle.
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration (CI) in Agile emphasizes frequent code integration for rapid feedback, while DevOps integrates CI with automated testing and deployment to streamline end-to-end software delivery.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
Agile accelerates Continuous Delivery (CD) by promoting iterative development and collaboration, while DevOps enhances CD through automation, infrastructure as code, and seamless integration between development and operations teams.
Scrum
Scrum, a key Agile framework, emphasizes iterative development and team collaboration, while DevOps focuses on automating deployment and continuous integration for faster software delivery.
Kanban
Kanban enhances Agile and DevOps by visualizing workflows, limiting work in progress, and enabling continuous delivery and faster feedback cycles.
Lean Software Development
Lean Software Development integrates Agile principles with DevOps practices to enhance continuous delivery, minimize waste, and accelerate value stream flow in software projects.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping in Agile identifies workflow inefficiencies to enhance iterative delivery, while in DevOps it integrates development and operations processes for continuous value flow and faster deployment.
Automation Pipeline
Agile accelerates development cycles through iterative planning while DevOps integrates Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) automation pipelines to streamline testing, deployment, and monitoring for faster and more reliable software delivery.
Cross-functional Teams
Cross-functional teams in Agile promote iterative development through collaborative roles, while DevOps enhances these teams by integrating continuous delivery and automated operations for faster, more reliable software deployment.
Release Management
Agile accelerates iterative release planning and continuous feedback, while DevOps enhances release management through automated deployments and integrated collaboration between development and operations teams.
Feedback Loops
Agile emphasizes fast, iterative feedback loops within development cycles, while DevOps extends these loops across development and operations to enhance continuous integration and delivery.
Agile vs DevOps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com