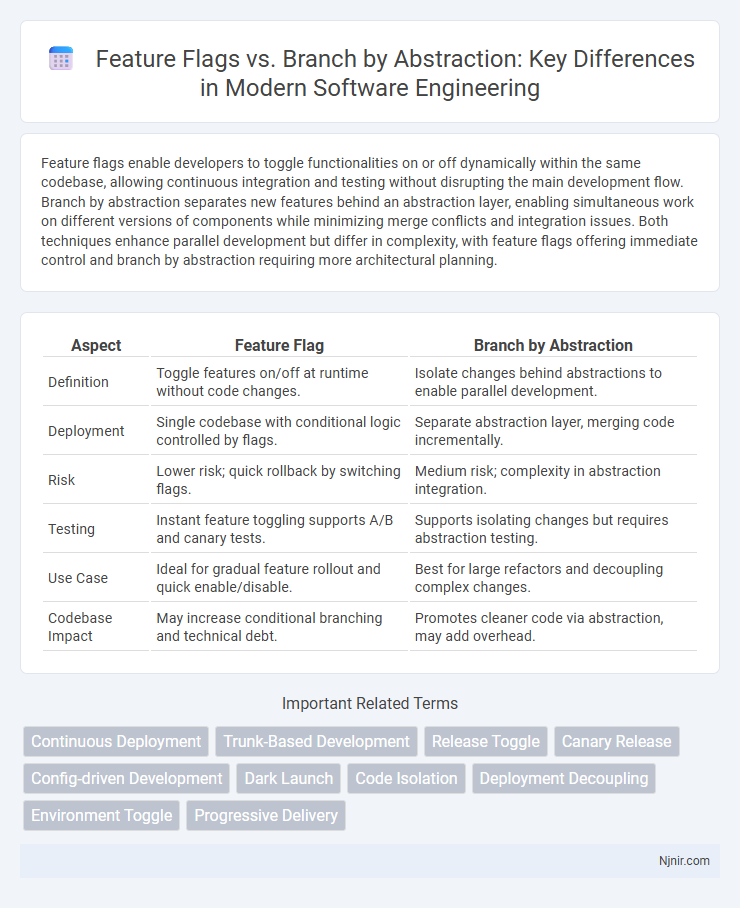
Feature flags enable developers to toggle functionalities on or off dynamically within the same codebase, allowing continuous integration and testing without disrupting the main development flow. Branch by abstraction separates new features behind an abstraction layer, enabling simultaneous work on different versions of components while minimizing merge conflicts and integration issues. Both techniques enhance parallel development but differ in complexity, with feature flags offering immediate control and branch by abstraction requiring more architectural planning.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Feature Flag | Branch by Abstraction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toggle features on/off at runtime without code changes. | Isolate changes behind abstractions to enable parallel development. |
| Deployment | Single codebase with conditional logic controlled by flags. | Separate abstraction layer, merging code incrementally. |
| Risk | Lower risk; quick rollback by switching flags. | Medium risk; complexity in abstraction integration. |
| Testing | Instant feature toggling supports A/B and canary tests. | Supports isolating changes but requires abstraction testing. |
| Use Case | Ideal for gradual feature rollout and quick enable/disable. | Best for large refactors and decoupling complex changes. |
| Codebase Impact | May increase conditional branching and technical debt. | Promotes cleaner code via abstraction, may add overhead. |
Introduction to Feature Flag and Branch by Abstraction
Feature Flags enable developers to toggle features on or off in production without deploying new code, allowing gradual rollouts and quick rollbacks. Branch by Abstraction separates new features behind an abstraction layer, enabling parallel development and integration without branching the codebase extensively. Both techniques facilitate continuous integration and deployment by minimizing risks associated with feature releases.
Understanding Feature Flag: Definition and Use Cases
Feature Flag is a software development technique that enables enabling or disabling features dynamically without deploying new code, facilitating gradual rollouts and controlled testing in production environments. Common use cases include A/B testing, canary releases, and emergency kill switches to mitigate risks and improve feature validation. This approach boosts agility by decoupling feature deployment from code release cycles, enhancing continuous delivery pipelines.
What is Branch by Abstraction? Core Concepts
Branch by Abstraction is a software development technique that enables teams to implement significant changes in the codebase without long-lived feature branches, reducing integration conflicts. It relies on creating an abstraction layer, such as interfaces or feature toggles, allowing new and old implementations to coexist and switch seamlessly during development. This approach promotes continuous integration, safer code refactoring, and incremental feature rollout while maintaining codebase stability.
Key Differences Between Feature Flag and Branch by Abstraction
Feature flags enable toggling features on or off dynamically within the same codebase, allowing incremental rollout and testing without deploying separate versions. Branch by abstraction separates concerns by introducing an abstraction layer that switches implementations, supporting long-term parallel development without frequent merges. While feature flags focus on runtime control for experimentation and fast rollbacks, branch by abstraction emphasizes architectural design to safely evolve complex systems.
Advantages of Using Feature Flags in Software Development
Feature flags enable developers to toggle features on or off in production without deploying new code, allowing for continuous integration and smooth feature rollouts. They reduce risk by isolating incomplete or experimental features, facilitating A/B testing and targeted user exposure. Feature flags also streamline rollback processes, enhance collaboration across teams, and support incremental development without complex branching strategies.
Benefits of Implementing Branch by Abstraction
Branch by Abstraction enables seamless integration of new features without disrupting the main codebase, reducing merge conflicts and facilitating parallel development. This method enhances code maintainability by isolating changes behind abstractions, allowing teams to iterate quickly and safely revert if needed. It supports continuous integration and delivery by minimizing deployment risks and improving collaboration across development teams.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges
Feature Flags can lead to increased technical debt if not managed properly, as accumulating dormant flags complicates code maintenance and testing. Branch by Abstraction may introduce architectural complexity and requires upfront design effort, potentially slowing down development velocity. Both techniques pose challenges in ensuring consistent integration and can increase risk if flags or abstractions are not systematically cleaned up after feature deployment.
Decision Factors: When to Use Feature Flags vs Branch by Abstraction
Feature flags are ideal for controlling feature rollout in production environments, enabling gradual exposure and quick rollback without codebase divergence. Branch by Abstraction suits complex, long-term refactoring projects where maintaining parallel implementations ensures system stability and continuous integration. Decision factors include deployment frequency, risk tolerance, team workflow, and the need for immediate feature toggling versus architectural isolation.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Feature Flag and Branch by Abstraction are popular deployment strategies that enable continuous integration and delivery in software development. For example, Microsoft uses Feature Flags extensively in Azure DevOps to deploy new features safely, allowing rapid rollbacks without code merges, whereas Etsy employs Branch by Abstraction to manage complex refactoring by decoupling new features from the main codebase. Case studies reveal that Feature Flags offer fine-grained control over feature exposure, while Branch by Abstraction excels in progressive codebase evolution, reducing merge conflicts and downtime during large-scale releases.
Best Practices for Modern Software Release Strategies
Feature flags enable gradual rollouts and quick rollback by toggling features at runtime, enhancing continuous delivery and minimizing deployment risk. Branch by abstraction decouples new code paths, allowing development in isolation without impacting the mainline code, thus supporting parallel workstreams and smoother integration. Combining feature flags with branch by abstraction supports agile practices and maximizes deployment flexibility, ensuring stable releases and faster user feedback loops.
Continuous Deployment
Feature Flags enable Continuous Deployment by allowing incremental feature releases within the main codebase, whereas Branch by Abstraction emphasizes architectural layering to deploy changes without branching, reducing integration risks during continuous delivery.
Trunk-Based Development
Feature flags enable continuous integration in trunk-based development by toggling incomplete features on or off within the main codebase, whereas branch by abstraction separates feature development via interface layers without diverging from the trunk.
Release Toggle
Release toggles in feature flags enable dynamic activation of new features without code branching, unlike branch by abstraction which relies on long-lived branches for feature integration.
Canary Release
Canary releases using Feature Flags enable incremental feature deployment by selectively activating features for specific user segments, enhancing control and reducing risks compared to Branch by Abstraction that requires extensive codebase changes.
Config-driven Development
Feature flags enable dynamic, config-driven development by toggling features at runtime without code branching, whereas Branch by Abstraction relies on config-driven abstractions to integrate changes continuously without feature toggles.
Dark Launch
Feature flags enable dark launches by toggling new functionality in production without code branching, whereas branch by abstraction separates development through code layers but requires merges before deployment.
Code Isolation
Feature Flags enable dynamic code toggling within the same branch ensuring minimal disruption, while Branch by Abstraction achieves code isolation through separate abstraction layers that isolate incomplete features without branching.
Deployment Decoupling
Feature flags enable deployment decoupling by toggling features independently within a single codebase, whereas branch by abstraction achieves deployment decoupling through layered abstractions that allow gradual integration without multiple code branches.
Environment Toggle
Environment toggles in feature flags enable dynamic activation of features without code branching, whereas branch by abstraction requires maintained parallel code paths complicating environment-specific control.
Progressive Delivery
Feature Flags enable controlled, incremental rollouts for Progressive Delivery by toggling features dynamically, whereas Branch by Abstraction abstracts code changes to integrate features continuously without long-lived branches, facilitating seamless progressive release and testing.
Feature Flag vs Branch by Abstraction Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com