Selenium offers broad browser compatibility and supports multiple programming languages, making it ideal for complex, cross-platform testing needs. Cypress provides faster test execution and better debugging capabilities through real-time reloads and a developer-friendly interface, but it currently supports only JavaScript and limited browser environments. Choosing between Selenium and Cypress depends on project requirements like language preference, browser support, and test complexity.
Table of Comparison
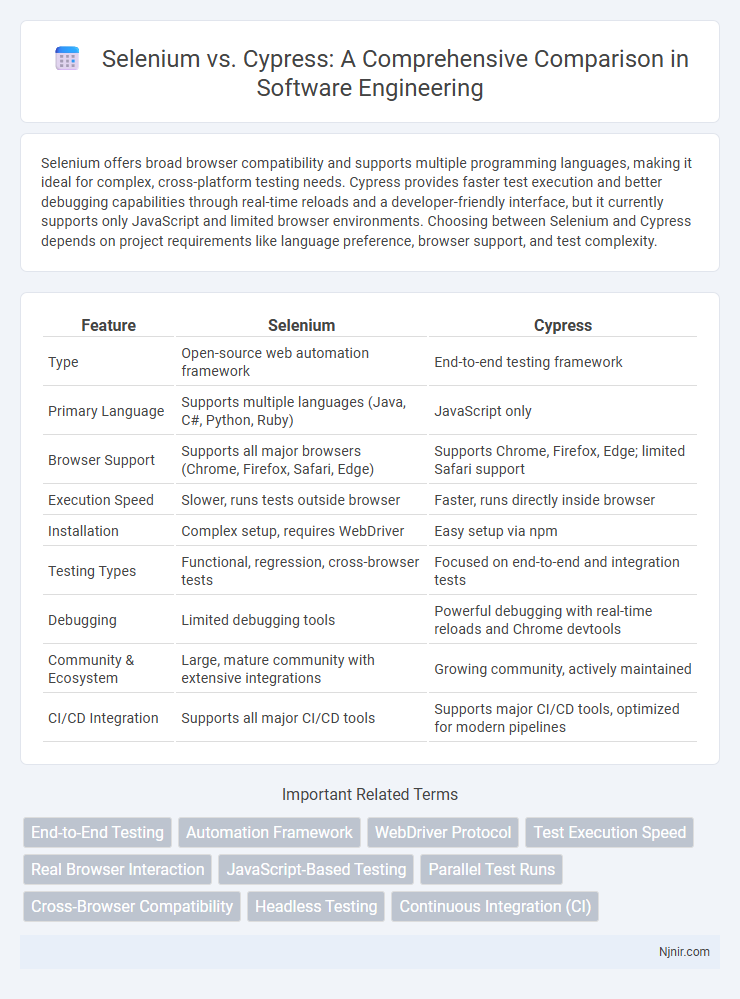
| Feature | Selenium | Cypress |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Open-source web automation framework | End-to-end testing framework |
| Primary Language | Supports multiple languages (Java, C#, Python, Ruby) | JavaScript only |
| Browser Support | Supports all major browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) | Supports Chrome, Firefox, Edge; limited Safari support |
| Execution Speed | Slower, runs tests outside browser | Faster, runs directly inside browser |
| Installation | Complex setup, requires WebDriver | Easy setup via npm |
| Testing Types | Functional, regression, cross-browser tests | Focused on end-to-end and integration tests |
| Debugging | Limited debugging tools | Powerful debugging with real-time reloads and Chrome devtools |
| Community & Ecosystem | Large, mature community with extensive integrations | Growing community, actively maintained |
| CI/CD Integration | Supports all major CI/CD tools | Supports major CI/CD tools, optimized for modern pipelines |
Introduction to Selenium and Cypress
Selenium is a widely adopted open-source framework for automating web browsers, supporting multiple programming languages such as Java, C#, and Python, which makes it highly versatile for cross-browser testing. Cypress is a modern JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework designed specifically for web applications, offering faster execution by running directly in the browser with real-time reloads and debugging capabilities. Both tools provide robust solutions for automated UI testing, but Selenium's extensive ecosystem contrasts with Cypress's developer-friendly experience focused on front-end testing.
Key Differences Between Selenium and Cypress
Selenium supports multiple programming languages such as Java, C#, and Python, while Cypress primarily uses JavaScript, catering to developers focused on modern web applications. Cypress operates directly in the browser, offering faster execution and real-time reloads, whereas Selenium relies on WebDriver, which can introduce latency during test execution. Selenium provides broader cross-browser compatibility, including support for Internet Explorer and Safari, whereas Cypress is mostly limited to Chromium-based browsers and Firefox.
Architecture Comparison
Selenium's architecture relies on a WebDriver protocol that supports multiple browsers by interacting directly with their native drivers, allowing for broad compatibility and language support. Cypress operates within the browser using a JavaScript execution engine, providing faster test execution with real-time reloads but limited cross-browser capabilities predominantly focused on Chrome-based browsers. The architectural difference makes Selenium more versatile for cross-browser testing, while Cypress offers enhanced developer experience and faster debugging through its in-browser execution model.
Supported Languages and Frameworks
Selenium supports multiple programming languages including Java, C#, Python, Ruby, and JavaScript, making it highly versatile for diverse development teams. It integrates seamlessly with various testing frameworks such as JUnit, TestNG, and NUnit, enabling robust test execution and reporting. Cypress primarily supports JavaScript and TypeScript, designed specifically for front-end testing with frameworks like Mocha and Chai, focusing on modern web application testing workflows.
Installation and Setup Process
Selenium requires installing WebDriver for each browser, along with language-specific bindings for Java, Python, or C#, making the setup process more complex and time-consuming. Cypress offers a straightforward installation through npm with a single command and includes an integrated test runner, eliminating the need for separate drivers or additional configurations. The simplicity of Cypress's setup accelerates the initiation of end-to-end testing, while Selenium's flexibility supports a wider range of browsers and languages.
Testing Capabilities and Features
Selenium supports a wide range of browsers and programming languages, enabling cross-platform testing with robust integration into various CI/CD pipelines. Cypress offers fast, real-time reloading with automatic waiting and powerful debugging capabilities, but it primarily supports JavaScript and runs only in Chrome-family browsers. Both tools provide comprehensive end-to-end testing frameworks, yet Cypress excels in developer experience and ease of setup, while Selenium remains the most versatile for large-scale, diverse testing environments.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Selenium and Cypress differ notably in performance and speed; Cypress executes tests directly in the browser, resulting in faster test execution and real-time reloads, whereas Selenium operates through WebDriver, causing slower interactions due to network communication overhead. Cypress's architecture allows for automatic waiting and quicker assertion handling, improving test execution times compared to Selenium's more complex setup. For large-scale, high-speed testing scenarios, Cypress generally outperforms Selenium by reducing test flakiness and providing more reliable speed metrics.
Community Support and Documentation
Selenium benefits from a large and mature global community with extensive documentation, offering numerous tutorials, forums, and plugin integrations that support diverse testing needs across multiple programming languages. Cypress, while newer, features a rapidly growing community and well-organized, developer-friendly documentation focused on modern JavaScript-centric testing frameworks. Both tools maintain active GitHub repositories and dedicated discussion channels, but Selenium's long-standing presence provides broader community resources and more comprehensive third-party support.
Use Cases and Best Fit Scenarios
Selenium excels in cross-browser testing and supports multiple programming languages, making it ideal for complex enterprise applications requiring broad browser compatibility and integration with CI/CD pipelines. Cypress offers faster test execution and real-time reloads, best suited for modern web applications built with JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on end-to-end testing with easier debugging. For projects needing robust multi-browser support and diverse language options, Selenium is preferred, while Cypress is optimal for developers seeking rapid, reliable testing within JavaScript environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool
Selenium offers extensive language support and broad browser compatibility, making it ideal for complex, cross-platform testing scenarios. Cypress provides a faster, more developer-friendly experience with real-time reloading and automatic waiting, optimized for modern JavaScript frameworks and front-end testing. Selecting the right tool depends on project requirements: Selenium excels in multi-language, diverse environment projects, while Cypress suits agile teams focused on rapid, reliable front-end testing.
End-to-End Testing
Selenium supports multiple browsers and languages for scalable end-to-end testing in complex environments, while Cypress offers faster execution and real-time reloads optimized for modern JavaScript applications.
Automation Framework
Selenium supports multiple programming languages and browsers for automation testing, while Cypress offers faster execution with a developer-friendly JavaScript environment focused on end-to-end testing.
WebDriver Protocol
Selenium utilizes the WebDriver Protocol for browser automation, enabling cross-browser testing by communicating directly with browser drivers, whereas Cypress operates without WebDriver, using a unique JavaScript-based architecture that runs inside the browser for faster, more efficient testing.
Test Execution Speed
Cypress executes tests significantly faster than Selenium due to its architecture running directly inside the browser and automatic waiting mechanisms.
Real Browser Interaction
Selenium enables real browser interaction across multiple browsers with native support for diverse environments, while Cypress operates primarily within Chromium-based browsers providing faster execution but limited real-world browser coverage.
JavaScript-Based Testing
Cypress offers a more developer-friendly JavaScript-based testing environment with faster execution and automatic waiting, while Selenium supports multiple languages and browsers but requires more configuration for JavaScript-centric testing.
Parallel Test Runs
Selenium supports parallel test runs through third-party tools like TestNG or Selenium Grid, while Cypress offers built-in parallelization with its Dashboard Service for faster test execution in continuous integration pipelines.
Cross-Browser Compatibility
Selenium supports extensive cross-browser compatibility with major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, whereas Cypress primarily supports Chrome-family browsers with limited cross-browser functionality.
Headless Testing
Selenium supports headless testing across multiple browsers like Chrome and Firefox using WebDriver, while Cypress offers built-in, fast headless testing primarily with Chromium-based browsers, delivering faster execution and easier setup for modern web applications.
Continuous Integration (CI)
Selenium's broad language support and compatibility with various CI tools make it ideal for complex CI pipelines, while Cypress offers faster test execution and seamless integration with modern CI/CD platforms for rapid feedback.
Selenium vs Cypress Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com