OAuth provides a secure authorization framework that enables third-party applications to access user resources without exposing credentials. JWT (JSON Web Token) serves as a compact, self-contained token format commonly used within OAuth flows for securely transmitting claims between parties. OAuth handles authorization processes while JWT focuses on token representation and verification, making them complementary technologies in modern authentication and authorization systems.
Table of Comparison
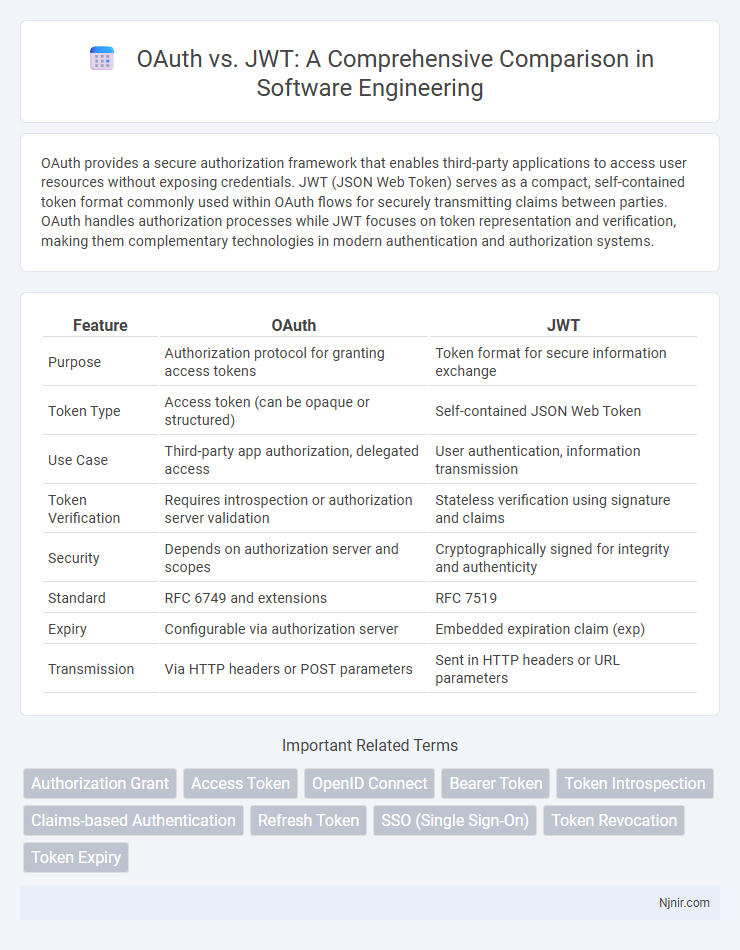
| Feature | OAuth | JWT |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Authorization protocol for granting access tokens | Token format for secure information exchange |
| Token Type | Access token (can be opaque or structured) | Self-contained JSON Web Token |
| Use Case | Third-party app authorization, delegated access | User authentication, information transmission |
| Token Verification | Requires introspection or authorization server validation | Stateless verification using signature and claims |
| Security | Depends on authorization server and scopes | Cryptographically signed for integrity and authenticity |
| Standard | RFC 6749 and extensions | RFC 7519 |
| Expiry | Configurable via authorization server | Embedded expiration claim (exp) |
| Transmission | Via HTTP headers or POST parameters | Sent in HTTP headers or URL parameters |
Introduction to OAuth and JWT
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to grant websites or applications limited access to user information without exposing passwords. JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe token format often employed within OAuth frameworks to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object. While OAuth manages authorization workflows, JWT serves as a token mechanism to convey user identity and permissions efficiently.
Core Concepts: Understanding OAuth
OAuth is an open standard for access delegation commonly used to grant websites or applications limited access to user information without exposing credentials. It functions through tokens issued by an authorization server, allowing third-party apps to interact with a resource server on behalf of the user. This protocol separates authentication from authorization, enabling secure and scalable access control in complex systems.
Core Concepts: Understanding JWT
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object composed of three parts: header, payload, and signature. The header specifies the token type and signing algorithm, the payload contains claims or user data, and the signature ensures data integrity and authenticity by verifying the token was not altered. JWTs enable stateless authentication by allowing servers to validate tokens without accessing a central database, making them essential in OAuth 2.0 for authorization and secure information exchange.
Key Differences Between OAuth and JWT
OAuth is an authorization framework that enables third-party applications to obtain limited access to a user's resources without sharing credentials, while JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used for securely transmitting information between parties. OAuth typically uses tokens, including JWTs, as a means of authorization, but JWT itself is just a token format that can encapsulate claims for authentication and authorization purposes. The key difference lies in OAuth being a protocol for delegation of access, whereas JWT is a method of representing claims to be transmitted securely.
Use Cases: When to Use OAuth vs JWT
OAuth is ideal for delegated access scenarios where users authorize third-party applications to access their resources without sharing credentials, commonly seen in social media login integrations and API authorization. JWT excels in stateless authentication inside distributed systems, securely transmitting claims between parties, often used for single sign-on (SSO) and web token-based user sessions. Use OAuth when managing user consent and access delegation, and choose JWT for compact, URL-safe token exchange and efficient session management.
Security Considerations: OAuth vs JWT
OAuth and JWT serve different roles in security architecture, with OAuth acting as an authorization framework that delegates access without exposing user credentials, while JWT functions as a compact, self-contained token format used to securely transmit information between parties. OAuth enhances security by enabling scoped access, time-limited tokens, and revocation mechanisms, but depends on token formats like JWT for actual data representation. JWTs carry embedded claims that require secure signature validation and encryption to prevent tampering and ensure confidentiality, highlighting the importance of robust key management and token lifespan strategies in security considerations.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing OAuth and JWT often involves challenges such as secure token storage, proper validation, and handling token expiration to prevent unauthorized access. Best practices include using HTTPS to encrypt token transmission, regularly rotating keys to enhance security, and implementing strict scopes and claims to limit token privileges. Developers should also ensure robust error handling and logging to monitor authentication flows and detect potential security breaches.
Performance Comparison: OAuth vs JWT
JWT offers faster performance than OAuth as it is a compact, URL-safe token format that enables stateless authentication without server-side storage. OAuth typically requires validation through authorization servers, adding network latency and processing overhead. Consequently, JWT's self-contained nature optimizes response times and reduces server load, making it preferable for high-performance applications requiring efficient token verification.
Common Pitfalls in OAuth and JWT Integrations
Common pitfalls in OAuth and JWT integrations include improper token validation, such as failing to verify the token signature or expiration, which can lead to security vulnerabilities. Developers often misuse JWT by embedding excessive user information, increasing the risk if tokens are compromised. OAuth implementations frequently struggle with inadequate scope management and token revocation, resulting in excessive access permissions and prolonged unauthorized access.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Choosing the right authentication solution depends on your project's needs: OAuth excels in delegated access scenarios by providing secure authorization, especially for third-party integrations, while JWT (JSON Web Token) offers a compact, self-contained way to transmit user identity and claims, ideal for stateless authentication. Consider OAuth when your application requires robust access delegation and token revocation capabilities, whereas JWT is better suited for scalable, stateless session management in distributed systems. Evaluate factors like security requirements, token lifespan, and server architecture to determine whether OAuth's authorization framework or JWT's token-based authentication aligns best with your project's goals.
Authorization Grant
OAuth uses Authorization Grants to securely delegate access through temporary tokens, while JWT serves as a compact, self-contained token format often used within OAuth protocols for stateless authorization.
Access Token
OAuth uses access tokens to grant limited access to user resources, while JWT access tokens encode user claims and can be verified without server-side storage.
OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect leverages OAuth 2.0 for authentication using JWTs as standardized ID tokens that securely convey user identity information.
Bearer Token
Bearer tokens in OAuth are often implemented as JSON Web Tokens (JWT) to securely transmit user authentication and authorization data.
Token Introspection
OAuth token introspection allows resource servers to validate and retrieve metadata about access tokens issued by an authorization server, while JWT tokens are self-contained and can be validated locally without the need for token introspection endpoints.
Claims-based Authentication
OAuth enables secure authorization by delegating access using tokens, while JWT implements claims-based authentication by encapsulating user claims within a compact, signed token for identity verification.
Refresh Token
OAuth refresh tokens securely extend user sessions by issuing new JWT access tokens without re-authentication, enhancing seamless and scalable authorization workflows.
SSO (Single Sign-On)
OAuth enables secure SSO by delegating authorization, while JWT provides compact, self-contained tokens that streamline identity verification in SSO implementations.
Token Revocation
OAuth supports token revocation through centralized authorization servers enabling immediate invalidation, whereas JWT tokens lack built-in revocation and typically require short expiration times or additional token blacklisting mechanisms for effective management.
Token Expiry
OAuth tokens typically include customizable expiration times defined by the authorization server, while JWTs contain an embedded expiry (`exp`) claim that specifies a fixed token validity period enforced by the token itself.
OAuth vs JWT Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com