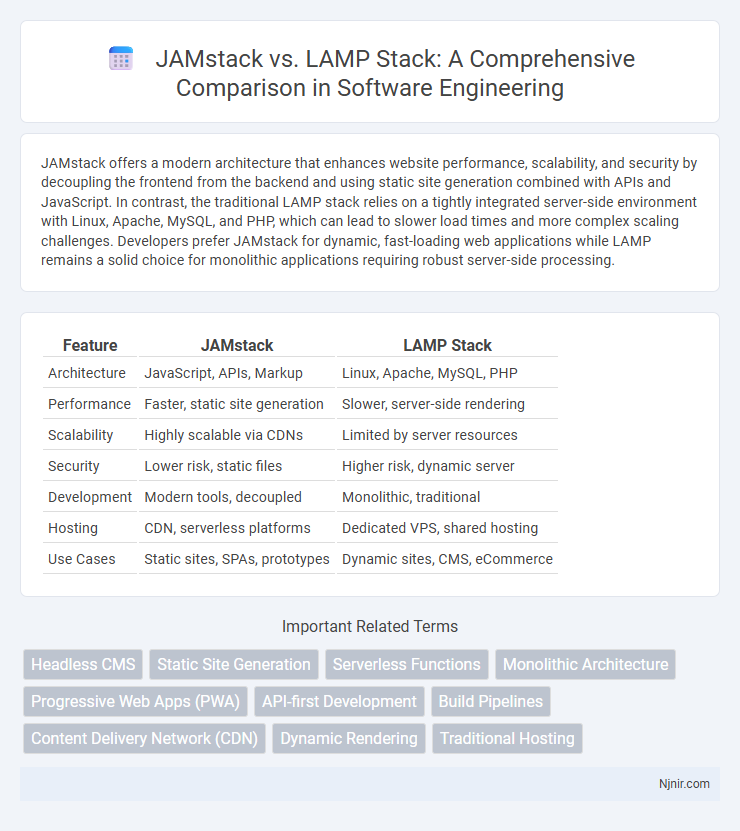
JAMstack offers a modern architecture that enhances website performance, scalability, and security by decoupling the frontend from the backend and using static site generation combined with APIs and JavaScript. In contrast, the traditional LAMP stack relies on a tightly integrated server-side environment with Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP, which can lead to slower load times and more complex scaling challenges. Developers prefer JAMstack for dynamic, fast-loading web applications while LAMP remains a solid choice for monolithic applications requiring robust server-side processing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | JAMstack | LAMP Stack |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | JavaScript, APIs, Markup | Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP |
| Performance | Faster, static site generation | Slower, server-side rendering |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via CDNs | Limited by server resources |
| Security | Lower risk, static files | Higher risk, dynamic server |
| Development | Modern tools, decoupled | Monolithic, traditional |
| Hosting | CDN, serverless platforms | Dedicated VPS, shared hosting |
| Use Cases | Static sites, SPAs, prototypes | Dynamic sites, CMS, eCommerce |
Introduction to JAMstack and LAMP Stack
JAMstack is a modern web development architecture based on client-side JavaScript, reusable APIs, and prebuilt Markup, designed for faster performance, better security, and improved scalability. LAMP stack, a traditional web service solution, consists of Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP, offering a reliable and well-established environment for developing dynamic websites and applications. JAMstack emphasizes decoupled front-end and back-end technologies, while LAMP integrates server-side scripting and database management within a unified stack.
Core Architecture Overview
JAMstack architecture decouples the frontend from backend services, leveraging JavaScript, APIs, and Markup to deliver fast, scalable, and secure web applications. LAMP stack combines Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP to create a monolithic server-side environment where the backend handles rendering and database management. JAMstack relies on pre-built static sites served via CDN, whereas LAMP dynamically generates content on the server, impacting performance and scalability.
Key Technologies and Components
JAMstack architecture leverages JavaScript, APIs, and Markup to deliver fast, scalable, and secure web applications by decoupling the frontend from backend services, relying heavily on static site generators like Gatsby or Next.js and headless CMS platforms. In contrast, the LAMP stack consists of Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP, serving as a traditional full-stack solution where server-side rendering and monolithic application structures dominate. The JAMstack emphasizes CDN distribution and client-side rendering, while LAMP relies on server-side processing and relational database management for dynamic content generation.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
JAMstack architecture delivers superior performance by serving pre-rendered static assets through content delivery networks (CDNs), dramatically reducing server load and latency compared to the traditional LAMP stack's reliance on dynamic server-side processing. Scalability in JAMstack is more efficient due to its decoupled nature, allowing independent scaling of frontend and backend services without overprovisioning servers, unlike LAMP's monolithic structure that often requires scaling entire server resources. This makes JAMstack ideal for high-traffic applications demanding rapid load times and seamless scalability, while LAMP stacks may face bottlenecks under heavy load due to their integrated server and database dependencies.
Security Considerations
JAMstack architecture minimizes attack surfaces by serving pre-built static files via CDNs, reducing server vulnerabilities common in LAMP stacks that rely on dynamic server-side processing with PHP, Apache, MySQL, and Linux. JAMstack eliminates database exposure and code injection risks inherent in LAMP setups, providing enhanced protection against SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other server-side exploits. Security in JAMstack is further strengthened through the use of third-party APIs and authentication services, isolating sensitive operations from the front-end and backend infrastructure.
Developer Experience and Workflow
JAMstack offers a modern developer experience with decoupled architectures and pre-built markup that enables faster deployment and easier scalability compared to the traditional LAMP stack. Developers benefit from improved workflows through static site generators, API-driven content, and seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines, enhancing performance and collaboration. In contrast, the LAMP stack relies on server-side rendering and tightly coupled components, which can slow development and complicate maintenance processes.
Hosting and Deployment Options
JAMstack offers flexible hosting solutions through static site generators, enabling deployment on CDN-backed platforms like Netlify, Vercel, and AWS Amplify for faster load times and enhanced scalability. LAMP stack requires traditional server environments such as Apache on Linux VMs for hosting dynamic web applications, often with more complex deployment processes involving manual configurations or FTP. JAMstack's decoupled architecture supports automated CI/CD pipelines and instant cache invalidation, while LAMP deployments typically depend on server-side scripting and database management, leading to longer deployment cycles.
Cost and Resource Management
JAMstack significantly reduces costs by leveraging static site generation and CDN distribution, minimizing server infrastructure and maintenance expenses compared to the traditional LAMP stack, which requires continuous backend server management and database administration. Resource management is streamlined with JAMstack as it decouples front-end and back-end, enabling independent scaling and faster deployment cycles, whereas LAMP's monolithic architecture demands synchronized updates and higher server resource allocation. The lower operational overhead and efficient scaling of JAMstack make it a cost-effective solution for dynamic, high-traffic websites compared to the resource-intensive LAMP environment.
Use Cases and Real-World Examples
JAMstack excels in building fast, scalable static websites and progressive web apps, with real-world examples including Netlify's deployment of high-traffic marketing sites and Smashing Magazine's shift to static site generation for improved load times. LAMP stack remains a robust choice for dynamic, server-side applications such as content management systems like WordPress and e-commerce platforms like Magento, enabling complex database interactions and high customizability. Enterprises often choose JAMstack for performance-centric projects and LAMP for traditional web applications requiring extensive backend processing and database management.
Future Trends and Stack Evolution
JAMstack architecture leverages modern APIs, static site generators, and CDNs, driving faster load times and enhanced scalability, making it a preferred choice for future-proof web development. LAMP stack, grounded in traditional server-side processing with Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP, faces challenges adapting to microservices and serverless trends. The evolution of web stacks favors JAMstack's decoupled front-end and cloud-based backend services, reflecting industry shifts toward performance, security, and developer experience improvements.
Headless CMS
JAMstack leverages Headless CMS for faster, scalable, and security-enhanced static site generation, while LAMP stack relies on traditional monolithic CMS with dynamic server-side rendering.
Static Site Generation
JAMstack leverages static site generation to deliver faster, more secure websites by pre-rendering content at build time, whereas LAMP stack relies on server-side rendering, dynamically generating pages on each request.
Serverless Functions
JAMstack leverages serverless functions for scalable, low-latency backend processing, while LAMP stack relies on traditional server-based PHP scripts limiting flexibility and scalability.
Monolithic Architecture
JAMstack offers a decoupled architecture enhancing scalability and performance, unlike the traditional monolithic LAMP stack which bundles backend and frontend tightly, often limiting flexibility and deployment speed.
Progressive Web Apps (PWA)
JAMstack enhances Progressive Web Apps with faster load times, better scalability, and improved security compared to the traditional LAMP stack's server-dependent architecture.
API-first Development
JAMstack prioritizes API-first development by decoupling the frontend from backend services for faster, scalable, and more secure web applications, while LAMP stack relies on a tightly integrated server-side architecture limiting API flexibility.
Build Pipelines
JAMstack build pipelines leverage static site generators and CDN distributions for rapid, scalable deployments, whereas LAMP stack build pipelines depend on traditional server-side scripting and manual deployment processes, often resulting in slower build and release cycles.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
JAMstack leverages CDN for faster global content delivery by pre-rendering static assets, while LAMP stack typically relies on server-side rendering, resulting in slower CDN performance.
Dynamic Rendering
JAMstack enhances dynamic rendering by leveraging APIs and client-side JavaScript for faster, scalable content delivery, while the LAMP stack relies on server-side processing with PHP and MySQL, often resulting in slower dynamic page generation.
Traditional Hosting
Traditional hosting for LAMP stack relies on monolithic servers with Apache, MySQL, and PHP tightly integrated, while JAMstack leverages static site generators and CDN distribution for faster, scalable, and more secure performance.
JAMstack vs LAMP stack Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com