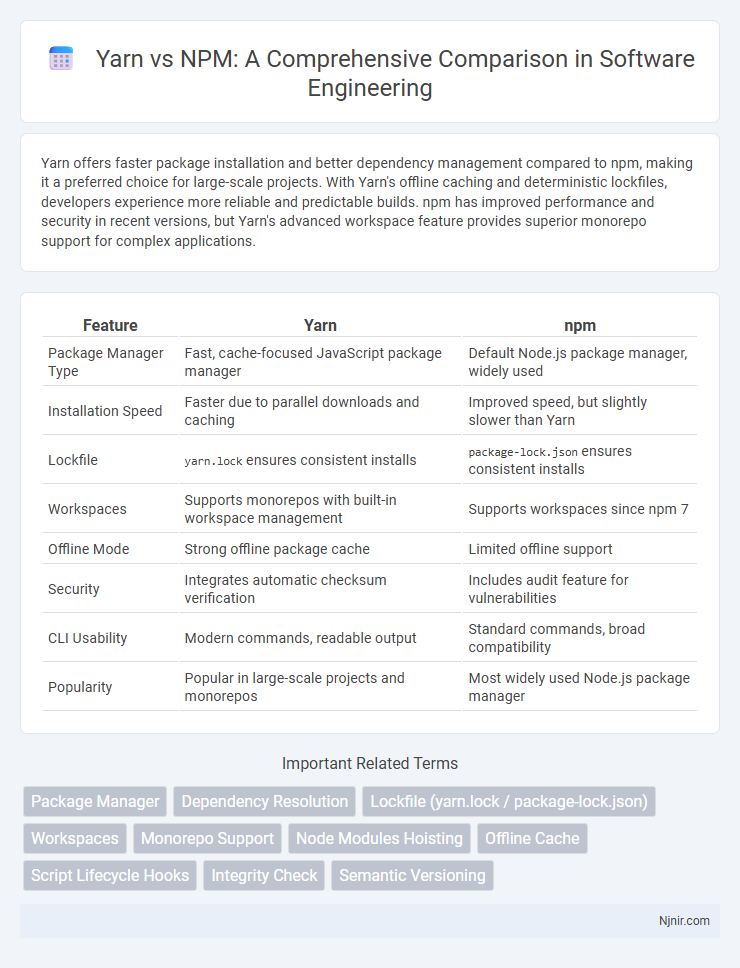
Yarn offers faster package installation and better dependency management compared to npm, making it a preferred choice for large-scale projects. With Yarn's offline caching and deterministic lockfiles, developers experience more reliable and predictable builds. npm has improved performance and security in recent versions, but Yarn's advanced workspace feature provides superior monorepo support for complex applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yarn | npm |
|---|---|---|
| Package Manager Type | Fast, cache-focused JavaScript package manager | Default Node.js package manager, widely used |
| Installation Speed | Faster due to parallel downloads and caching | Improved speed, but slightly slower than Yarn |
| Lockfile | yarn.lock ensures consistent installs |
package-lock.json ensures consistent installs |
| Workspaces | Supports monorepos with built-in workspace management | Supports workspaces since npm 7 |
| Offline Mode | Strong offline package cache | Limited offline support |
| Security | Integrates automatic checksum verification | Includes audit feature for vulnerabilities |
| CLI Usability | Modern commands, readable output | Standard commands, broad compatibility |
| Popularity | Popular in large-scale projects and monorepos | Most widely used Node.js package manager |
Introduction to Package Managers: Yarn and npm
Yarn and npm are popular JavaScript package managers designed to streamline dependency management and project workflows. npm, the default package manager for Node.js, offers a vast registry and seamless integration with the Node ecosystem, while Yarn improves performance with its offline capabilities, deterministic dependency resolution, and enhanced security features. Both tools handle package installation, versioning, and script execution, facilitating efficient code sharing and modular development.
Installation and Setup: Yarn vs npm
Yarn offers a fast, reliable installation process with offline caching and deterministic dependency resolution, ensuring consistent builds across different environments. npm, integrated with Node.js by default, provides ease of setup and widespread community support, with recent improvements like package-lock.json for better dependency management. Both package managers support straightforward installation commands, but Yarn's parallel installation often results in quicker setup times compared to npm.
Dependency Management and Lock Files
Yarn and npm both utilize lock files--Yarn uses yarn.lock, while npm employs package-lock.json--to ensure consistent dependency versions across installations, significantly enhancing reproducibility. Yarn's deterministic dependency resolution algorithm often installs packages faster and handles nested dependencies more efficiently, reducing potential conflicts compared to npm's earlier versions. npm's recent improvements in dependency management and lock file generation have narrowed this gap, offering robust version control and security auditing directly integrated into its package-lock.json system.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Yarn outperforms npm in installation speed due to its aggressive caching and parallel download capabilities, significantly reducing package retrieval times. npm has improved with version 7 and 8 by incorporating workspaces and better concurrency but still lags behind Yarn's deterministic lockfile handling and offline mode, which boost performance in repeated installs. Benchmarks show Yarn can complete installs up to 30% faster, especially in large-scale projects with numerous dependencies.
Security Features: Yarn vs npm
Yarn and npm both offer robust security features, including package integrity checks through checksums and support for two-factor authentication to protect user accounts. Yarn employs Plug'n'Play (PnP) technology to eliminate node_modules, reducing the risk of malicious code injection, while npm has introduced improvements like automatic auditing and vulnerability scanning with npm audit. Both package managers actively monitor registries for compromised packages, but Yarn's offline caching and deterministic installs provide an extra layer of security by ensuring consistent and verified dependencies.
Workspace and Monorepo Support
Yarn Workspaces provide efficient management of multiple packages within a monorepo by enabling easy linking and dependency sharing, significantly speeding up installs and reducing duplication. npm also supports Workspaces, allowing developers to define multiple packages in a single repository with simplified dependency resolution and streamlined scripts execution. Both tools enhance monorepo workflows, but Yarn's caching and parallel installation features often deliver faster performance in large-scale projects.
Community Support and Ecosystem
Yarn and npm both enjoy robust community support, with npm benefiting from the vast backing of the Node.js foundation and millions of package maintainers contributing to its registry of over 1.5 million packages. Yarn, developed by Facebook, has cultivated a passionate community focused on performance and reliability, offering features like Plug'n'Play and deterministic installs that enhance developer workflows. The npm ecosystem's seamless integration with tools like GitHub and the security auditing capabilities complement Yarn's innovative approach, creating diverse but overlapping ecosystems that cater to different project needs.
Compatibility with Existing Projects
Yarn and npm both provide strong compatibility with existing JavaScript projects by supporting the same package.json format and npm registry. Yarn's offline cache feature enhances reliability without altering project dependencies, ensuring seamless integration with legacy codebases. npm's widespread usage and native integration with Node.js guarantee that existing projects maintain stability and compatibility during package management transitions.
CLI Features and Usability
Yarn offers a more intuitive CLI with commands like `yarn add` and `yarn upgrade` designed for simplicity and speed, while npm's CLI has improved significantly with features such as `npm ci` for clean installs and workspaces for monorepo support. Yarn's command output is generally clearer, providing detailed progress and status information, enhancing developer feedback during package management tasks. npm now includes enhanced audit and security features directly accessible from the CLI, bolstering usability in maintaining secure dependencies.
Choosing the Right Package Manager for Your Project
Choosing the right package manager between Yarn and npm depends on factors like project size, speed, and dependency management features. Yarn offers faster installation due to its caching system and deterministic lockfile, ensuring consistent builds across environments. npm has improved significantly with features like npm ci for clean installs and better audit capabilities, making it suitable for projects seeking native integration with the Node.js ecosystem.
Package Manager
Yarn and npm are popular JavaScript package managers, with Yarn offering faster performance and offline caching, while npm provides a larger package registry and improved security features.
Dependency Resolution
Yarn uses a deterministic algorithm for faster and more reliable dependency resolution compared to npm's legacy flat dependency structure, ensuring consistent installations across environments.
Lockfile (yarn.lock / package-lock.json)
Yarn's yarn.lock provides deterministic dependency resolution with better performance and enhanced security compared to npm's package-lock.json, ensuring consistent installs across environments.
Workspaces
Yarn Workspaces optimize monorepo management by enabling efficient dependency sharing and faster installs compared to npm Workspaces, which have improved but still lag in performance and feature maturity.
Monorepo Support
Yarn offers superior monorepo support through features like workspaces and efficient dependency resolution compared to npm's limited native monorepo capabilities.
Node Modules Hoisting
Yarn uses deterministic hoisting to optimize Node Modules structure for faster installs and reduced duplication, while npm employs a more decentralized hoisting approach that can lead to larger node_modules folders.
Offline Cache
Yarn's offline cache feature allows developers to install packages without an internet connection by storing dependencies locally, unlike npm which requires manual caching setup or third-party tools.
Script Lifecycle Hooks
Yarn offers faster execution and more efficient caching of script lifecycle hooks compared to npm, enhancing build automation and development workflow performance.
Integrity Check
Yarn enhances package integrity checks by using checksums to verify the exact content of installed packages, whereas npm performs integrity verification primarily through SHA-512 checksums embedded in package-lock.json files.
Semantic Versioning
Yarn and npm both support Semantic Versioning to ensure package compatibility by strictly handling versioning patterns such as MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH for automatic dependency resolution and updates.
Yarn vs npm Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com