Manual testing offers flexibility for exploratory and ad-hoc scenarios where human judgment is essential, while automated testing excels at repetitive, large-scale test execution that ensures faster feedback and consistent results. Automated tests increase coverage and efficiency by running scripts across multiple environments simultaneously, reducing human error. Combining both approaches creates a robust quality assurance strategy that leverages the strengths of human intuition and machine consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
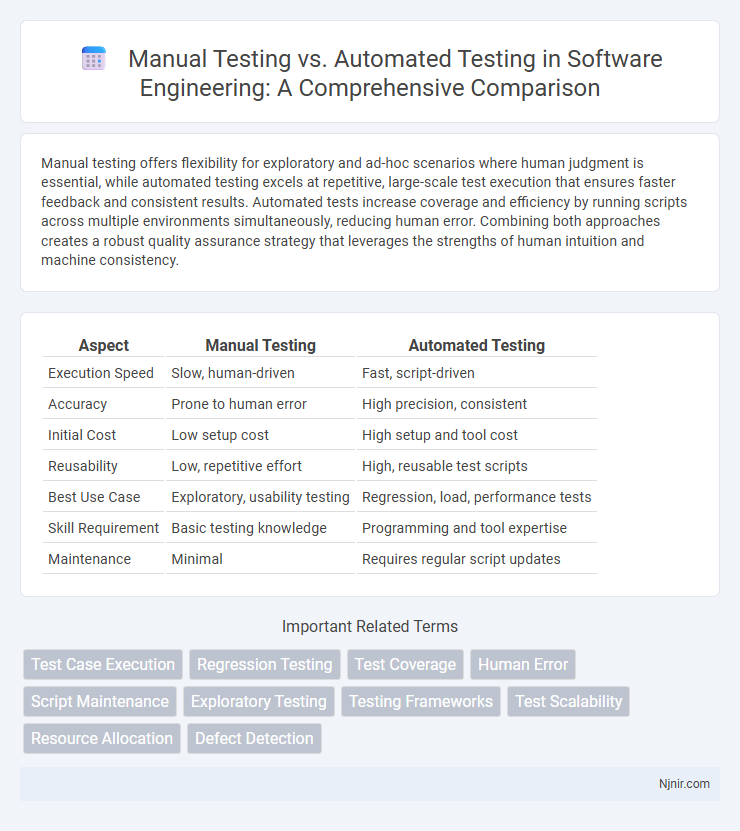
| Execution Speed | Slow, human-driven | Fast, script-driven |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | High precision, consistent |
| Initial Cost | Low setup cost | High setup and tool cost |
| Reusability | Low, repetitive effort | High, reusable test scripts |
| Best Use Case | Exploratory, usability testing | Regression, load, performance tests |
| Skill Requirement | Basic testing knowledge | Programming and tool expertise |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires regular script updates |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Testing
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases without the use of scripts or automation tools, allowing for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing. Automated testing uses specialized software to run predefined test scripts, improving efficiency and repeatability for regression, performance, and load testing. Both approaches are essential in software quality assurance, addressing different testing needs and complementing each other in the development lifecycle.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Testing
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases without the assistance of scripts, allowing for exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing, while automated testing uses specialized tools and scripts to run predefined test cases rapidly and repetitively. Manual testing is time-consuming and prone to human error but offers flexibility in detecting unexpected issues; automated testing provides faster execution, higher accuracy, and better scalability for regression and performance testing. Choosing between manual and automated testing depends on project requirements, test complexity, budget constraints, and the frequency of test case execution.
Advantages of Manual Testing
Manual testing offers flexibility in identifying user interface and user experience issues that automated testing tools might overlook. It allows testers to apply human intuition and empathy, adapting test cases dynamically based on real-time observations. This approach is highly effective in exploratory, usability, and ad hoc testing scenarios where nuanced feedback is critical.
Advantages of Automated Testing
Automated testing offers significant advantages such as increased test execution speed, allowing for rapid regression testing and continuous integration environments. It enhances test accuracy by eliminating human errors and enables extensive test coverage across multiple platforms and configurations. Automated testing also reduces long-term costs through reusable scripts and supports early detection of defects, improving overall software quality and time-to-market.
Limitations of Manual Testing
Manual testing faces limitations such as human error, inconsistency in test execution, and time-consuming repetitive tasks that reduce overall efficiency. It struggles to handle large-scale test cases and regression testing due to slower execution speed compared to automated testing tools like Selenium or QTP. Additionally, manual testing lacks reusability and scalability, making it less effective for continuous integration and delivery in agile development environments.
Limitations of Automated Testing
Automated testing struggles with handling complex user interface changes and cannot easily adapt to unexpected application behavior or visual inconsistencies. It often requires significant upfront investment in script development and maintenance, leading to increased costs when applications frequently change. Automated tests may miss nuanced bugs that a manual tester's intuition and exploratory skills can detect, highlighting the ongoing importance of manual testing in quality assurance.
When to Choose Manual Testing
Manual testing is ideal when exploratory testing, usability feedback, or ad-hoc tests are required, especially in early development stages or when testing new features without pre-defined test scripts. It is preferred for cases where human intuition and subjective evaluation of interface elements, user experience, and visual design are critical. Manual testing is also essential when automation is cost-prohibitive due to rapidly changing requirements or when the testing scope involves one-time or infrequent test execution.
When to Opt for Automated Testing
Automated testing is ideal when executing repetitive test cases, performing regression tests, or validating large datasets that require consistent and fast verification. It excels in environments demanding high accuracy, quick feedback loops, and integration with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Automated testing reduces manual effort, increases test coverage, and accelerates the software development lifecycle, especially during frequent code changes.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Approaches
Combining manual and automated testing enhances software quality by leveraging the precision of automation for repetitive, data-driven tests and the insightful exploratory abilities of manual testing for usability and edge cases. Best practices include designing automated scripts for regression and performance testing while allocating manual efforts to complex scenarios, user experience evaluation, and ad hoc testing. Regularly updating automated tests based on manual findings and maintaining clear documentation ensures continuous integration and alignment between both testing methods.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Balance
Manual testing provides human insight and adaptability crucial for exploratory and usability testing, while automated testing excels in speed, repeatability, and handling large-scale regression tests. The right balance depends on project requirements, complexity, and resource availability, ensuring critical functionalities receive thorough manual evaluation, complemented by automated testing for repetitive and time-consuming tasks. Effective test strategies integrate both methods to enhance software quality, reduce time to market, and optimize testing efficiency.
Test Case Execution
Automated testing executes test cases faster and more consistently than manual testing, significantly reducing human error and enabling repeated execution across multiple environments.
Regression Testing
Automated testing accelerates regression testing by quickly revalidating existing functionalities after code changes, while manual testing offers detailed exploratory insights but is time-consuming and less efficient for repetitive regression tasks.
Test Coverage
Automated testing significantly enhances test coverage by enabling repetitive and extensive execution of test cases, while manual testing often limits coverage due to time and human resource constraints.
Human Error
Manual testing is more prone to human error due to repetitive tasks and subjective judgment, while automated testing significantly reduces these errors by executing predefined test scripts consistently.
Script Maintenance
Script maintenance in manual testing requires frequent human intervention to update test cases, whereas automated testing streamlines maintenance through reusable and easily modifiable scripts, reducing time and effort.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing excels in manual testing by leveraging human intuition and adaptability to uncover hidden defects that automated testing tools often miss.
Testing Frameworks
Automated testing frameworks such as Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG offer greater efficiency and repeatability compared to manual testing by enabling scripted test execution and continuous integration.
Test Scalability
Automated testing significantly enhances test scalability by enabling rapid execution of large test suites across multiple environments, whereas manual testing often struggles to maintain efficiency and consistency as test volume increases.
Resource Allocation
Manual testing requires more human resources and time, while automated testing demands upfront investment in tools and scripting but significantly reduces long-term resource allocation.
Defect Detection
Automated testing detects defects faster and more consistently than manual testing, increasing defect detection efficiency and reducing human error.
manual testing vs automated testing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com