Composer, designed specifically for PHP package management, excels in handling dependencies with precision and version constraints tailored to PHP projects, while npm dominates the JavaScript ecosystem with a vast registry and seamless management of front-end and back-end packages. Composer uses a declarative approach with its composer.json and composer.lock files, ensuring consistent dependency resolution, whereas npm employs a package.json and package-lock.json structure emphasizing rapid installation and extensive community support. Both tools automate dependency management efficiently but cater to distinct programming environments and development workflows.
Table of Comparison
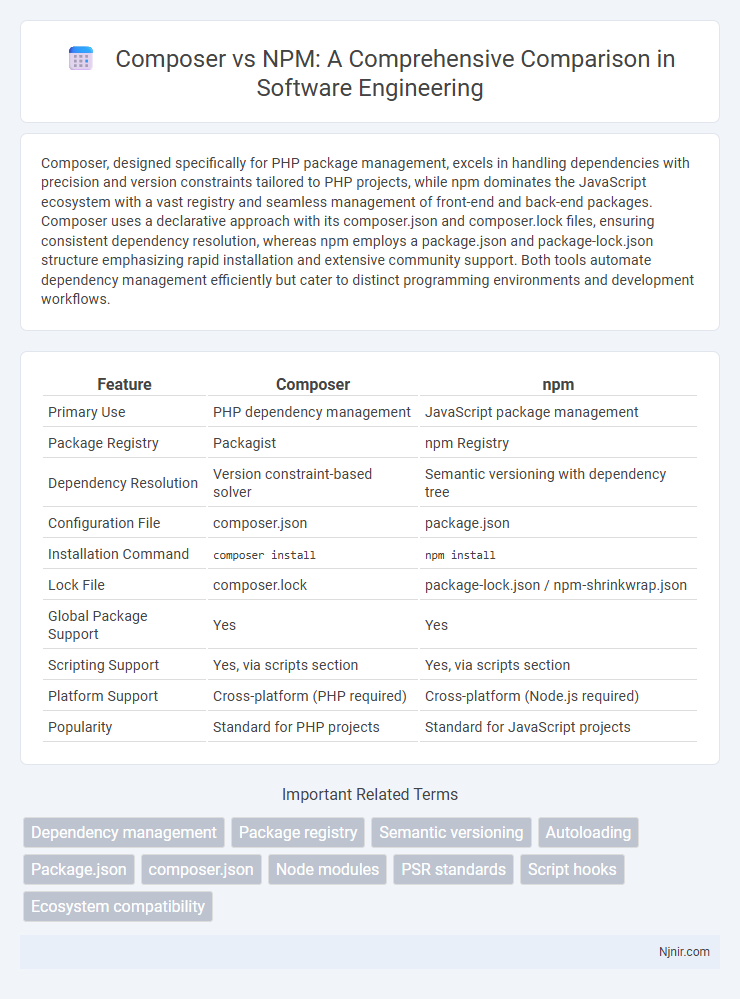
| Feature | Composer | npm |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | PHP dependency management | JavaScript package management |
| Package Registry | Packagist | npm Registry |
| Dependency Resolution | Version constraint-based solver | Semantic versioning with dependency tree |
| Configuration File | composer.json | package.json |
| Installation Command | composer install |
npm install |
| Lock File | composer.lock | package-lock.json / npm-shrinkwrap.json |
| Global Package Support | Yes | Yes |
| Scripting Support | Yes, via scripts section | Yes, via scripts section |
| Platform Support | Cross-platform (PHP required) | Cross-platform (Node.js required) |
| Popularity | Standard for PHP projects | Standard for JavaScript projects |
Introduction to Composer and npm
Composer is a dependency management tool specifically designed for PHP projects, enabling developers to declare and manage libraries required in their applications. npm, short for Node Package Manager, serves as the default package manager for JavaScript runtime environments like Node.js, facilitating the installation and management of packages. Both tools optimize project development by automating the handling of external libraries and their versions, tailored to their respective programming languages.
Key Differences Between Composer and npm
Composer is a dependency manager specifically designed for PHP projects, whereas npm handles JavaScript packages and node modules. Composer relies on a `composer.json` file to manage PHP libraries and version constraints, while npm uses `package.json` to control JavaScript dependencies and scripts. Dependency resolution in Composer emphasizes semantic versioning and autoloading, contrasting with npm's focus on managing both front-end and back-end JavaScript packages with its extensive registry.
Supported Languages and Ecosystems
Composer primarily supports PHP, enabling developers to manage dependencies and libraries within the PHP ecosystem efficiently. In contrast, npm is designed for JavaScript and Node.js environments, facilitating package management for both front-end and back-end JavaScript development. While Composer integrates seamlessly with PHP frameworks like Laravel and Symfony, npm supports a vast array of JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.js, highlighting their ecosystem-specific optimization.
Dependency Management Features
Composer offers advanced dependency management specifically tailored for PHP projects, handling version constraints and automatic package resolution through Packagist with a focus on semantic versioning. npm manages JavaScript dependencies with a robust ecosystem, enabling precise version control via package-lock.json and supports nested dependencies for complex project structures. Both tools provide dependency caching and offline installation options, but Composer excels in managing PHP-specific libraries while npm is optimized for JavaScript frameworks and modules.
Package Repository Comparison
Composer uses Packagist as its primary package repository, specializing in PHP libraries with over 350,000 available packages, while npm hosts the world's largest collection of JavaScript packages, boasting more than 1.9 million modules. npm's repository offers faster package publishing and a more extensive ecosystem for front-end and back-end development, whereas Packagist provides PHP-specific dependency resolution and versioning tailored for PHP projects. Both repositories support semantic versioning and dependency management but cater to different programming language communities and project requirements.
Installation and Usage
Composer, a PHP dependency manager, installs packages with the command `composer require [package-name]`, creating a `composer.json` and `composer.lock` to manage versions precisely. npm, the Node.js package manager, uses `npm install [package-name]` or `npm i [package-name]`, storing dependencies in `package.json` and `package-lock.json` files for consistent builds. Both tools resolve dependencies and update libraries efficiently, but Composer is tailored for PHP environments while npm dominates JavaScript project ecosystems.
Versioning and Update Strategies
Composer manages PHP dependencies with explicit version constraints and semantic versioning, allowing precise control over package updates through composer.lock files. npm uses semantic versioning for JavaScript packages, leveraging package.json and package-lock.json to maintain consistent dependency trees while enabling flexible update ranges via caret (^) and tilde (~) symbols. Both systems support automated update commands--Composer's `composer update` refreshes dependencies within defined constraints, while npm's `npm update` upgrades packages respecting semver rules--ensuring reliable version management and streamlined upgrade workflows.
Community Support and Ecosystem Health
Composer benefits from a highly active PHP developer community with extensive package repositories on Packagist, ensuring consistent updates and robust support for diverse PHP projects. npm boasts the largest and most dynamic ecosystem for JavaScript, featuring millions of packages and continuous contributions from thousands of developers worldwide, which drives rapid innovation and comprehensive tooling. Both platforms maintain strong community engagement and frequent releases, but npm's broader language scope results in a more varied and expansive ecosystem compared to Composer's PHP-centric focus.
Security Considerations
Composer and npm handle security vulnerabilities differently, with Composer primarily relying on static analysis and security advisories from the PHP community, while npm integrates automated vulnerability scanning and provides detailed reports via npm audit. Composer's security depends heavily on the vigilance of package maintainers and community-driven advisories, whereas npm offers real-time detection of insecure packages and suggests fixes during installation. Both tools require developers to actively monitor dependency updates to mitigate risks from outdated or compromised packages.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Project
Composer excels in PHP dependency management, offering seamless integration with PHP frameworks like Laravel and Symfony, making it ideal for PHP-centric projects. npm, the default package manager for Node.js, dominates JavaScript ecosystems and excels at managing front-end and server-side JS libraries, providing extensive modules for React, Angular, and Vue.js. Selecting the right tool depends on the primary programming language and project requirements, with Composer suited for PHP environments and npm for JavaScript-based applications.
Dependency management
Composer excels in PHP dependency management by resolving package versions and handling autoloading efficiently, while npm provides extensive JavaScript dependency management with a robust ecosystem and support for semantic versioning and lockfiles.
Package registry
Composer uses Packagist as its primary package registry specifically for PHP libraries, while npm relies on the npm Registry, which hosts a vast collection of JavaScript packages.
Semantic versioning
Composer and npm both implement Semantic Versioning (SemVer) to manage package dependencies, allowing developers to specify compatible version ranges and ensure consistent software builds.
Autoloading
Composer's autoloading uses PSR-4 standards to automatically load PHP classes via optimized-classmaps, while npm relies on manual module imports with no built-in autoloading mechanism.
Package.json
Composer primarily manages PHP dependencies using composer.json, while npm handles JavaScript packages via package.json, both defining project metadata and dependency versions.
composer.json
Composer.json is a PHP dependency management file that defines project libraries and their versions, whereas npm uses package.json for JavaScript dependencies, highlighting Composer's specialization in PHP ecosystems.
Node modules
npm efficiently manages Node modules by handling package dependencies, versions, and distribution specifically for JavaScript projects, whereas Composer serves a similar role exclusively for PHP packages, making npm the primary tool for Node.js module management.
PSR standards
Composer enforces PHP PSR standards for autoloading and coding style more rigorously than npm, which primarily manages JavaScript package dependencies without strict adherence to language-specific coding standards.
Script hooks
Composer script hooks enable PHP developers to automate tasks during package management, while npm script hooks offer JavaScript developers customizable lifecycle events for running scripts in application workflows.
Ecosystem compatibility
Composer seamlessly integrates with PHP ecosystems for dependency management, while npm excels in JavaScript environments, ensuring optimal compatibility within their respective development communities.
Composer vs npm Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com