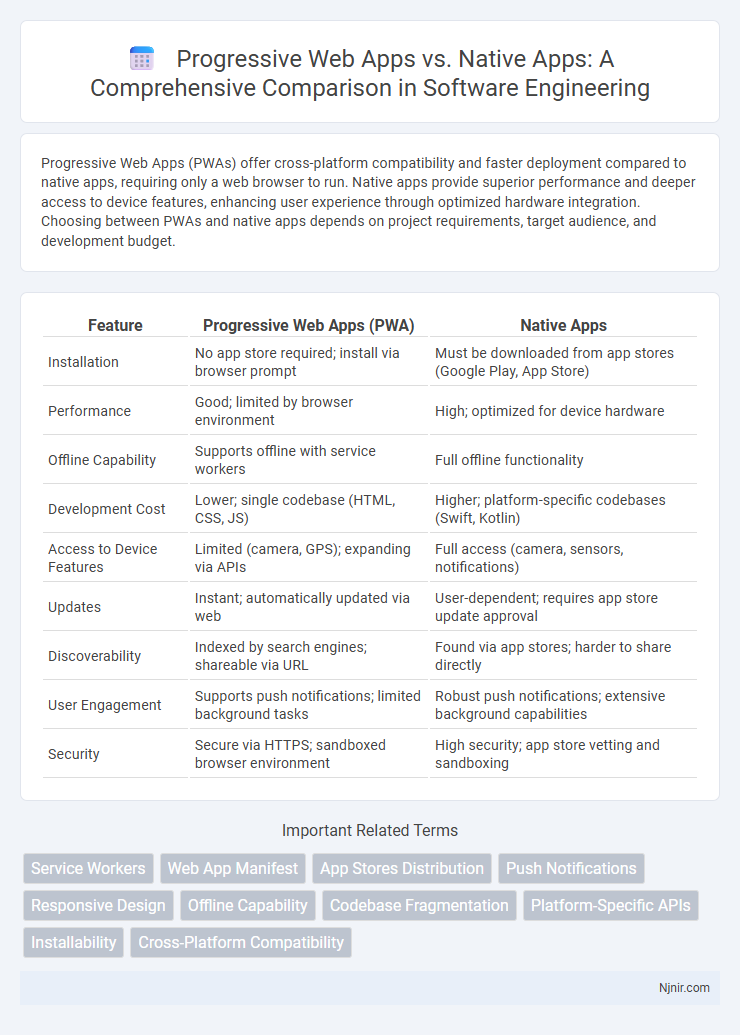
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer cross-platform compatibility and faster deployment compared to native apps, requiring only a web browser to run. Native apps provide superior performance and deeper access to device features, enhancing user experience through optimized hardware integration. Choosing between PWAs and native apps depends on project requirements, target audience, and development budget.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Progressive Web Apps (PWA) | Native Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | No app store required; install via browser prompt | Must be downloaded from app stores (Google Play, App Store) |
| Performance | Good; limited by browser environment | High; optimized for device hardware |
| Offline Capability | Supports offline with service workers | Full offline functionality |
| Development Cost | Lower; single codebase (HTML, CSS, JS) | Higher; platform-specific codebases (Swift, Kotlin) |
| Access to Device Features | Limited (camera, GPS); expanding via APIs | Full access (camera, sensors, notifications) |
| Updates | Instant; automatically updated via web | User-dependent; requires app store update approval |
| Discoverability | Indexed by search engines; shareable via URL | Found via app stores; harder to share directly |
| User Engagement | Supports push notifications; limited background tasks | Robust push notifications; extensive background capabilities |
| Security | Secure via HTTPS; sandboxed browser environment | High security; app store vetting and sandboxing |
Introduction to Progressive Web Apps and Native Apps
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) leverage modern web technologies to deliver app-like experiences through browsers, offering advantages such as offline access, push notifications, and seamless updates without app store installations. Native Apps are built specifically for a particular operating system like iOS or Android, providing deep integration with device hardware and superior performance. Both PWAs and Native Apps serve distinct purposes, with PWAs focusing on cross-platform accessibility and native apps prioritizing optimized functionality on their respective platforms.
Key Features of Progressive Web Apps
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer key features such as offline functionality through service workers, allowing users to access content without an internet connection. PWAs are installable on any device with a web browser without requiring app store downloads, enhancing accessibility and ease of updates. Responsive design and fast load times optimize user experience across multiple devices, combining the best aspects of web and native applications.
Core Advantages of Native Apps
Native apps deliver superior performance by leveraging device-specific hardware and software capabilities, resulting in faster load times and smoother interactions. They provide enhanced access to device features such as cameras, GPS, and sensors, enabling richer functionality and better user experiences. Native apps also offer robust offline capabilities and advanced security measures, making them ideal for demanding applications in gaming, finance, and enterprise environments.
Performance Comparison: PWA vs Native Apps
Native apps generally offer superior performance by directly utilizing device hardware and optimized code tailored for specific operating systems. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) rely on web technologies and run within a browser environment, which may introduce latency and limit access to certain device features, slightly impacting speed and responsiveness. However, advancements in service workers, caching strategies, and hardware acceleration have significantly narrowed the performance gap between PWAs and native apps.
Cross-Platform Development: Efficiency and Cost
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) enable cross-platform development by using a single codebase compatible with multiple devices and operating systems, significantly reducing development time and costs compared to Native Apps that require separate coding for iOS and Android. PWAs offer streamlined updates and maintenance through web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, enhancing efficiency and lowering ongoing expenses. In contrast, Native Apps demand specialized skills and more resources for platform-specific development, impacting overall project budgets and timelines.
User Experience and Accessibility
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer seamless user experiences with fast loading times, offline access, and responsive design that adapts to various devices and screen sizes, enhancing accessibility for users with disabilities through features like screen reader compatibility and adjustable text sizes. Native Apps provide robust performance and deeper integration with device hardware, enabling advanced functionalities such as biometric authentication and push notifications, which contribute to a more personalized and secure user experience. Both PWAs and Native Apps prioritize accessibility, but PWAs excel in cross-platform availability without installation barriers, making digital content more universally reachable.
Offline Functionality and Reliability
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) leverage service workers to enable robust offline functionality by caching resources and delivering content without an active internet connection, ensuring continuous access and reliability. Native apps store data locally and utilize device-specific APIs for seamless offline operation, often providing superior performance and more comprehensive offline capabilities. Both approaches enhance user experience by maintaining app usability during connectivity interruptions, but native apps typically offer deeper integration with the device's hardware and offline features.
Security Considerations for PWAs and Native Apps
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) leverage HTTPS to ensure secure data transmission and implement service workers with strict origin policies, reducing risks of man-in-the-middle attacks, but they rely heavily on browser security frameworks and have limited access to device-specific security features. Native apps benefit from platform-level security controls such as sandboxing, biometric authentication, and hardware-backed key storage, offering enhanced protection for sensitive data and offline capabilities. Both platforms must address vulnerabilities through regular updates and secure coding practices, but native apps inherently provide a more robust security environment due to tighter OS integration.
Distribution and Updates: App Stores vs URLs
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are distributed via URLs, enabling instant access through browsers without app store approval, streamlining updates by delivering changes directly to users without downloads. Native Apps rely on app stores like Google Play and Apple App Store for distribution, requiring adherence to platform guidelines and approval processes that can delay updates. The app store ecosystem offers centralized visibility and monetization options, while PWAs provide flexibility in deployment and faster iteration cycles through direct web delivery.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing between Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and Native Apps depends on your project's goals, target audience, and budget. PWAs offer cross-platform compatibility, faster development, and lower costs, making them ideal for reaching users on multiple devices via web browsers. Native Apps provide superior performance, offline capabilities, and access to device-specific features, making them suitable for resource-intensive applications requiring high user engagement.
Service Workers
Service Workers enable Progressive Web Apps to offer offline functionality, background sync, and push notifications, providing near-native performance and reliability unlike traditional native apps.
Web App Manifest
Web App Manifest enables Progressive Web Apps to deliver a native-like experience by allowing users to install apps directly from the browser with customizable icons, offline support, and home screen access, unlike Native Apps that require platform-specific installation and updates.
App Stores Distribution
Progressive Web Apps bypass traditional app stores by enabling direct web-based distribution, while native apps rely on app stores like Apple App Store and Google Play for installation and updates.
Push Notifications
Push notifications in Progressive Web Apps leverage service workers for real-time user engagement across devices without requiring app installation, while Native Apps provide deeper integration and more customizable notification features through platform-specific APIs.
Responsive Design
Progressive Web Apps deliver seamless responsive design across devices using flexible layouts and media queries, while Native Apps rely on platform-specific UI components optimized for diverse screen sizes.
Offline Capability
Progressive Web Apps provide offline capability through service workers and cached content, while Native Apps inherently support offline functionality with full access to device resources and storage.
Codebase Fragmentation
Progressive Web Apps reduce codebase fragmentation by using a single codebase for multiple platforms, unlike Native Apps that require separate codebases for iOS and Android development.
Platform-Specific APIs
Native apps leverage platform-specific APIs for deeper hardware integration and optimized performance, while Progressive Web Apps access limited APIs through web standards to ensure cross-platform compatibility.
Installability
Progressive Web Apps offer lightweight, cross-platform installability via browsers without app stores, while Native Apps require platform-specific installation through app stores, impacting accessibility and user adoption.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Progressive Web Apps offer superior cross-platform compatibility by running seamlessly on any device with a web browser, while native apps require separate development for each operating system.
Progressive Web Apps vs Native Apps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com