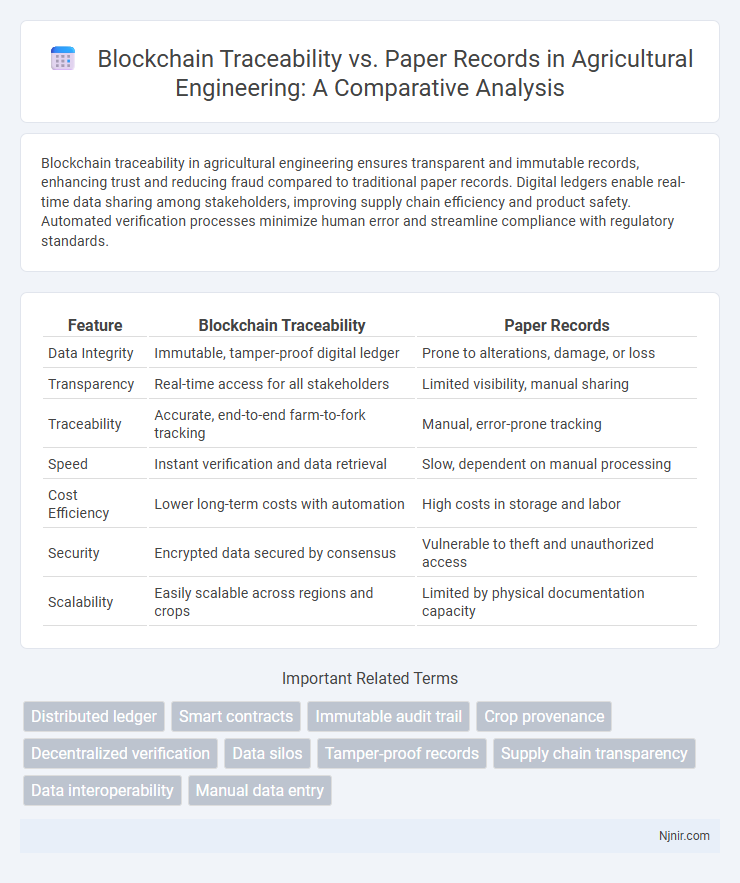
Blockchain traceability in agricultural engineering ensures transparent and immutable records, enhancing trust and reducing fraud compared to traditional paper records. Digital ledgers enable real-time data sharing among stakeholders, improving supply chain efficiency and product safety. Automated verification processes minimize human error and streamline compliance with regulatory standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blockchain Traceability | Paper Records |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable, tamper-proof digital ledger | Prone to alterations, damage, or loss |
| Transparency | Real-time access for all stakeholders | Limited visibility, manual sharing |
| Traceability | Accurate, end-to-end farm-to-fork tracking | Manual, error-prone tracking |
| Speed | Instant verification and data retrieval | Slow, dependent on manual processing |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term costs with automation | High costs in storage and labor |
| Security | Encrypted data secured by consensus | Vulnerable to theft and unauthorized access |
| Scalability | Easily scalable across regions and crops | Limited by physical documentation capacity |
Introduction to Traceability in Agricultural Engineering
Blockchain traceability revolutionizes agricultural engineering by providing immutable, transparent digital records that surpass traditional paper-based systems in accuracy and security. This technology enhances the tracking of crop origins, supply chain processes, and quality assurance, enabling real-time verification and reducing fraud or errors common in manual documentation. Implementing blockchain in agriculture improves data integrity, streamlines audits, and supports sustainable farming practices through reliable traceability.
Overview of Blockchain Technology in Agriculture
Blockchain technology in agriculture offers a decentralized and immutable ledger that significantly enhances traceability compared to traditional paper records. By enabling real-time tracking of crops from farm to table, blockchain ensures transparency, reduces fraud, and increases efficiency in supply chains. This digital approach surpasses paper records by providing secure data sharing among stakeholders while minimizing errors and delays inherent in manual documentation.
Traditional Paper Records: Processes and Limitations
Traditional paper records rely on manual data entry and physical documentation, often resulting in errors, delays, and difficulties in data retrieval. These processes lack real-time visibility and transparency, creating challenges in verifying authenticity and tracking product history. Paper-based systems are vulnerable to loss, damage, and tampering, which compromise traceability and regulatory compliance.
Data Accuracy and Integrity: Blockchain vs Paper
Blockchain traceability ensures superior data accuracy and integrity by recording transactions in an immutable ledger, preventing unauthorized alterations and errors common in paper records. Unlike paper documents prone to damage, loss, or manual entry mistakes, blockchain provides cryptographic verification and real-time updates, guaranteeing transparent and consistent data across all participants. This decentralized approach significantly reduces fraud risk and enhances auditability, outperforming traditional paper-based systems in maintaining reliable and precise records.
Real-Time Access and Transparency in Traceability
Blockchain traceability offers real-time access to data, enabling instant verification and updates across the supply chain, unlike traditional paper records that require manual processing and delay information flow. This transparency ensures all stakeholders have a tamper-proof, immutable audit trail accessible 24/7, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Real-time visibility through blockchain enhances decision-making and boosts trust by providing a single source of truth that paper records cannot match.
Security and Fraud Prevention Mechanisms
Blockchain traceability enhances security through cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus, making data tampering virtually impossible compared to traditional paper records, which are vulnerable to forgery and unauthorized alterations. Smart contracts automate validation processes, reducing human error and enabling real-time fraud detection that manual audits of paper documents cannot match. Immutable ledger properties of blockchain ensure auditable, transparent transaction histories, significantly strengthening fraud prevention mechanisms beyond the limited traceability of physical paperwork.
Cost Implications: Digital vs Manual Recordkeeping
Blockchain traceability significantly reduces operational costs compared to manual paper records by eliminating the need for physical storage, minimizing human errors, and automating data verification processes. Digital recordkeeping enhances transparency and auditability, which lowers compliance expenses and reduces the risk of fraud-related financial losses. While initial setup costs for blockchain technology can be higher, long-term savings from increased efficiency and reduced administrative overhead provide a more cost-effective solution than traditional paper-based systems.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Blockchain traceability enhances compliance with regulatory standards by providing tamper-proof, transparent, and easily accessible digital records that reduce the risk of fraud and errors common in paper-based systems. Regulatory bodies increasingly recognize blockchain's immutable ledger as a reliable audit trail, ensuring real-time verification and adherence to data integrity requirements. Paper records, prone to loss and manipulation, often fail to meet stringent compliance mandates, making blockchain a superior solution for industries like pharmaceuticals, finance, and food safety.
Scalability for Large-Scale Agricultural Operations
Blockchain traceability offers unparalleled scalability for large-scale agricultural operations by enabling real-time tracking of vast quantities of produce across multiple supply chain nodes, unlike traditional paper records which are prone to errors and slow processing times. The decentralized ledger system supports seamless integration with IoT devices and automated data capture, facilitating efficient handling of complex datasets without bottlenecks. Enhanced transparency and faster auditing processes increase operational efficiency, proving blockchain a superior solution for managing extensive agricultural traceability demands.
Future Trends: Digital Transformation in Agricultural Traceability
Blockchain traceability is set to revolutionize agricultural traceability by enabling real-time, immutable records that surpass the limitations of traditional paper records prone to errors and fraud. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors with blockchain creates comprehensive, transparent supply chains, enhancing food safety and quality assurance. Future trends highlight the rise of smart contracts and AI-driven analytics within blockchain systems, driving efficiency and sustainability in global agriculture.
Distributed ledger
Distributed ledger technology enhances blockchain traceability by providing immutable, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping compared to traditional paper records vulnerable to errors and tampering.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts enhance blockchain traceability by automating and securing transaction verification, offering greater accuracy and transparency compared to traditional paper records.
Immutable audit trail
Blockchain traceability ensures an immutable audit trail by recording every transaction transparently and permanently, unlike paper records susceptible to tampering and loss.
Crop provenance
Blockchain traceability significantly enhances crop provenance by providing immutable, real-time records compared to traditional paper records prone to errors and fraud.
Decentralized verification
Blockchain traceability ensures decentralized verification through immutable, distributed ledgers, outperforming centralized paper records vulnerable to tampering and fraud.
Data silos
Blockchain traceability eliminates data silos by providing a decentralized, transparent ledger, unlike paper records which often create isolated, inaccessible data repositories.
Tamper-proof records
Blockchain traceability ensures tamper-proof records through cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus, unlike paper records which are vulnerable to physical alteration and forgery.
Supply chain transparency
Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable, real-time digital records that surpass the accuracy and accessibility of traditional paper records.
Data interoperability
Blockchain traceability enhances data interoperability by enabling secure, transparent, and standardized information exchange across diverse systems unlike fragmented and inconsistent paper records.
Manual data entry
Blockchain traceability eliminates errors and fraud common in manual data entry of paper records by automating secure, real-time tracking of information.
blockchain traceability vs paper records Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com