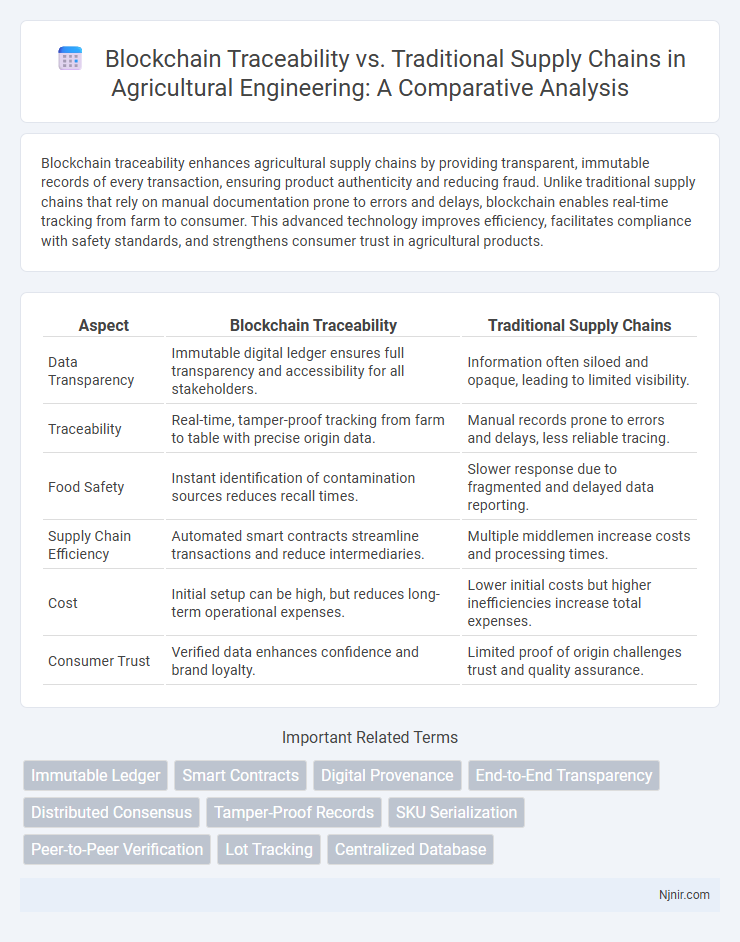
Blockchain traceability enhances agricultural supply chains by providing transparent, immutable records of every transaction, ensuring product authenticity and reducing fraud. Unlike traditional supply chains that rely on manual documentation prone to errors and delays, blockchain enables real-time tracking from farm to consumer. This advanced technology improves efficiency, facilitates compliance with safety standards, and strengthens consumer trust in agricultural products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blockchain Traceability | Traditional Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transparency | Immutable digital ledger ensures full transparency and accessibility for all stakeholders. | Information often siloed and opaque, leading to limited visibility. |
| Traceability | Real-time, tamper-proof tracking from farm to table with precise origin data. | Manual records prone to errors and delays, less reliable tracing. |
| Food Safety | Instant identification of contamination sources reduces recall times. | Slower response due to fragmented and delayed data reporting. |
| Supply Chain Efficiency | Automated smart contracts streamline transactions and reduce intermediaries. | Multiple middlemen increase costs and processing times. |
| Cost | Initial setup can be high, but reduces long-term operational expenses. | Lower initial costs but higher inefficiencies increase total expenses. |
| Consumer Trust | Verified data enhances confidence and brand loyalty. | Limited proof of origin challenges trust and quality assurance. |
Understanding Blockchain Traceability in Agriculture
Blockchain traceability in agriculture enhances transparency by recording every transaction from farm to consumer on an immutable ledger, ensuring data integrity and reducing fraud. Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases prone to errors, delays, and lack of real-time updates, limiting visibility and accountability. Implementing blockchain technology improves food safety compliance, optimizes inventory management, and strengthens consumer trust through verifiable provenance.
Key Components of Traditional Agricultural Supply Chains
Traditional agricultural supply chains rely heavily on physical documentation, manual record-keeping, and centralized databases, which often result in limited transparency and delayed information flow. Key components include farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and regulatory authorities, all connected through complex logistics and quality control processes. These systems face challenges in real-time traceability and fraud prevention due to fragmented data and lack of standardized tracking methods.
Transparency and Data Integrity: Blockchain vs. Traditional Methods
Blockchain traceability enhances transparency by providing an immutable and decentralized ledger that records every transaction in real-time, eliminating the risks of data tampering prevalent in traditional supply chains. Traditional methods rely heavily on centralized databases prone to human error, fraud, and opaque reporting, which can compromise data integrity. Blockchain's cryptographic validation and consensus mechanisms ensure high data accuracy and trustworthiness, fostering greater accountability across supply chain participants.
Enhancing Food Safety through Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability revolutionizes food safety by providing immutable, real-time tracking of products from farm to table, reducing the risk of contamination and fraud. Unlike traditional supply chains, blockchain enables transparent, tamper-proof records, allowing rapid identification and isolation of tainted goods to prevent widespread outbreaks. This enhanced visibility improves accountability among suppliers, ensures compliance with safety standards, and fosters consumer trust through verifiable provenance data.
Cost Efficiency: Comparing Blockchain and Traditional Supply Chains
Blockchain traceability significantly reduces costs by automating record-keeping and minimizing intermediaries, leading to lower administrative and reconciliation expenses compared to traditional supply chains that rely on manual processes and paperwork. Transparent and immutable ledger technology in blockchain enhances fraud detection and reduces losses, which decreases insurance and compliance costs typically higher in conventional supply chain systems. With real-time data access and streamlined operations, blockchain enables better inventory management, reducing holding costs and improving cash flow efficiency relative to traditional supply chain models.
Real-Time Monitoring and Tracking in Agricultural Logistics
Blockchain traceability revolutionizes real-time monitoring and tracking in agricultural logistics by providing immutable, transparent records of product origin, handling, and transit at every stage. Unlike traditional supply chains that rely on periodic updates and paper-based documentation prone to errors and delays, blockchain enables instant access to verified data through IoT sensors and smart contracts. This real-time visibility enhances accountability, reduces fraud, and improves response times to contamination or spoilage, ultimately ensuring fresher produce and safer food consumption.
Reducing Fraud and Counterfeiting with Blockchain Solutions
Blockchain traceability significantly enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable records of every transaction and movement of goods, making it exceedingly difficult for counterfeit products to enter the system. Traditional supply chains often rely on centralized databases prone to tampering and data manipulation, whereas blockchain's decentralized ledger ensures data integrity and real-time verification across all parties. This technology enables brands and consumers to authenticate product origins and certifications, drastically reducing fraud through secure, tamper-proof tracking of assets from source to delivery.
Blockchain Impact on Farmer and Consumer Trust
Blockchain traceability enhances farmer and consumer trust by providing transparent, immutable records of product origin and handling, reducing fraud and errors common in traditional supply chains. This decentralized ledger enables farmers to verify fair compensation and sustainable practices, while consumers gain real-time access to product history, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing. By improving accountability and traceability, blockchain fosters stronger relationships and confidence between producers and end-users.
Scalability: Challenges and Opportunities in Both Approaches
Blockchain traceability offers enhanced transparency and security in supply chains but faces scalability challenges due to high computational costs and slower transaction speeds compared to traditional systems. Traditional supply chains benefit from established infrastructure and faster processing but lack real-time, tamper-proof data verification, limiting traceability accuracy. Innovations in blockchain technology, such as layer-two solutions and sharding, present opportunities to overcome scalability issues, enabling broader adoption without sacrificing data integrity.
Future Prospects: Integrating Blockchain into Agri-Supply Chains
Integrating blockchain into agri-supply chains promises enhanced transparency, enabling real-time tracking of produce from farm to consumer while reducing fraud and inefficiencies common in traditional systems. Future prospects include leveraging smart contracts to automate payments and quality checks, which improves trust and speeds up transactions in global agricultural trade. Advanced blockchain adoption is set to revolutionize supply chain resilience by providing immutable data, empowering stakeholders with verified information critical for sustainable agriculture and regulatory compliance.
Immutable Ledger
Blockchain traceability uses an immutable ledger to provide transparent, tamper-proof records throughout the supply chain, overcoming the vulnerabilities and data manipulation risks inherent in traditional supply chain systems.
Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts enable blockchain traceability to automate and secure supply chain transactions with real-time transparency and immutable audit trails, outperforming traditional supply chain methods reliant on manual documentation and centralized databases.
Digital Provenance
Blockchain traceability enhances digital provenance by providing immutable, transparent, and real-time tracking of assets, surpassing traditional supply chains' limited visibility and susceptibility to fraud.
End-to-End Transparency
Blockchain traceability offers unparalleled end-to-end transparency by securely recording every transaction on an immutable ledger, unlike traditional supply chains that often rely on fragmented, opaque data systems.
Distributed Consensus
Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain transparency through decentralized distributed consensus, eliminating single points of failure common in traditional centralized supply chains.
Tamper-Proof Records
Blockchain traceability ensures tamper-proof records through decentralized, immutable ledgers, surpassing traditional supply chains that rely on vulnerable, centralized data storage systems.
SKU Serialization
Blockchain traceability enhances SKU serialization by providing immutable, real-time tracking data that reduces errors and improves transparency compared to traditional supply chains relying on manual or fragmented record-keeping.
Peer-to-Peer Verification
Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain transparency and security by enabling decentralized peer-to-peer verification, which reduces fraud and errors compared to traditional centralized supply chain systems.
Lot Tracking
Blockchain traceability enhances lot tracking by providing immutable, real-time records across supply chains, unlike traditional methods that rely on fragmented, manual documentation prone to errors and delays.
Centralized Database
Blockchain traceability provides decentralized, immutable records that enhance transparency and reduce fraud compared to traditional centralized database supply chains prone to data manipulation and single points of failure.
Blockchain traceability vs traditional supply chains Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com