Solar-powered pumps offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for irrigation by harnessing renewable energy, significantly reducing fuel expenses and greenhouse gas emissions. Diesel-powered pumps provide reliable operation regardless of sunlight availability but incur higher operational costs and contribute to environmental pollution. Implementing solar pumps enhances long-term agricultural productivity through energy efficiency and environmental conservation.
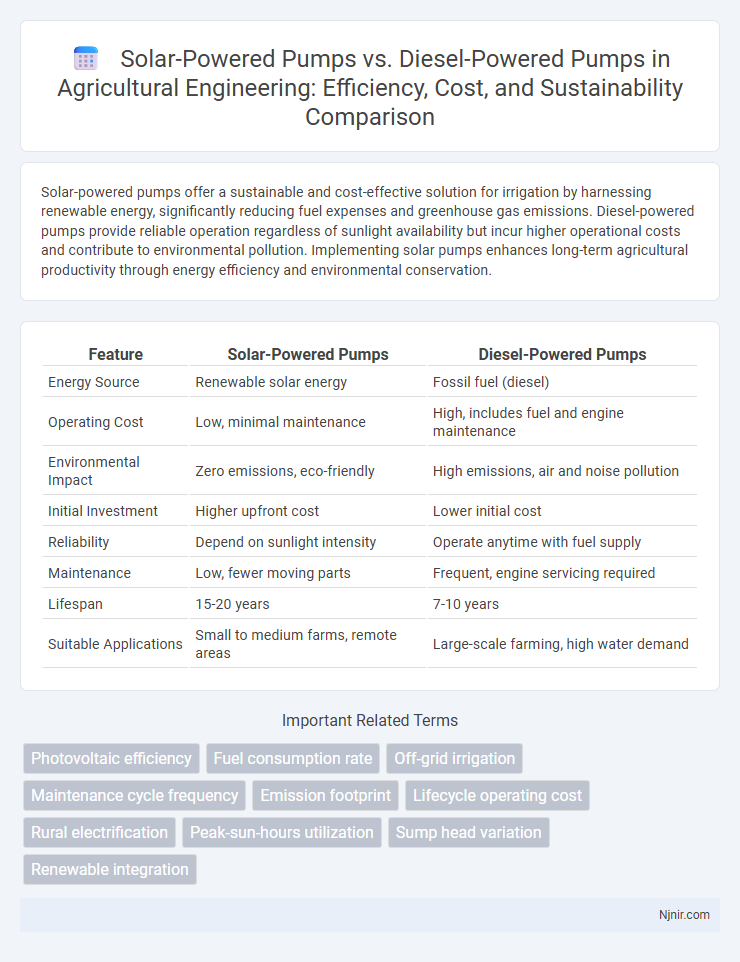
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solar-Powered Pumps | Diesel-Powered Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Renewable solar energy | Fossil fuel (diesel) |
| Operating Cost | Low, minimal maintenance | High, includes fuel and engine maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions, eco-friendly | High emissions, air and noise pollution |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Reliability | Depend on sunlight intensity | Operate anytime with fuel supply |
| Maintenance | Low, fewer moving parts | Frequent, engine servicing required |
| Lifespan | 15-20 years | 7-10 years |
| Suitable Applications | Small to medium farms, remote areas | Large-scale farming, high water demand |
Introduction to Pumping Systems in Agriculture
Solar-powered pumps utilize photovoltaic energy to operate irrigation systems, offering sustainable and cost-effective solutions for agriculture. Diesel-powered pumps rely on internal combustion engines fueled by diesel, providing high power output but incurring fuel costs and emissions. Efficient water management in agriculture increasingly favors solar technology for its environmental benefits and reduced operational expenses.
Overview of Solar-Powered Pumps
Solar-powered pumps utilize photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, enabling efficient water pumping without fuel consumption or emissions. They offer cost-effective operation with minimal maintenance and are ideal for remote agricultural and residential water supply systems. Solar pumps provide sustainable energy solutions by harnessing renewable solar power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels compared to diesel-powered alternatives.
Overview of Diesel-Powered Pumps
Diesel-powered pumps operate using internal combustion engines fueled by diesel, providing high power output and reliability in various agricultural and industrial applications. They are known for their ability to work continuously under heavy loads and in remote areas without electricity, but they tend to have higher operational costs due to fuel consumption and maintenance. Emissions and noise pollution are significant drawbacks compared to solar-powered alternatives, which offer cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Solar-powered pumps require higher initial installation costs due to solar panels and battery systems but offer significantly lower operational expenses by eliminating fuel costs and reducing maintenance frequency. Diesel-powered pumps have lower upfront installation costs but incur ongoing fuel expenses and higher maintenance due to engine wear and emissions control. Over a 5-10 year lifespan, solar pumps demonstrate superior cost-efficiency and return on investment, particularly in remote or off-grid locations.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Solar-powered pumps convert sunlight directly into electrical energy with efficiencies typically ranging from 15% to 22%, offering a renewable and cost-effective alternative to diesel-powered pumps that rely on internal combustion engines with thermal efficiencies around 20% to 30%. These diesel engines consume fossil fuels, emitting greenhouse gases and incurring higher operational costs due to fuel and maintenance, whereas solar pumps operate silently, require minimal upkeep, and harness an inexhaustible energy source. In terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact, solar-powered pumps outperform diesel options by delivering sustainable water pumping solutions with lower lifetime costs and zero emissions.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Solar-powered pumps significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions by utilizing renewable energy and eliminating the need for fossil fuels, which contrasts sharply with diesel-powered pumps known for high carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter emissions. The environmental impact assessment favors solar-powered pumps due to their minimal air and noise pollution, lower water contamination risk, and reduced carbon footprint over the lifecycle. Diesel pumps require fuel extraction, transportation, and storage processes that contribute further to environmental degradation, while solar alternatives promote sustainability and reduce dependence on non-renewable resources.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Solar-powered pumps require minimal maintenance due to fewer moving parts and the absence of fuel-related components, resulting in longer operational life compared to diesel-powered pumps. Diesel pumps demand regular engine servicing, fuel system checks, and oil changes, which increase maintenance costs and downtime. Longevity of solar pumps can exceed 15-20 years with proper care, while diesel pumps typically last 5-7 years under consistent use.
Performance in Varied Field Conditions
Solar-powered pumps deliver consistent performance in sunny and remote field conditions, operating efficiently with minimal maintenance and zero fuel costs. Diesel-powered pumps provide reliable power regardless of sunlight availability, performing well during overcast or night-time conditions but require regular fuel supply and higher maintenance. Solar pumps excel in sustainable irrigation and low operational expense, while diesel pumps are preferred for immediate, high-power demands in diverse environments.
Suitability for Small vs Large Farms
Solar-powered pumps are highly suitable for small farms due to their low operating costs, ease of installation, and minimal maintenance, making them ideal for remote or off-grid locations. Diesel-powered pumps, with higher fuel consumption and maintenance needs, are more appropriate for large farms requiring high water volumes and continuous operation. The scalability and energy efficiency of solar pumps favor small-scale irrigation, while diesel pumps offer the power and reliability needed for extensive agricultural demands.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Solar-powered pumps are experiencing rapid adoption due to decreasing solar panel costs and increasing emphasis on sustainable agriculture, with expected growth driven by government incentives and advances in battery storage technology. Diesel-powered pumps face declining usage because of rising fuel prices and stricter emissions regulations, prompting a shift towards hybrid models that integrate renewable energy sources. Future recommendations include prioritizing investment in solar pump infrastructure, improving efficiency through smart IoT monitoring systems, and enhancing local manufacturing to reduce costs and promote environmental sustainability.
Photovoltaic efficiency
Solar-powered pumps achieve higher photovoltaic efficiency by converting up to 20-22% of sunlight into energy, outperforming diesel-powered pumps that rely on combustion efficiency typically below 40%.
Fuel consumption rate
Solar-powered pumps eliminate fuel consumption entirely, whereas diesel-powered pumps consume an average of 0.4 to 0.7 liters of diesel per hour depending on engine size and load.
Off-grid irrigation
Solar-powered pumps provide cost-effective, sustainable off-grid irrigation by harnessing renewable energy, reducing fuel dependency, and lowering operational expenses compared to diesel-powered pumps.
Maintenance cycle frequency
Solar-powered pumps require maintenance every 6 to 12 months, significantly less frequent than diesel-powered pumps, which need servicing every 250 to 500 operating hours.
Emission footprint
Solar-powered pumps produce zero direct emissions, significantly reducing the carbon footprint compared to diesel-powered pumps, which emit high levels of CO2 and particulate matter during operation.
Lifecycle operating cost
Solar-powered pumps have significantly lower lifecycle operating costs than diesel-powered pumps due to minimal fuel expenses and reduced maintenance requirements.
Rural electrification
Solar-powered pumps provide cost-effective, sustainable water access for rural electrification by reducing fuel dependence and maintenance compared to diesel-powered pumps.
Peak-sun-hours utilization
Solar-powered pumps maximize efficiency by operating optimally during peak sun hours, whereas diesel-powered pumps function independently of sunlight but incur higher fuel and maintenance costs.
Sump head variation
Solar-powered pumps maintain consistent sump head performance with minimal fluctuations, whereas diesel-powered pumps exhibit significant sump head variation due to fuel efficiency and engine load changes.
Renewable integration
Solar-powered pumps integrate seamlessly with renewable energy systems, offering cost-effective, sustainable water pumping solutions that reduce carbon emissions compared to diesel-powered pumps reliant on fossil fuels.
Solar-powered pumps vs Diesel-powered pumps Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com