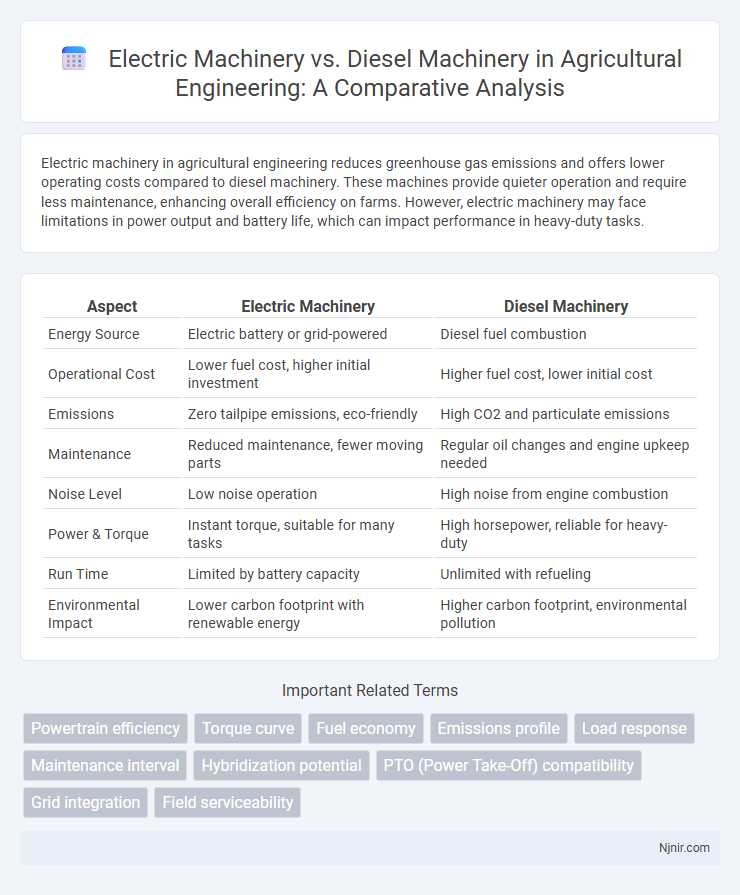
Electric machinery in agricultural engineering reduces greenhouse gas emissions and offers lower operating costs compared to diesel machinery. These machines provide quieter operation and require less maintenance, enhancing overall efficiency on farms. However, electric machinery may face limitations in power output and battery life, which can impact performance in heavy-duty tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Electric Machinery | Diesel Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electric battery or grid-powered | Diesel fuel combustion |
| Operational Cost | Lower fuel cost, higher initial investment | Higher fuel cost, lower initial cost |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions, eco-friendly | High CO2 and particulate emissions |
| Maintenance | Reduced maintenance, fewer moving parts | Regular oil changes and engine upkeep needed |
| Noise Level | Low noise operation | High noise from engine combustion |
| Power & Torque | Instant torque, suitable for many tasks | High horsepower, reliable for heavy-duty |
| Run Time | Limited by battery capacity | Unlimited with refueling |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint with renewable energy | Higher carbon footprint, environmental pollution |
Introduction to Power Sources in Agricultural Machinery
Electric machinery in agriculture offers enhanced energy efficiency and lower emissions compared to diesel machinery, making it a sustainable choice for modern farming. Diesel machinery remains prevalent due to its high power output and established infrastructure, essential for heavy-duty tasks and extended fieldwork. Advances in battery technology and electric motors are gradually bridging the performance gap, promoting a shift towards cleaner and quieter power sources in agricultural machinery.
Overview of Electric Machinery in Agriculture
Electric machinery in agriculture offers increased energy efficiency and lower operational costs compared to diesel-powered equipment. These machines leverage advanced battery technology and electric motors to provide quieter, emission-free operation, enhancing sustainability in farming practices. Rapid advancements in electric drivetrains and precision control systems enable improved performance, reduced maintenance, and integration with smart farming technologies.
Diesel-Powered Equipment: Strengths and Limitations
Diesel-powered machinery offers high torque output and fuel efficiency, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and agriculture. Its durability and availability of fuel infrastructure provide reliable operation in remote areas where electric charging stations are scarce. However, diesel equipment produces significant emissions contributing to environmental pollution and requires regular maintenance to manage engine wear and fuel system issues.
Energy Efficiency: Electric vs Diesel Machinery
Electric machinery exhibits significantly higher energy efficiency compared to diesel machinery, converting over 85% of electrical energy into mechanical power, whereas diesel engines typically operate around 30-40% efficiency due to combustion losses. Reduced energy waste in electric machinery leads to lower operating costs and decreased greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for industrial applications. Advances in battery technology and electric motor design continue to enhance the performance and efficiency gap between electric and diesel-powered equipment.
Environmental Impact and Emissions Comparison
Electric machinery produces zero direct emissions, significantly reducing air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) compared to diesel machinery, which emits high levels of these harmful substances. Lifecycle assessments indicate that electric machinery's overall carbon footprint depends on the energy mix used for electricity generation but generally remains lower than diesel-powered equipment due to greater energy efficiency and potential for renewable energy integration. Diesel machinery contributes substantially to greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and black carbon, exacerbating climate change and deteriorating air quality in industrial and urban environments.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Expenses
Electric machinery typically requires a higher initial investment due to advanced technology and battery systems, whereas diesel machinery often has lower upfront costs but incurs higher long-term fuel and maintenance expenses. Over time, electric machinery benefits from reduced energy costs, fewer mechanical parts, and lower emissions compliance fees, resulting in decreased operational expenses. Total cost of ownership analysis reveals electric machinery offers cost savings through efficiency and sustainability incentives despite the steeper initial capital outlay.
Maintenance Needs and Reliability Factors
Electric machinery requires less frequent maintenance due to fewer moving parts and reduced wear compared to diesel machinery, which demands regular oil changes, fuel system checks, and filter replacements. Reliability factors favor electric machinery in consistent performance and lower breakdown rates, whereas diesel machinery's reliability can be impacted by fuel quality variations and mechanical complexity. Maintenance costs for electric machinery are generally lower over time, contributing to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime in industrial applications.
Performance in Different Agricultural Applications
Electric machinery offers superior torque at low speeds, making it highly efficient for precision tasks such as planting and harvesting in agriculture. Diesel machinery excels in high-power applications and extended operation times, suitable for heavy-duty tasks like plowing and large-scale fieldwork. The performance difference is evident in fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and environmental impact, with electric machines providing cleaner, quieter operation but limited by battery life and charging infrastructure.
Technological Innovations and Future Trends
Electric machinery leverages advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries and fast-charging capabilities, enabling higher energy density and reduced downtime compared to diesel machinery. Innovations in electric motors and power electronics improve efficiency, torque control, and integration with IoT for predictive maintenance, surpassing traditional diesel engine performance. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid systems with enhanced regenerative braking, AI-driven energy management, and widespread adoption of renewable energy-powered charging infrastructure, positioning electric machinery as the sustainable alternative in industrial and transportation sectors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Machinery for Modern Farms
Electric machinery offers enhanced energy efficiency, lower operational costs, and reduced environmental impact compared to diesel machinery. Diesel machinery still provides higher power output and longer run times for heavy-duty applications, making it suitable for larger-scale farming operations. Choosing the right machinery depends on farm size, crop type, sustainability goals, and available infrastructure for charging or fueling.
Powertrain efficiency
Electric machinery achieves up to 90% powertrain efficiency, significantly outperforming diesel machinery, which typically operates at 30-40% efficiency.
Torque curve
Electric machinery delivers a consistent high torque curve from zero RPM, outperforming diesel machinery which exhibits peak torque at higher RPMs with variable output.
Fuel economy
Electric machinery achieves significantly higher fuel economy by converting over 90% of electrical energy into mechanical power, compared to diesel machinery's 30-40% efficiency due to combustion losses.
Emissions profile
Electric machinery produces zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing greenhouse gases and air pollutants compared to diesel machinery, which emits high levels of carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
Load response
Electric machinery offers faster and more precise load response compared to diesel machinery, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing energy waste.
Maintenance interval
Electric machinery offers significantly longer maintenance intervals compared to diesel machinery due to fewer moving parts and reduced wear components.
Hybridization potential
Hybrid electric-diesel machinery leverages electric power systems to enhance fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and optimize performance by combining the high torque of electric motors with the extended operational range of diesel engines.
PTO (Power Take-Off) compatibility
Electric machinery often requires specialized Power Take-Off (PTO) adapters for compatibility, whereas diesel machinery typically features standardized PTO interfaces allowing broader equipment integration.
Grid integration
Electric machinery offers superior grid integration by enabling real-time energy management and seamless incorporation of renewable energy sources, unlike diesel machinery which relies on independent, fuel-based operation.
Field serviceability
Electric machinery offers superior field serviceability with fewer mechanical components and simpler diagnostics compared to diesel machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
electric machinery vs diesel machinery Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com