IoT-based irrigation systems leverage real-time data from soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts to optimize water use, ensuring precise and efficient irrigation tailored to crop needs. Timer-based irrigation relies on preset schedules that may lead to overwatering or underwatering due to lack of environmental responsiveness. Integrating IoT technology reduces water waste, enhances crop yield, and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
Table of Comparison
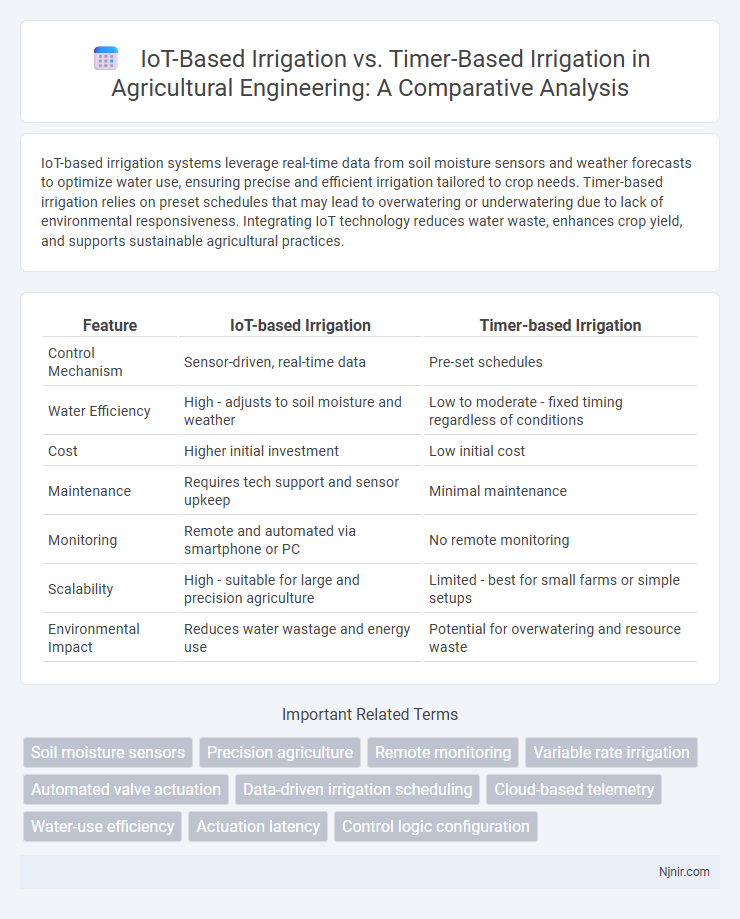
| Feature | IoT-based Irrigation | Timer-based Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Control Mechanism | Sensor-driven, real-time data | Pre-set schedules |
| Water Efficiency | High - adjusts to soil moisture and weather | Low to moderate - fixed timing regardless of conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Low initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires tech support and sensor upkeep | Minimal maintenance |
| Monitoring | Remote and automated via smartphone or PC | No remote monitoring |
| Scalability | High - suitable for large and precision agriculture | Limited - best for small farms or simple setups |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces water wastage and energy use | Potential for overwatering and resource waste |
Introduction to Modern Irrigation Techniques
IoT-based irrigation leverages sensor data and real-time weather information to optimize water usage, enhancing crop yield and resource efficiency compared to traditional timer-based systems that operate on fixed schedules without environmental input. Modern irrigation techniques prioritize data-driven decision-making, enabling precise water application tailored to soil moisture and plant needs. This shift from static timers to dynamic IoT solutions reflects advancements in agricultural technology aimed at sustainable water management.
Overview of Timer-Based Irrigation Systems
Timer-based irrigation systems operate by scheduling water delivery at predetermined intervals, relying on fixed timing settings without real-time environmental feedback. These systems are straightforward to install and manage, making them a cost-effective solution for consistent watering needs in gardens and agricultural fields. However, they may lead to water wastage due to lack of soil moisture sensing and inability to adjust watering based on weather conditions.
Fundamentals of IoT-Based Irrigation Systems
IoT-based irrigation systems leverage real-time data from soil moisture sensors, weather forecasts, and crop requirements to optimize water usage, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. These systems use wireless communication protocols such as Zigbee, LoRaWAN, or Wi-Fi to connect sensors and actuators, enabling precise control over irrigation schedules based on dynamic environmental conditions. Unlike timer-based irrigation, which operates on fixed intervals regardless of actual need, IoT-based technologies reduce water waste and improve crop health through intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making.
Water Efficiency: IoT vs Timer-Based Irrigation
IoT-based irrigation systems utilize real-time soil moisture data and weather forecasts to precisely control water application, significantly reducing water wastage compared to traditional timer-based irrigation. Timer-based systems operate on fixed schedules without considering actual soil or environmental conditions, often leading to overwatering or underwatering. Studies show IoT irrigation can improve water efficiency by up to 30% by optimizing irrigation timing and volume based on dynamic field data.
Cost Analysis: Initial Setup and Maintenance
IoT-based irrigation systems generally incur higher initial setup costs due to advanced sensors, connectivity modules, and smart controllers, whereas timer-based irrigation requires minimal upfront investment with simple mechanical or digital timers. Maintenance expenses for IoT systems include periodic sensor calibration, software updates, and potential network troubleshooting, contrasting with the relatively low maintenance costs of timer-based systems, typically limited to occasional battery replacement or timer adjustments. Over time, IoT irrigation can offer cost savings through optimized water usage and reduced labor, potentially offsetting initial and ongoing expenses compared to the straightforward but less adaptive timer-based solution.
Automation and Remote Monitoring Capabilities
IoT-based irrigation systems enable precise automation by using real-time data from soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts to optimize watering schedules, significantly reducing water waste compared to timer-based systems. Remote monitoring capabilities of IoT irrigation allow farmers to adjust and control watering processes through smartphone apps or web platforms from any location, enhancing responsiveness to changing environmental conditions. Timer-based irrigation lacks dynamic feedback, operating on fixed schedules without adapting to soil or weather variations, which often leads to inefficient water use and limited remote control.
Data-Driven Decision Making in Irrigation
IoT-based irrigation leverages real-time data from soil moisture sensors, weather forecasts, and crop health metrics to optimize water usage, ensuring precise and efficient irrigation. Timer-based irrigation operates on fixed schedules without adapting to environmental conditions, often leading to overwatering or water stress. Data-driven decision making in IoT-enabled systems enhances water conservation, improves crop yield, and reduces operational costs compared to traditional timer-based methods.
Compatibility with Sustainable Agriculture
IoT-based irrigation systems optimize water usage by integrating real-time sensor data and weather forecasts, promoting sustainable agriculture through precise water management and reduced resource waste. Timer-based irrigation operates on fixed schedules without adaptive responses to environmental conditions, potentially leading to overwatering or underwatering, which undermines sustainability goals. Sustainable agriculture benefits more from IoT-based irrigation due to its compatibility with dynamic ecosystem needs and efficient resource allocation.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Systems
IoT-based irrigation systems face challenges such as high initial costs, reliance on stable internet connectivity, and security vulnerabilities in data transmission. Timer-based irrigation struggles with the inability to adapt to real-time environmental changes, leading to potential water wastage and inefficient irrigation schedules. Both systems may suffer from maintenance demands, but IoT solutions require more technical expertise for setup and troubleshooting compared to the simpler mechanical operation of timer-based models.
Future Prospects in Smart Irrigation Technologies
IoT-based irrigation systems leverage real-time sensor data and AI algorithms to optimize water usage with precision, offering significant improvements over traditional timer-based irrigation methods that operate on fixed schedules regardless of environmental conditions. Future prospects for smart irrigation technologies include enhanced integration with weather forecasts, soil moisture analytics, and predictive maintenance, enabling adaptive watering that reduces water waste and boosts crop yields. Advancements in low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) and edge computing will further expand IoT irrigation scalability and reliability in diverse agricultural settings.
Soil moisture sensors
IoT-based irrigation systems use soil moisture sensors to precisely optimize water usage by monitoring real-time soil conditions, unlike timer-based irrigation which operates on fixed schedules without sensing soil moisture levels.
Precision agriculture
IoT-based irrigation enhances precision agriculture by using real-time soil moisture data and weather forecasts to optimize water usage, unlike timer-based irrigation which relies on fixed schedules and often leads to water waste.
Remote monitoring
IoT-based irrigation enables precise remote monitoring and real-time soil moisture data analysis, vastly improving water efficiency compared to traditional timer-based irrigation systems.
Variable rate irrigation
IoT-based irrigation leverages real-time soil moisture and weather data for precise variable rate irrigation, optimizing water use far more efficiently than fixed-schedule timer-based systems.
Automated valve actuation
IoT-based irrigation enables precise automated valve actuation based on real-time soil moisture data, significantly improving water efficiency compared to the fixed schedules of timer-based irrigation systems.
Data-driven irrigation scheduling
IoT-based irrigation leverages real-time soil moisture and weather data to optimize watering schedules, significantly reducing water waste compared to fixed timer-based irrigation systems.
Cloud-based telemetry
IoT-based irrigation leverages cloud-based telemetry for real-time soil moisture monitoring and adaptive watering schedules, outperforming timer-based irrigation's fixed, non-responsive timing systems in water efficiency and crop yield optimization.
Water-use efficiency
IoT-based irrigation improves water-use efficiency by leveraging real-time soil moisture data and weather forecasts, reducing water waste compared to fixed-schedule timer-based irrigation systems.
Actuation latency
IoT-based irrigation systems reduce actuation latency by enabling real-time soil moisture monitoring and dynamic water delivery, while timer-based irrigation relies on pre-set schedules causing delayed response to changing environmental conditions.
Control logic configuration
IoT-based irrigation enables dynamic control logic configuration through real-time sensor data and remote access, whereas timer-based irrigation relies on static, pre-set schedules without environmental feedback.
IoT-based irrigation vs Timer-based irrigation Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com