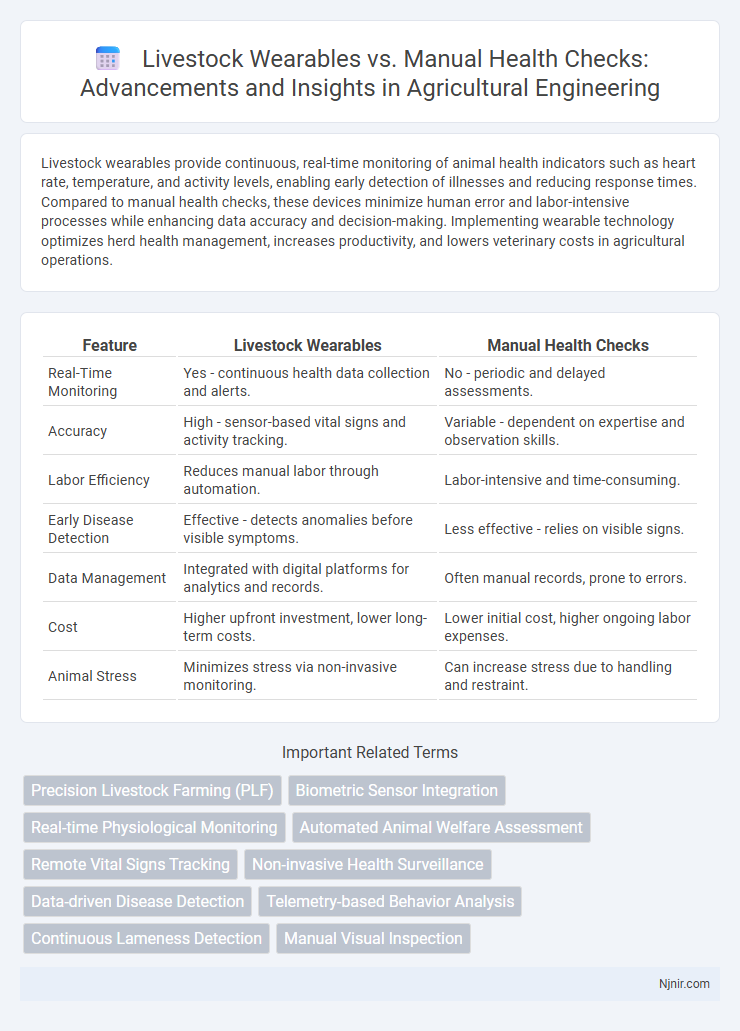
Livestock wearables provide continuous, real-time monitoring of animal health indicators such as heart rate, temperature, and activity levels, enabling early detection of illnesses and reducing response times. Compared to manual health checks, these devices minimize human error and labor-intensive processes while enhancing data accuracy and decision-making. Implementing wearable technology optimizes herd health management, increases productivity, and lowers veterinary costs in agricultural operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Livestock Wearables | Manual Health Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Yes - continuous health data collection and alerts. | No - periodic and delayed assessments. |
| Accuracy | High - sensor-based vital signs and activity tracking. | Variable - dependent on expertise and observation skills. |
| Labor Efficiency | Reduces manual labor through automation. | Labor-intensive and time-consuming. |
| Early Disease Detection | Effective - detects anomalies before visible symptoms. | Less effective - relies on visible signs. |
| Data Management | Integrated with digital platforms for analytics and records. | Often manual records, prone to errors. |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment, lower long-term costs. | Lower initial cost, higher ongoing labor expenses. |
| Animal Stress | Minimizes stress via non-invasive monitoring. | Can increase stress due to handling and restraint. |
Introduction to Livestock Monitoring Technologies
Livestock wearables utilize advanced sensors to continuously monitor animal health metrics such as heart rate, temperature, and activity levels, providing real-time data for early disease detection and improved welfare. Manual health checks rely on periodic physical inspections, which can be labor-intensive and less precise due to human error and infrequent monitoring. The integration of wearable technology in livestock management enhances accuracy and efficiency, enabling proactive health interventions and optimizing overall farm productivity.
Evolution from Manual Health Checks to Wearables
Livestock wearables have revolutionized animal health monitoring by providing real-time data on vital signs, activity levels, and behavior patterns, which manual health checks often miss due to their intermittent nature. These devices enhance early disease detection, reduce human error, and enable continuous remote monitoring, drastically improving animal welfare and farm productivity. The evolution from traditional hands-on inspections to advanced wearable technology marks a significant shift towards precision livestock farming and data-driven decision-making.
Key Features of Livestock Wearable Devices
Livestock wearable devices offer real-time health monitoring through sensors that track vital signs such as heart rate, temperature, and activity levels, enabling early disease detection and prevention. These devices feature GPS tracking for location monitoring, automated data collection, and wireless transmission to cloud-based platforms for advanced analytics. Compared to manual health checks, wearables provide continuous, objective, and precise data, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error in livestock health management.
Manual Health Checks: Methods and Limitations
Manual health checks in livestock primarily involve visual inspections, physical palpation, and basic physiological measurements such as temperature and respiratory rate. These methods rely heavily on the skill and availability of the farmer or veterinarian, leading to inconsistencies and delayed detection of health issues. Limitations include time-intensive procedures, stress on animals, and the inability to continuously monitor subtle changes, which may result in missed early signs of disease.
Data Accuracy: Wearables versus Manual Assessments
Livestock wearables provide continuous, real-time health data with higher precision and objectivity compared to manual health checks, which can be prone to human error and inconsistencies. Wearable sensors track vital signs such as heart rate, temperature, and activity levels, enabling early detection of health issues and reducing the risk of missed symptoms. Manual assessments rely on periodic observations that may delay diagnosis and lack the granular data necessary for proactive livestock management.
Real-Time Monitoring and Early Disease Detection
Livestock wearables enable continuous real-time monitoring of vital signs such as temperature, heart rate, and activity levels, providing early warnings of disease before visible symptoms appear. This technology surpasses manual health checks, which rely on periodic observations and may miss subtle health changes, resulting in delayed diagnosis. Early disease detection through wearable sensors improves herd health management, reduces treatment costs, and minimizes the risk of widespread infections.
Labor Efficiency and Operational Costs
Livestock wearables significantly enhance labor efficiency by enabling continuous, real-time monitoring without the need for frequent manual health checks, reducing time spent by farm workers on routine inspections. These devices collect precise data on vital signs, activity levels, and behavior patterns, allowing for early detection of health issues and minimizing costly interventions. Operational costs decrease as wearables reduce labor demands and prevent productivity losses associated with undetected illnesses, optimizing overall farm management expenses.
Animal Welfare: Impact of Wearables vs Manual Checks
Livestock wearables provide continuous, real-time monitoring of animal health indicators such as heart rate, temperature, and activity levels, enabling early detection of illness and stress that manual health checks may miss. This technology enhances animal welfare by reducing the need for frequent physical handling, minimizing stress and potential injury, and promoting timely interventions. In contrast, manual health checks are periodic, labor-intensive, and risk delayed identification of health issues, potentially compromising animal well-being.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
Livestock wearables face challenges such as high initial costs, limited wireless connectivity in rural areas, and concerns about data accuracy compared to traditional manual health checks. Farmers encounter barriers including the need for technical skills to interpret data, resistance to changing established veterinary routines, and uncertainty about long-term return on investment. Integration with existing farm management systems and reliable battery life also hinder widespread adoption of wearable technology in livestock health monitoring.
Future Trends in Livestock Health Monitoring
Livestock wearables are transforming health monitoring by providing real-time data on vital signs, activity levels, and behavioral patterns, enabling early disease detection and improved animal welfare. Future trends indicate integration of AI-powered analytics and IoT connectivity, enhancing predictive insights and automated health interventions. These advancements promise to reduce reliance on labor-intensive manual health checks, increase monitoring accuracy, and optimize herd management efficiency.
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF)
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) leverages wearable sensors to provide real-time, accurate health monitoring of livestock, significantly outperforming manual health checks in efficiency and early disease detection.
Biometric Sensor Integration
Biometric sensor integration in livestock wearables enables continuous, real-time health monitoring with higher accuracy and early disease detection compared to periodic manual health checks.
Real-time Physiological Monitoring
Livestock wearables provide real-time physiological monitoring that enables immediate health assessments, unlike manual health checks which are periodic and prone to delays and inaccuracies.
Automated Animal Welfare Assessment
Automated animal welfare assessment through livestock wearables enables continuous, real-time monitoring of health metrics, significantly improving accuracy and early disease detection compared to manual health checks.
Remote Vital Signs Tracking
Livestock wearables enable continuous remote vital signs tracking, providing real-time health data and early disease detection, unlike manual health checks that are infrequent and labor-intensive.
Non-invasive Health Surveillance
Non-invasive livestock wearables provide continuous, real-time health surveillance with higher accuracy and earlier disease detection compared to periodic manual health checks.
Data-driven Disease Detection
Livestock wearables enable real-time, data-driven disease detection with higher accuracy and faster response times compared to manual health checks.
Telemetry-based Behavior Analysis
Telemetry-based behavior analysis in livestock wearables provides continuous, real-time monitoring of animal health, enabling early detection of abnormalities and improving accuracy compared to periodic manual health checks.
Continuous Lameness Detection
Livestock wearables enable continuous lameness detection by providing real-time gait analysis and early symptom alerts, outperforming traditional manual health checks that rely on sporadic observations and subjective assessments.
Manual Visual Inspection
Manual visual inspection for livestock health checks remains widely used despite wearables offering real-time data and continuous monitoring advantages.
Livestock wearables vs manual health checks Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com