Solar-powered irrigation systems reduce energy costs and environmental impact by harnessing renewable energy directly from the sun, making them ideal for remote agricultural areas without reliable grid access. Grid-powered irrigation offers consistent energy supply but often involves higher operational costs and dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing solar-powered solutions enhances sustainable water management and promotes energy efficiency in modern farming practices.
Table of Comparison
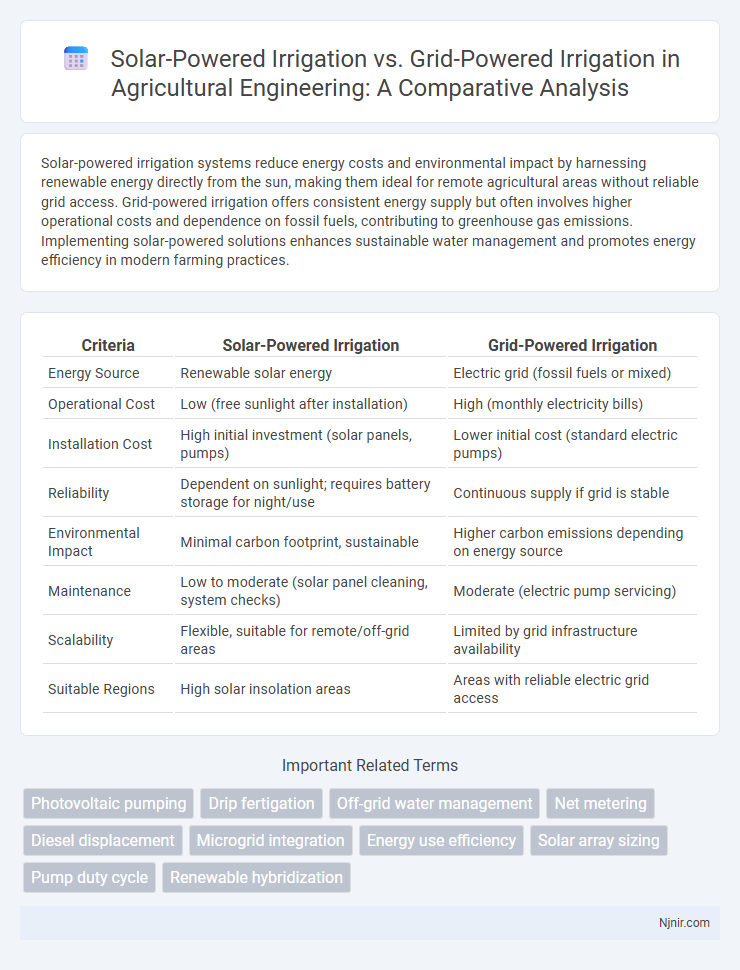
| Criteria | Solar-Powered Irrigation | Grid-Powered Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Renewable solar energy | Electric grid (fossil fuels or mixed) |
| Operational Cost | Low (free sunlight after installation) | High (monthly electricity bills) |
| Installation Cost | High initial investment (solar panels, pumps) | Lower initial cost (standard electric pumps) |
| Reliability | Dependent on sunlight; requires battery storage for night/use | Continuous supply if grid is stable |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher carbon emissions depending on energy source |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate (solar panel cleaning, system checks) | Moderate (electric pump servicing) |
| Scalability | Flexible, suitable for remote/off-grid areas | Limited by grid infrastructure availability |
| Suitable Regions | High solar insolation areas | Areas with reliable electric grid access |
Introduction to Irrigation Power Sources
Solar-powered irrigation utilizes photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, enabling sustainable water pumping for agricultural fields without relying on traditional power grids. Grid-powered irrigation depends on electricity supplied through mains infrastructure, often leading to higher operational costs and vulnerability to power outages. The choice between solar and grid power significantly impacts energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and long-term cost-effectiveness in irrigation systems.
Overview of Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems
Solar-powered irrigation systems leverage photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, enabling efficient water pumping without relying on grid electricity. These systems offer sustainable irrigation solutions by reducing energy costs and carbon emissions, making them ideal for remote or off-grid agricultural areas. Solar pumps typically require lower maintenance and provide consistent energy supply during daylight hours, promoting enhanced crop yields and water management.
Grid-Powered Irrigation: Setup and Operation
Grid-powered irrigation systems rely on a stable electrical connection from the utility grid, ensuring consistent water supply for crop irrigation without dependency on weather conditions. The setup involves connecting submersible or surface pumps to the grid, controlled by automated timers or sensors to optimize watering schedules and reduce energy waste. Operational costs depend on electricity tariffs, but the system offers high reliability and scalability for large-scale agricultural operations.
Cost Comparison: Solar vs Grid Irrigation
Solar-powered irrigation systems typically require higher initial capital investment due to the cost of solar panels and installation but offer significantly lower operational expenses as they eliminate ongoing electricity bills. In contrast, grid-powered irrigation incurs lower upfront costs but leads to continuous energy expenses that can fluctuate with local electricity rates. Over time, the total cost of ownership for solar irrigation becomes more economical, especially in regions with high electricity prices and ample sunlight, making it a financially sustainable solution for agricultural water management.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Solar-powered irrigation systems deliver superior energy efficiency by harnessing renewable sunlight, significantly reducing electricity costs and eliminating reliance on grid power fluctuations. These systems provide consistent performance in sunny regions and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to grid-powered irrigation, which depends on fossil fuel-generated electricity. Grid-powered irrigation may offer more stable water pressure in areas with unreliable solar conditions but often incurs higher operational expenses and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar-powered irrigation systems significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions by utilizing renewable energy, leading to lower carbon footprints compared to grid-powered systems that often rely on fossil fuels. The sustainability of solar irrigation stems from its minimal operational costs and long-term energy independence, promoting water conservation through efficient, solar-driven pumps. Conversely, grid-powered irrigation contributes to air pollution and resource depletion, making solar-powered alternatives crucial for environmentally responsible and sustainable agricultural practices.
Reliability and Availability of Power
Solar-powered irrigation systems offer high reliability during sunny periods with consistent energy supply directly from photovoltaic panels, significantly reducing dependency on external power sources. Grid-powered irrigation depends on the stability of the electrical grid, which can face outages and fluctuations, impacting availability and continuous operation. Solar systems provide greater autonomy and are especially advantageous in remote or off-grid areas where grid reliability is low.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Systems
Solar-powered irrigation systems generally require lower maintenance compared to grid-powered systems due to fewer moving parts and no dependence on fuel or electrical fluctuations, enhancing durability. The lifespan of solar panels often exceeds 25 years with minimal degradation, whereas grid-powered pumps may experience more frequent wear and tear due to mechanical stress and electrical issues. Maintenance costs for solar systems are typically lower, focusing mainly on panel cleaning and occasional battery replacement, while grid-powered systems demand regular servicing of motors, wiring, and fuel components.
Suitability for Different Farm Scales
Solar-powered irrigation systems are highly suitable for small to medium-sized farms due to their lower operational costs and independence from grid electricity, making them ideal for remote or off-grid areas. Grid-powered irrigation is better suited for large-scale farms with consistent, high-energy demands, as it provides reliable power without the need for large upfront investments in solar equipment. Both systems require evaluation based on farm size, water needs, and local energy availability to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Future Trends in Irrigation Power Technologies
Solar-powered irrigation systems are increasingly favored for their sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to reduce dependency on conventional electricity grids. Advances in photovoltaic technology, energy storage solutions, and smart irrigation controllers are driving more efficient water and energy use in agriculture. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid systems integrating solar with grid power and IoT-enabled platforms for precision irrigation management, enhancing crop yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Photovoltaic pumping
Solar-powered photovoltaic pumping systems reduce operational costs and carbon emissions compared to grid-powered irrigation by harnessing renewable energy for efficient water delivery in agriculture.
Drip fertigation
Solar-powered drip fertigation systems reduce energy costs and carbon emissions while providing efficient water and nutrient delivery compared to grid-powered irrigation.
Off-grid water management
Solar-powered irrigation enables efficient off-grid water management by providing sustainable, cost-effective energy without reliance on grid infrastructure.
Net metering
Solar-powered irrigation with net metering enables farmers to feed surplus electricity back to the grid, reducing overall energy costs and enhancing sustainability compared to grid-powered irrigation systems.
Diesel displacement
Solar-powered irrigation systems displace up to 90% of diesel fuel usage compared to grid-powered irrigation, significantly reducing operational costs and carbon emissions.
Microgrid integration
Solar-powered irrigation systems enhance microgrid integration by reducing grid dependency, lowering operational costs, and enabling sustainable water management in off-grid and rural areas.
Energy use efficiency
Solar-powered irrigation systems achieve up to 40% higher energy use efficiency compared to grid-powered irrigation by utilizing renewable energy and reducing transmission losses.
Solar array sizing
Solar-powered irrigation requires precise solar array sizing based on crop water demand, pump capacity, and sunlight availability to ensure efficient energy use, while grid-powered irrigation depends on consistent electrical supply without the need for array sizing.
Pump duty cycle
Solar-powered irrigation systems optimize pump duty cycles by operating primarily during peak sunlight hours, reducing energy costs and improving efficiency compared to grid-powered irrigation which allows flexible pump usage regardless of time but incurs higher electricity expenses.
Renewable hybridization
Solar-powered irrigation systems reduce operational costs and carbon emissions compared to grid-powered irrigation, and hybridizing these systems with grid power enhances reliability and maximizes renewable energy utilization.
Solar-powered irrigation vs Grid-powered irrigation Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com