Star connection offers a neutral point, providing a reliable path for unbalanced loads and enhancing system stability in three-phase systems. Delta connection allows for higher power transmission and better fault tolerance by circulating current within phases, reducing harmonics. Choosing between star and delta configurations depends on load requirements, voltage levels, and system protection needs.
Table of Comparison
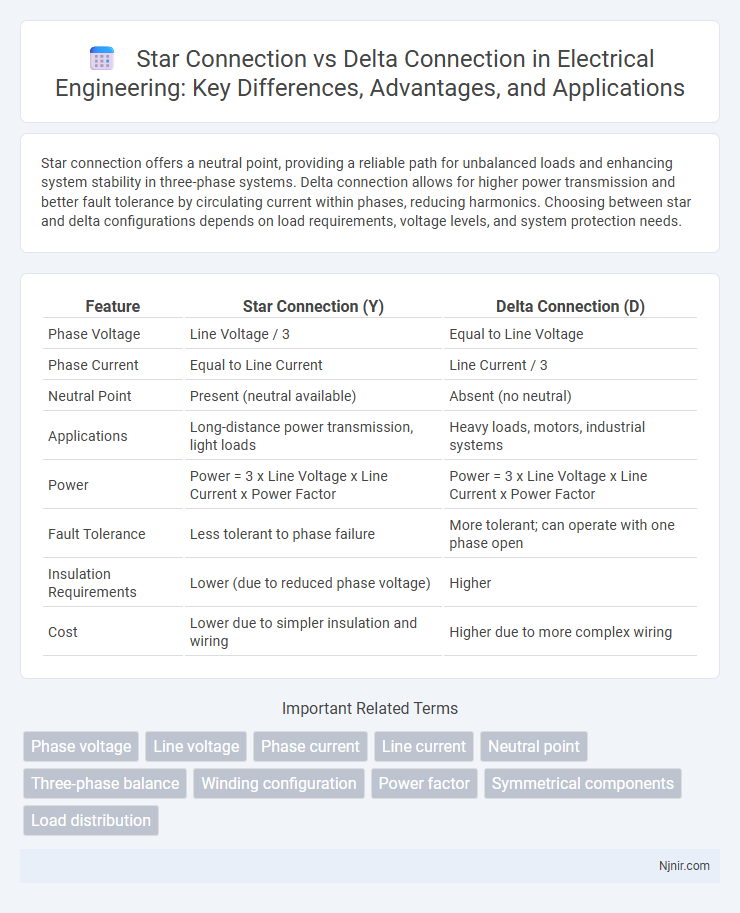
| Feature | Star Connection (Y) | Delta Connection (D) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Voltage | Line Voltage / 3 | Equal to Line Voltage |
| Phase Current | Equal to Line Current | Line Current / 3 |
| Neutral Point | Present (neutral available) | Absent (no neutral) |
| Applications | Long-distance power transmission, light loads | Heavy loads, motors, industrial systems |
| Power | Power = 3 x Line Voltage x Line Current x Power Factor | Power = 3 x Line Voltage x Line Current x Power Factor |
| Fault Tolerance | Less tolerant to phase failure | More tolerant; can operate with one phase open |
| Insulation Requirements | Lower (due to reduced phase voltage) | Higher |
| Cost | Lower due to simpler insulation and wiring | Higher due to more complex wiring |
Introduction to Star and Delta Connections
Star connection (Y-connection) features three load points connected to a common neutral, creating a stable system with lower phase voltage ideal for long-distance power transmission. Delta connection (D-connection) links each load in a closed loop, resulting in higher phase voltage and balanced three-phase currents suited for high power applications. Both configurations impact electrical systems' voltage levels, current distribution, and load balancing in three-phase circuits.
Fundamental Differences Between Star and Delta
Star connection features three phases connected at a common neutral point, allowing for both phase and line voltage measurements, while delta connection forms a closed loop with each phase connected end-to-end, enabling the line voltage to equal phase voltage. Star configuration provides a neutral for grounding and is commonly used in low voltage distribution, whereas delta connection supports higher starting torque and is preferred for motor applications. Electrical currents in star connection split evenly through the neutral, contrasting with delta where currents circulate within the closed loop, affecting the overall load and fault tolerance.
Construction and Configuration of Star Connection
Star connection features three-phase windings connected at a common neutral point forming a 'Y' shape, enabling the phase voltage to be lower than line voltage, which is ideal for balanced loads. Each winding is connected to one line terminal, and the neutral wire provides a return path, enhancing stability and safety in electrical systems. This configuration allows for both single-phase and three-phase power supply, commonly used in distribution systems and motor applications.
Construction and Configuration of Delta Connection
Delta connection features three coils connected end-to-end forming a closed loop, creating a triangular shape. Each coil's junction points serve as line terminals, enabling direct phase-to-phase voltage supply. This configuration allows balanced load sharing and typically supports higher starting torque for motors compared to star connection.
Voltage and Current Relationships in Star vs Delta
In star connection, line voltage equals the phase voltage multiplied by 3, while line current is the same as phase current, enabling lower line voltage and higher current handling. Conversely, in delta connection, line voltage equals phase voltage, and line current is 3 times the phase current, allowing higher voltage with lower current per phase. These voltage and current relationships impact efficiency and application suitability in three-phase power systems.
Applications of Star Connection in Electrical Systems
Star connection is widely used in electrical systems for distributing power at lower voltage levels, making it ideal for supplying residential and commercial buildings. This configuration provides a neutral point, enabling the use of single-phase loads alongside three-phase loads, which enhances flexibility in power distribution. Star connection also facilitates safer motor starting, reducing inrush current and minimizing stress on electrical components in industrial applications.
Applications of Delta Connection in Electrical Systems
Delta connection is widely used in electrical systems for three-phase motors, providing higher starting torque and allowing motor operation under heavy loads. It is favored in industrial settings for power distribution to balance loads and reduce harmonics in high-power transformers and large-scale motors. The delta configuration supports phase voltage continuity, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent voltage supply and reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Connection
Star connection offers advantages such as a neutral point for grounding, which enhances safety and reduces the risk of electric shock. It provides lower phase voltage, resulting in reduced insulation requirements and improved insulation cost-efficiency. However, star connection delivers lower power output compared to delta connection and may cause unbalanced load issues if one phase fails, affecting system stability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Delta Connection
Delta connection offers higher efficiency in transmitting power with reduced voltage drops, making it suitable for high-power applications and heavy industrial loads. It provides reliable operation under unbalanced load conditions and allows for the continuation of service if one phase fails, enhancing system robustness. However, delta connections are more complex to design and maintain, can generate higher circulating currents leading to increased losses, and often require more insulation due to line-to-line voltage exposure.
Star vs Delta: Selection Criteria and Practical Considerations
Star and delta connections differ primarily in voltage configuration and current capacity, influencing their selection for specific applications. Star connections offer a neutral point, making them suitable for systems requiring neutral grounding and lower starting currents, while delta connections provide higher starting torque and better suited for heavy-duty motors. Practical considerations include load type, required phase voltages, system grounding, and motor starting performance, with star favored for long-distance power transmission and delta preferred for industrial motor operation.
Phase voltage
In star connection, the phase voltage equals the line voltage divided by 3, whereas in delta connection, the phase voltage is equal to the line voltage.
Line voltage
In star connection, the line voltage is 3 times the phase voltage, whereas in delta connection, the line voltage equals the phase voltage.
Phase current
In star connection, the phase current equals the line current divided by 3, whereas in delta connection, the phase current equals the line current.
Line current
In star connection, the line current equals the phase current, whereas in delta connection, the line current is 3 times the phase current.
Neutral point
Star connection provides a neutral point for grounding and phase voltage measurement, while delta connection lacks a neutral point, limiting its use in certain electrical systems.
Three-phase balance
A star connection provides a neutral point for improved three-phase load balancing, while a delta connection inherently supports balanced three-phase currents without a neutral.
Winding configuration
Star connection features windings connected at a common neutral point forming a Y shape, while delta connection arranges windings in a closed loop resembling a triangle, influencing voltage, current, and phase characteristics in three-phase systems.
Power factor
Star connection typically offers a higher power factor in low-voltage applications compared to delta connection, improving overall system efficiency.
Symmetrical components
Symmetrical components analysis simplifies fault calculations by decomposing unbalanced star and delta connections into balanced sets, revealing that star connections provide a neutral point for zero-sequence currents while delta connections circulate zero-sequence currents internally without a neutral path.
Load distribution
Star connection evenly distributes load voltage across three phases while delta connection balances load current, optimizing overall power distribution efficiency.
star connection vs delta connection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com