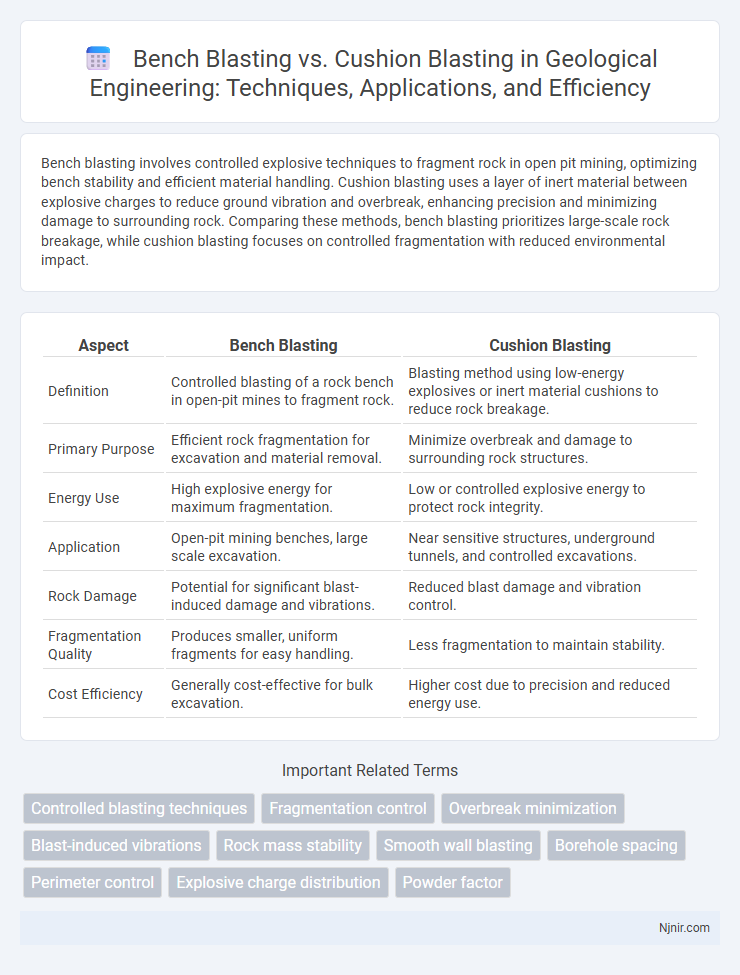
Bench blasting involves controlled explosive techniques to fragment rock in open pit mining, optimizing bench stability and efficient material handling. Cushion blasting uses a layer of inert material between explosive charges to reduce ground vibration and overbreak, enhancing precision and minimizing damage to surrounding rock. Comparing these methods, bench blasting prioritizes large-scale rock breakage, while cushion blasting focuses on controlled fragmentation with reduced environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bench Blasting | Cushion Blasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled blasting of a rock bench in open-pit mines to fragment rock. | Blasting method using low-energy explosives or inert material cushions to reduce rock breakage. |
| Primary Purpose | Efficient rock fragmentation for excavation and material removal. | Minimize overbreak and damage to surrounding rock structures. |
| Energy Use | High explosive energy for maximum fragmentation. | Low or controlled explosive energy to protect rock integrity. |
| Application | Open-pit mining benches, large scale excavation. | Near sensitive structures, underground tunnels, and controlled excavations. |
| Rock Damage | Potential for significant blast-induced damage and vibrations. | Reduced blast damage and vibration control. |
| Fragmentation Quality | Produces smaller, uniform fragments for easy handling. | Less fragmentation to maintain stability. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally cost-effective for bulk excavation. | Higher cost due to precision and reduced energy use. |
Introduction to Bench Blasting and Cushion Blasting
Bench blasting involves controlled explosions used to break up rock in open-pit mining or quarrying, facilitating easier excavation and material removal. Cushion blasting uses a carefully designed layer of loose material to absorb explosive energy, minimizing overbreak and improving fragmentation precision. Both techniques optimize rock breakage efficiency while managing vibration and flyrock risks in mining operations.
Fundamental Principles of Bench Blasting
Bench blasting involves the controlled use of explosives in a horizontal bench to fragment rock effectively, relying on precise timing and drilling patterns to maximize breakage and stability. Cushion blasting, a subset of bench blasting, incorporates a layer of inert material or stemming to absorb explosive energy, reducing ground vibrations and improving safety. Both methods emphasize the balance between explosive energy and rock confinement to optimize fragmentation while minimizing environmental impact.
Key Concepts of Cushion Blasting
Cushion blasting utilizes a layer of inert material, such as soil or gravel, placed above the explosive charge to control ground vibrations and direct energy more efficiently compared to bench blasting. This technique minimizes the risk of excessive flyrock and surface damage, making it ideal for sensitive environments or urban areas. Cushion blasting enhances fragmentation and blast control by optimizing the energy distribution and reducing overbreak in rock excavation projects.
Comparative Blasting Techniques and Applications
Bench blasting offers high precision and controlled fragmentation for open-pit mining, allowing efficient removal of large rock volumes with minimal ground vibration. Cushion blasting uses a layer of inert material to absorb explosive energy, reducing fly rock and ground damage, making it ideal for sensitive environments and urban construction sites. Compared to bench blasting, cushion blasting provides enhanced safety and environmental control but with potentially lower fragmentation efficiency in hard rock conditions.
Equipment and Materials for Each Blasting Method
Bench blasting requires heavy-duty drilling rigs, scalable blast hole drills, and high-capacity blasting mats to contain fly rock, while materials include large-diameter explosives such as ANFO or emulsion explosives tailored for uniform rock fragmentation. Cushion blasting utilizes precise scale drills and lighter explosives with controlled energy output, commonly emulsions or charged detonators, minimizing overbreak and ground vibration to ensure selective rock removal. Equipment for cushion blasting often features advanced delay detonators and stemming materials to absorb shock waves, optimizing safety and efficiency in confined blasting scenarios.
Influence on Rock Fragmentation and Wall Stability
Bench blasting produces larger rock fragments due to higher explosive energy focused on breaking the rock mass, which can improve fragmentation but may compromise wall stability by inducing vibrations and overbreak. Cushion blasting uses controlled, smaller charges placed in a cushion of undisturbed rock or with stemming to reduce explosive energy transmission, resulting in finer fragmentation and enhanced wall stability by minimizing damage to the bench face. Optimal selection between bench and cushion blasting depends on balancing fragmentation efficiency with the preservation of wall integrity to ensure safe and cost-effective mining operations.
Safety Considerations in Bench and Cushion Blasting
Bench blasting involves sequentially detonating explosives in a stepped pattern, requiring precise timing and controlled initiation to minimize flyrock and ground vibrations, ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment. Cushion blasting uses smaller, controlled explosive charges placed carefully to reduce overbreak and limit ground shock, enhancing site stability and reducing the risk of structural damage. Implementing rigorous monitoring and adherence to regulatory safety standards in both methods is critical to manage hazardous materials and protect workers in mining and construction operations.
Environmental Impacts and Vibration Control
Bench blasting generates higher vibration levels and dust emissions due to the unrestricted explosive energy release, increasing environmental disturbance and requiring robust mitigation measures. Cushion blasting uses a layer of inert material or controlled parameters to absorb explosive energy, significantly reducing ground vibration and airborne particulate matter. This method offers superior vibration control, minimizing damage to nearby structures and lessening the ecological footprint compared to conventional bench blasting.
Cost Analysis: Bench Blasting vs Cushion Blasting
Bench blasting generally incurs higher operational costs due to the extensive equipment and manpower required for large-scale rock removal, whereas cushion blasting offers cost savings by minimizing overbreak and reducing the need for secondary excavation. Cushion blasting improves fragmentation efficiency, leading to lower drilling and blasting expenses, which significantly impacts overall project budgets. Careful analysis of site conditions and project scale is essential to determine the most cost-effective blasting method.
Best Practices and Case Studies in Blasting Optimization
Bench blasting and cushion blasting require precise control of charge placement and burden to maximize fragmentation and minimize ground vibration. Case studies in mining operations reveal that optimizing blast design parameters, such as timing sequences and explosive types, significantly improves rock breakage efficiency and reduces operational costs. Best practices emphasize detailed site characterization and continuous monitoring to adapt blasting techniques for varying geological conditions, enhancing overall productivity and environmental compliance.
Controlled blasting techniques
Controlled bench blasting uses precise charge placement and timing to minimize ground vibration, while cushion blasting employs buffer material layers to absorb shock, both techniques enhancing safety and fragmentation control in mining operations.
Fragmentation control
Bench blasting offers greater fragmentation control through precise burden and spacing adjustments, whereas cushion blasting utilizes a layer of inert material to absorb energy, reducing over-fragmentation and minimizing fines.
Overbreak minimization
Cushion blasting minimizes overbreak more effectively than bench blasting by controlling explosive energy and reducing ground vibration.
Blast-induced vibrations
Bench blasting generates higher blast-induced vibrations due to larger explosive charges and open bench geometry, whereas cushion blasting minimizes vibrations by using smaller, controlled charges and energy-absorbing materials to protect surrounding structures.
Rock mass stability
Bench blasting enhances rock mass stability by controlling vibration and fragmentation, whereas cushion blasting improves stability by minimizing overbreak and reducing damage to the surrounding rock.
Smooth wall blasting
Smooth wall blasting achieves superior surface uniformity by employing cushion blasting techniques that reduce substrate damage compared to traditional bench blasting methods.
Borehole spacing
Bench blasting typically requires wider borehole spacing of 1.2 to 1.5 meters to optimize fragmentation, while cushion blasting uses closer spacing of approximately 0.9 to 1.1 meters to control vibration and minimize backbreak.
Perimeter control
Bench blasting offers precise perimeter control by using carefully designed blast patterns and controlled explosive charges, whereas cushion blasting enhances perimeter stability by employing buffer zones and reduced explosive energy to minimize flyrock and vibration.
Explosive charge distribution
Bench blasting employs uniform explosive charge distribution along the bench to optimize rock fragmentation, while cushion blasting uses a lighter, carefully distributed charge near the bench toe to reduce vibration and flyrock.
Powder factor
Bench blasting typically requires a higher powder factor ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 kg/m3, while cushion blasting uses a significantly lower powder factor around 0.1 to 0.3 kg/m3 to minimize vibrations and damage in sensitive environments.
bench blasting vs cushion blasting Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com