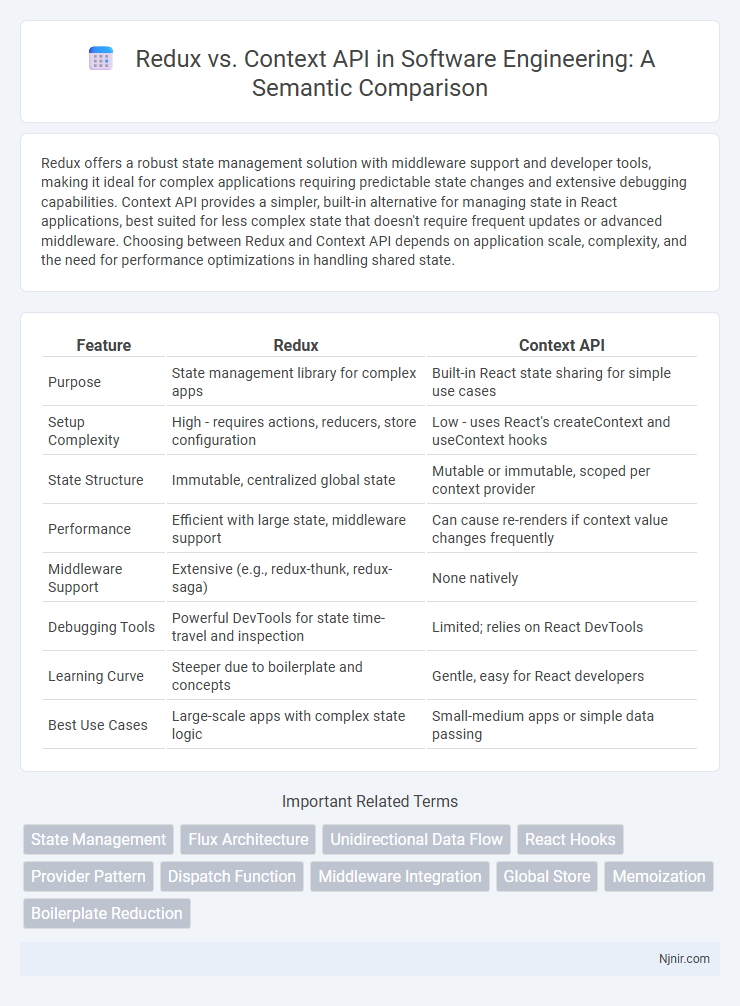
Redux offers a robust state management solution with middleware support and developer tools, making it ideal for complex applications requiring predictable state changes and extensive debugging capabilities. Context API provides a simpler, built-in alternative for managing state in React applications, best suited for less complex state that doesn't require frequent updates or advanced middleware. Choosing between Redux and Context API depends on application scale, complexity, and the need for performance optimizations in handling shared state.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Redux | Context API |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | State management library for complex apps | Built-in React state sharing for simple use cases |
| Setup Complexity | High - requires actions, reducers, store configuration | Low - uses React's createContext and useContext hooks |
| State Structure | Immutable, centralized global state | Mutable or immutable, scoped per context provider |
| Performance | Efficient with large state, middleware support | Can cause re-renders if context value changes frequently |
| Middleware Support | Extensive (e.g., redux-thunk, redux-saga) | None natively |
| Debugging Tools | Powerful DevTools for state time-travel and inspection | Limited; relies on React DevTools |
| Learning Curve | Steeper due to boilerplate and concepts | Gentle, easy for React developers |
| Best Use Cases | Large-scale apps with complex state logic | Small-medium apps or simple data passing |
Introduction to State Management in React
State management in React involves organizing and controlling the flow of data between components, crucial for building scalable applications. Redux provides a predictable state container with a centralized store, enabling complex state logic, middleware integration, and time-travel debugging. The Context API offers a simpler, built-in solution for passing data through the component tree without prop drilling, ideal for managing global state in smaller or medium-sized applications.
Overview of Redux
Redux is a predictable state container commonly used in JavaScript applications to manage application state efficiently. It centralizes state in a single store, allowing for consistent state updates through pure functions called reducers. Redux enables advanced features like time-travel debugging and middleware integration, making it well-suited for complex state management scenarios.
Overview of Context API
Context API is a built-in feature of React designed for managing state across components without prop drilling, making it ideal for simpler state management scenarios. It provides a way to share values like themes, user authentication, or language preferences through a centralized context object. Unlike Redux, Context API is lightweight and requires less boilerplate code, but it lacks the advanced middleware and developer tools that make Redux suitable for complex state logic and large-scale applications.
Core Differences Between Redux and Context API
Redux centralizes state management using a single store with strict unidirectional data flow and middleware support for complex asynchronous logic, making it ideal for large-scale applications. Context API provides a simpler, built-in way to pass state down the component tree without prop drilling, best suited for lightweight or localized state sharing. Redux enforces immutability and predictable state changes via reducers, while Context API lacks built-in controls for state mutations and debugging tools.
Performance Comparison: Redux vs Context API
Redux offers superior performance in large-scale applications by minimizing unnecessary component re-renders through selective state updates and advanced middleware support. Context API can lead to performance bottlenecks in complex apps due to its tendency to trigger re-renders of all consuming components on state changes, which affects UI responsiveness. Developers often prefer Redux for scalable state management with optimized rendering and Context API for simpler, less intensive state-sharing needs.
Scalability and Code Structure
Redux offers superior scalability by centralizing state management and enabling predictable state transitions, which supports large-scale applications with complex data flows. Its strict structure enforces a clear separation between actions, reducers, and state, resulting in maintainable and testable code. Context API suits simpler or medium-sized projects but can lead to performance issues and tangled code when scaling due to frequent re-renders and less organized state logic.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Redux requires understanding of action creators, reducers, and middleware, which can present a steeper learning curve compared to the Context API's straightforward use of React's built-in features for state management. Context API offers simplicity for managing global state in smaller applications without extra libraries, making it easier for beginners to grasp. Developers may find Redux more complex but scalable, while Context API is favored for minimal setup and intuitive integration.
Middleware and Side Effects Handling
Redux offers robust middleware support such as Redux Thunk and Redux Saga, enabling efficient handling of asynchronous side effects and complex state logic outside of the components. The Context API, while simpler and suitable for smaller applications, lacks built-in middleware capabilities, requiring developers to manage side effects manually within components or use external libraries. Middleware in Redux intercepts actions before they reach reducers, providing a powerful mechanism for logging, error handling, and asynchronous operations, which the Context API does not natively support.
Community Support and Ecosystem
Redux boasts a robust community with extensive resources, plugins, and middleware that enhance scalability and maintainability in large-scale React applications. The Context API, being a native React feature, benefits from seamless integration but has a smaller ecosystem and fewer third-party tools compared to Redux. Developers often prefer Redux for complex state management needs due to its mature ecosystem and strong community-driven support.
When to Use Redux vs Context API
Redux excels in managing complex state logic and large-scale applications with frequent state updates and middleware requirements. Context API is ideal for simpler state sharing scenarios, such as theming or user authentication, where performance overhead must be minimal. Choose Redux for predictable state management and extensive debugging tools, while Context API suits lightweight state propagation without third-party dependencies.
State Management
Redux offers a centralized, predictable state management solution with middleware support and time-travel debugging, while Context API provides a simpler, built-in React tool ideal for managing small to medium state sharing without complex side effects.
Flux Architecture
Redux strictly implements Flux architecture with a unidirectional data flow and centralized store, whereas Context API provides simpler state sharing but lacks Flux's structured dispatcher and middleware capabilities.
Unidirectional Data Flow
Redux enforces strict unidirectional data flow through a centralized store and pure reducers, while Context API allows simpler state sharing but may lead to less predictable data updates without middleware.
React Hooks
Redux offers a centralized state management with immutable updates and middleware support, while Context API provides a simpler, built-in solution for sharing state across components using React Hooks like useContext and useReducer.
Provider Pattern
Redux's Provider pattern centralizes global state management with a single store, while React's Context API Provider offers a lightweight, component-scoped way to share state without the need for external libraries.
Dispatch Function
Redux's dispatch function offers centralized, predictable state management with middleware support, while Context API's dispatch is simpler and better suited for lightweight, local state updates without external dependencies.
Middleware Integration
Redux offers robust middleware integration through libraries like redux-thunk and redux-saga, enabling advanced asynchronous logic and side-effect management, whereas Context API lacks built-in middleware support, making Redux the preferred choice for complex state management requiring middleware.
Global Store
Redux provides a centralized global store with predictable state management through actions and reducers, while Context API offers a simpler, built-in solution for sharing state globally without middleware or complex setup.
Memoization
Redux efficiently manages state with built-in memoization for optimized re-rendering, while Context API requires manual memoization to prevent unnecessary component updates.
Boilerplate Reduction
Redux's boilerplate reduction can be achieved with tools like Redux Toolkit, but Context API inherently minimizes boilerplate by simplifying state management without requiring action types, reducers, or middleware setups.
Redux vs Context API Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com