Livestock automation integrates advanced technologies such as sensors, robotic feeders, and automated milking systems to enhance efficiency and animal welfare compared to traditional husbandry methods. This approach reduces labor costs, improves monitoring accuracy, and optimizes resource management, leading to higher productivity. Traditional husbandry relies heavily on manual labor and experience-based practices, which may result in inconsistent care and lower operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
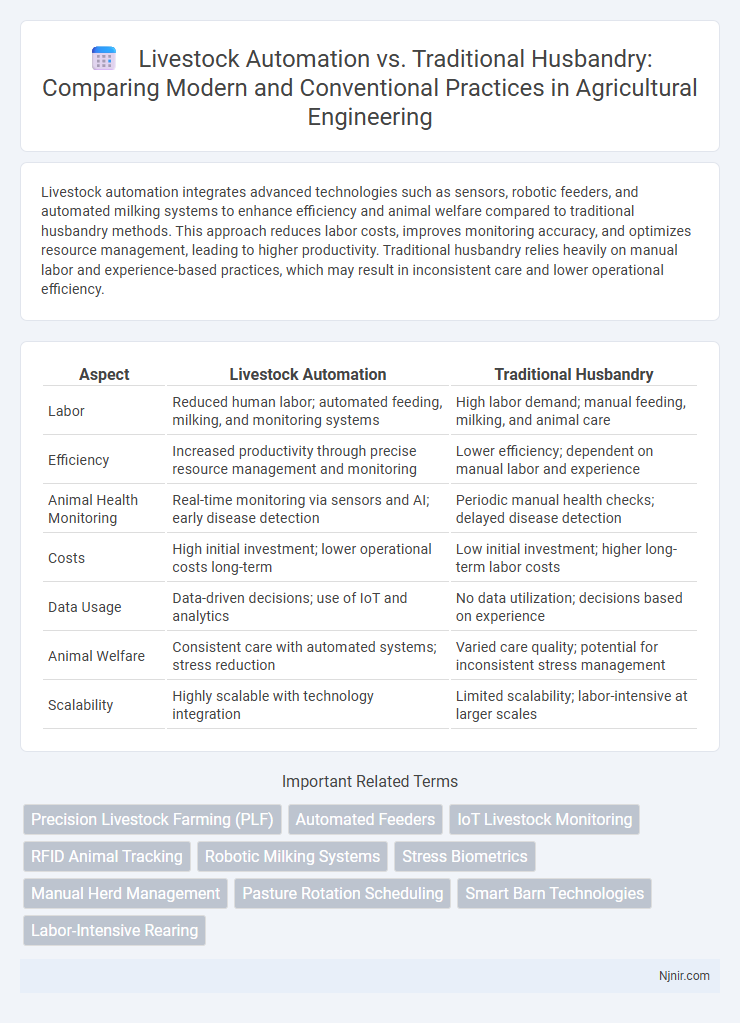
| Aspect | Livestock Automation | Traditional Husbandry |
|---|---|---|
| Labor | Reduced human labor; automated feeding, milking, and monitoring systems | High labor demand; manual feeding, milking, and animal care |
| Efficiency | Increased productivity through precise resource management and monitoring | Lower efficiency; dependent on manual labor and experience |
| Animal Health Monitoring | Real-time monitoring via sensors and AI; early disease detection | Periodic manual health checks; delayed disease detection |
| Costs | High initial investment; lower operational costs long-term | Low initial investment; higher long-term labor costs |
| Data Usage | Data-driven decisions; use of IoT and analytics | No data utilization; decisions based on experience |
| Animal Welfare | Consistent care with automated systems; stress reduction | Varied care quality; potential for inconsistent stress management |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with technology integration | Limited scalability; labor-intensive at larger scales |
Introduction to Livestock Automation and Traditional Husbandry
Livestock automation leverages advanced technologies such as robotic feeders, automated milking systems, and sensor-based health monitoring to enhance productivity and animal welfare. Traditional husbandry relies on manual labor and time-tested practices for feeding, breeding, and managing livestock, emphasizing human skills and experience. The shift towards automation aims to address labor shortages, increase efficiency, and improve data-driven decision-making in livestock management.
Technological Innovations in Livestock Management
Technological innovations in livestock management, such as automated feeding systems, precision monitoring sensors, and AI-driven health diagnostics, significantly enhance productivity and animal welfare compared to traditional husbandry methods. Automated systems optimize feed efficiency and reduce labor costs by delivering precise nutrient amounts based on real-time animal data. Integration of IoT devices enables continuous monitoring of livestock behavior and environmental conditions, facilitating early disease detection and improving overall herd management.
Labor Efficiency: Automated Systems vs Manual Practices
Livestock automation significantly boosts labor efficiency by integrating advanced technologies like robotic feeders, automated milking systems, and sensor-based health monitoring, reducing manual labor and minimizing human error. Traditional husbandry relies heavily on manual practices such as hand feeding, manual milking, and visual health inspections, which are time-intensive and prone to inconsistencies. Automated systems enable continuous animal monitoring and precise resource allocation, optimizing labor productivity and allowing farmers to manage larger herds with fewer workers.
Health Monitoring in Automated and Traditional Systems
Automated livestock health monitoring utilizes sensors, wearable devices, and real-time data analytics to detect early signs of illness, enabling prompt intervention and reducing disease spread. Traditional husbandry relies on manual observation and physical examination by farmers, which can delay detection and increase labor intensity. Integration of automated systems improves accuracy, consistency, and scalability compared to the subjective nature and limited frequency of traditional health assessments.
Environmental Impact: Automation Compared to Traditional Methods
Livestock automation significantly reduces environmental impact by optimizing feed usage, lowering methane emissions through precise diet management, and minimizing waste through advanced waste processing systems. Traditional husbandry often results in higher greenhouse gas emissions and inefficient resource use due to manual feeding and less controlled waste management. Automated systems enhance sustainability and reduce the carbon footprint of livestock farming compared to conventional methods.
Cost Analysis: Upfront Investment and Long-Term Returns
Livestock automation demands a higher upfront investment due to advanced technologies like automated feeders, climate controls, and monitoring systems, yet significantly reduces labor costs and enhances productivity over time. Traditional husbandry requires lower initial expenses but incurs continuous labor costs and often results in less efficient resource management. Long-term returns from automation include improved animal health, optimized feed usage, and data-driven decision-making, offering superior cost-efficiency compared to conventional practices.
Animal Welfare: Automated Monitoring vs Human Supervision
Automated monitoring in livestock management employs advanced sensors and AI technology to provide real-time health tracking, early disease detection, and precise environmental control, enhancing animal welfare by reducing stress and improving timely interventions. In contrast, traditional husbandry relies on human supervision, which is subject to observational limitations and variability in skill, potentially delaying responses to animal distress or illness. Automated systems offer continuous, objective data collection that complements human judgment, promoting more consistent and proactive animal care practices.
Data-Driven Decision Making in Automated Husbandry
Automated livestock husbandry leverages IoT sensors and AI algorithms to collect real-time data on animal health, behavior, and environmental conditions, enabling precise and timely interventions. Data-driven decision making enhances productivity, animal welfare, and resource efficiency by predicting disease outbreaks and optimizing feeding schedules based on continuous analytics. Traditional husbandry relies on manual observations and experience, which limits responsiveness and scalability compared to the data-centric approach of automated systems.
Challenges and Barriers to Automation Adoption
Livestock automation faces significant challenges including high initial costs, complex integration with existing farm systems, and the need for specialized technical skills among farmers. Traditional husbandry benefits from established practices and low technology dependence but struggles with labor intensity and inconsistent productivity. Barriers to automation adoption also include resistance to change, data privacy concerns, and limited access to reliable internet connectivity in rural areas.
Future Trends in Livestock Husbandry
Future trends in livestock husbandry emphasize automation technologies such as AI-driven feeding systems, robotic milking machines, and sensor-based health monitoring to enhance productivity and animal welfare. Integration of IoT devices enables real-time data collection and predictive analytics, optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impact compared to traditional husbandry methods. Precision livestock farming is projected to revolutionize the industry by improving sustainability, efficiency, and traceability throughout the production cycle.
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF)
Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) enhances productivity and animal welfare by using automated sensors and data analytics to monitor health, behavior, and environmental conditions, outperforming traditional husbandry methods in efficiency and sustainability.
Automated Feeders
Automated feeders enhance livestock automation by precisely delivering feed on schedule, improving efficiency and health compared to traditional husbandry methods reliant on manual feeding.
IoT Livestock Monitoring
IoT livestock monitoring enhances automation by providing real-time health and activity data, improving efficiency and accuracy compared to traditional husbandry methods.
RFID Animal Tracking
RFID animal tracking in livestock automation significantly enhances real-time monitoring accuracy, health management, and operational efficiency compared to traditional husbandry methods reliant on manual identification and record-keeping.
Robotic Milking Systems
Robotic Milking Systems increase efficiency and animal welfare in livestock automation by providing precise, continuous milking and data-driven herd management compared to labor-intensive traditional husbandry methods.
Stress Biometrics
Livestock automation using stress biometrics technology enables real-time monitoring and reduces animal stress more effectively than traditional husbandry methods reliant on manual observation.
Manual Herd Management
Manual herd management in traditional husbandry involves time-intensive tasks such as feeding, health monitoring, and movement control, whereas livestock automation employs sensors, robotic feeders, and data analytics to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Pasture Rotation Scheduling
Pasture rotation scheduling in livestock automation enhances grazing efficiency and animal health by using sensor data and algorithms, outperforming traditional husbandry methods that rely on fixed schedules and manual observation.
Smart Barn Technologies
Smart Barn Technologies enhance livestock automation by integrating IoT sensors, automated feeding, climate control, and real-time health monitoring, significantly improving efficiency and animal welfare compared to traditional husbandry methods.
Labor-Intensive Rearing
Livestock automation significantly reduces labor-intensive rearing by employing robotics and AI for feeding, monitoring, and health management, unlike traditional husbandry methods that rely heavily on manual labor and human intervention.
Livestock automation vs Traditional husbandry Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com