Renewable energy sources in agricultural engineering significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower operational costs compared to fossil fuels. Solar panels, wind turbines, and bioenergy systems enhance sustainability by providing clean, reliable power for irrigation and machinery. Transitioning to renewables promotes energy independence and mitigates environmental degradation associated with traditional fossil fuel use.
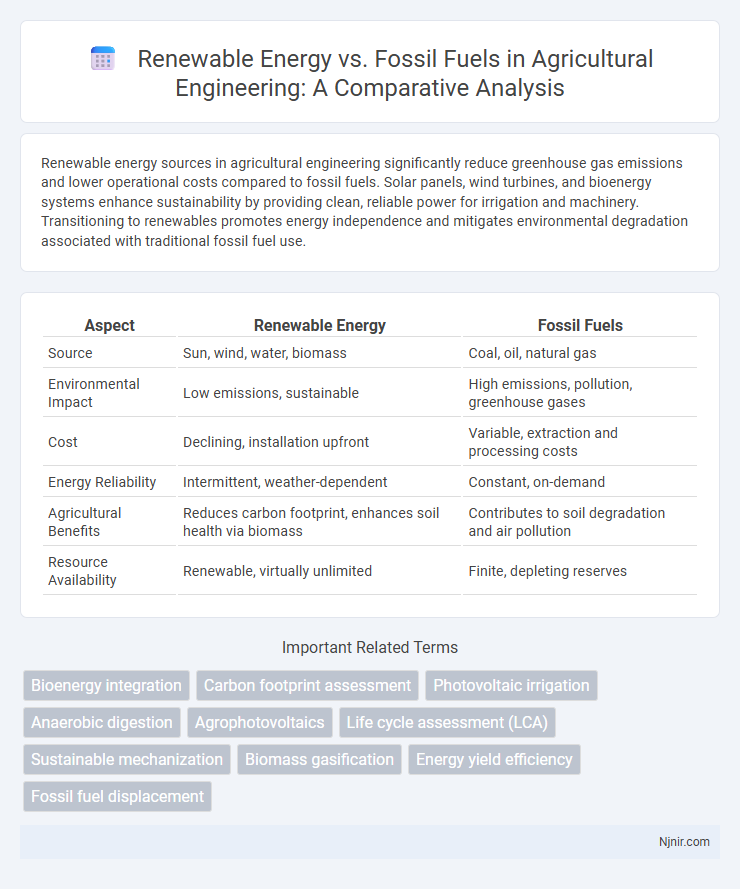
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Renewable Energy | Fossil Fuels |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sun, wind, water, biomass | Coal, oil, natural gas |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions, sustainable | High emissions, pollution, greenhouse gases |
| Cost | Declining, installation upfront | Variable, extraction and processing costs |
| Energy Reliability | Intermittent, weather-dependent | Constant, on-demand |
| Agricultural Benefits | Reduces carbon footprint, enhances soil health via biomass | Contributes to soil degradation and air pollution |
| Resource Availability | Renewable, virtually unlimited | Finite, depleting reserves |
Introduction to Renewable Energy and Fossil Fuels in Agriculture
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and bioenergy are increasingly integrated into agricultural practices to reduce reliance on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. These sustainable energy options power irrigation systems, machinery, and greenhouses, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewables in agriculture enhances energy efficiency and supports environmental conservation.
Energy Consumption Patterns in Modern Farming
Modern farming increasingly relies on renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines to power irrigation systems, machinery, and processing facilities, reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuels like diesel and natural gas. This shift decreases greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs while promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Energy consumption patterns in agriculture now favor decentralized, clean energy solutions tailored to local farm needs, enhancing efficiency and environmental impact.
Environmental Impact of Renewable vs Fossil Energy in Agriculture
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, mitigating climate change effects on agriculture. Fossil fuel reliance contributes to soil degradation, air pollution, and water contamination, impairing crop yield and food security. Transitioning to renewables supports sustainable farming practices by decreasing the carbon footprint and preserving natural resources critical for agricultural productivity.
Economic Analysis: Cost Comparison for Farmers
Renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, offer farmers lower long-term operational costs and protection against volatile fossil fuel prices. While initial investments in renewable technologies may be higher, government subsidies and tax incentives significantly reduce upfront expenses, improving overall return on investment. Fossil fuels incur ongoing costs linked to fuel price fluctuations and maintenance, making renewable energy a more economically stable and sustainable option for agricultural operations.
Availability and Accessibility of Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro are abundant and geographically widespread, offering a more sustainable and accessible option compared to fossil fuels, which are concentrated in specific regions and subject to depletion. Solar and wind energy can be harnessed locally, reducing dependence on imported fuels and enhancing energy security. In contrast, fossil fuel extraction and transportation involve complex infrastructure, often leading to supply disruptions and higher costs.
Integration of Renewable Technologies in Agricultural Machinery
Integration of renewable energy technologies in agricultural machinery enhances sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Solar-powered irrigation systems and bioenergy-driven tractors improve efficiency while maintaining productivity in farming operations. Advancements in battery storage and electric drivetrains enable seamless adoption of renewable-powered equipment, promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices.
Reliability and Efficiency of Energy Supply for Rural Areas
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind provide reliable and sustainable power for rural areas by leveraging local natural resources, reducing dependence on distant fossil fuel supplies. Modern renewable technologies often surpass traditional fossil fuels in efficiency by converting energy more directly, minimizing losses during transmission and distribution. The integration of energy storage systems further enhances supply reliability, making renewables a viable and efficient alternative for rural energy needs.
Government Policies and Incentives for Sustainable Energy
Government policies increasingly favor renewable energy through subsidies, tax credits, and grants aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting clean energy technologies. Fossil fuel industries face growing regulatory pressures, including carbon pricing and emissions caps, which shift investments toward sustainable alternatives. Incentive programs such as feed-in tariffs and renewable portfolio standards accelerate the adoption of solar, wind, and other green energy sources, fostering economic growth and energy security.
Case Studies: Successful Transitions to Renewable Energy on Farms
Case studies from farms in California and Denmark highlight the successful transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy through the adoption of solar panels and wind turbines, resulting in significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. These farms report enhanced energy independence and cost savings, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. Data from the USDA confirms that farms utilizing renewable energy show increased profitability and lower carbon footprints compared to those relying on fossil fuels.
Future Trends and Innovations in Agricultural Energy Systems
Future trends in agricultural energy systems emphasize the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and bioenergy to replace traditional fossil fuels. Innovations like solar-powered irrigation pumps, anaerobic digesters for bioenergy production, and smart grid technologies optimize energy efficiency and sustainability in farming operations. These advancements contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy resilience in the agricultural sector.
Bioenergy integration
Bioenergy integration enhances renewable energy portfolios by converting organic waste into sustainable power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon footprint assessment
Renewable energy sources have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% across their lifecycle.
Photovoltaic irrigation
Photovoltaic irrigation systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels by harnessing solar energy to power efficient and sustainable agricultural water pumping.
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion provides a sustainable renewable energy source by converting organic waste into biogas, significantly reducing reliance on carbon-intensive fossil fuels.
Agrophotovoltaics
Agrophotovoltaics combines solar energy generation with agricultural production, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels by increasing land use efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.
Life cycle assessment (LCA)
Life cycle assessment (LCA) reveals renewable energy sources typically generate lower greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impacts throughout their entire lifespan compared to fossil fuels.
Sustainable mechanization
Sustainable mechanization in renewable energy systems significantly reduces carbon emissions and operational costs compared to fossil fuel-based machinery.
Biomass gasification
Biomass gasification converts organic materials into clean syngas, offering a renewable energy alternative that reduces dependency on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy yield efficiency
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind achieve higher energy yield efficiency by converting a larger percentage of natural resources into usable power compared to the diminishing returns and high carbon emissions of fossil fuels.
Fossil fuel displacement
Renewable energy deployment accelerates fossil fuel displacement by reducing carbon emissions, lowering operational costs, and enhancing energy security worldwide.
renewable energy vs fossil fuels Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com