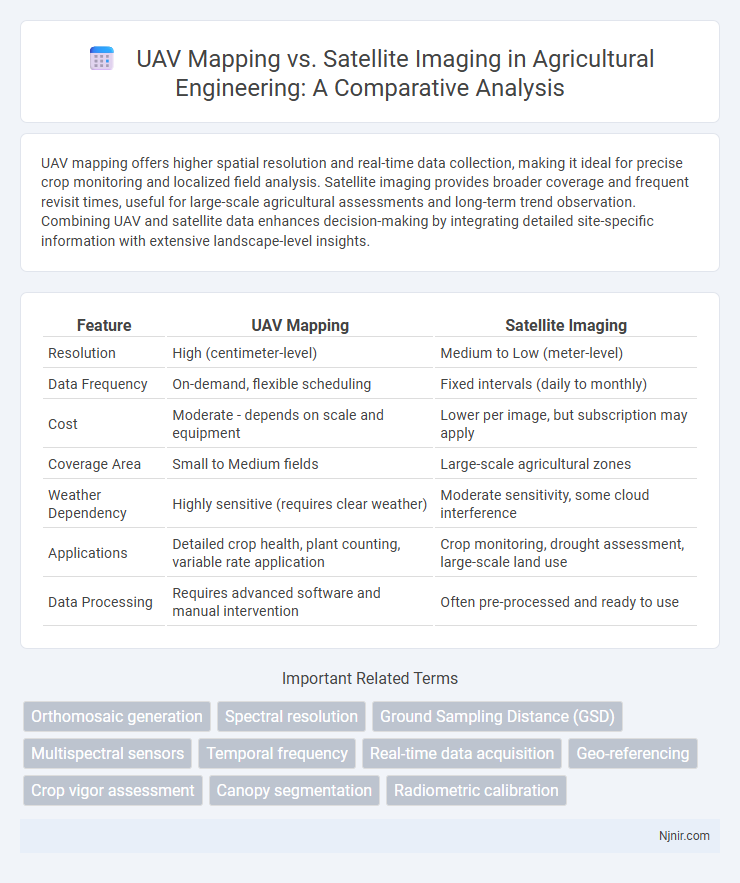
UAV mapping offers higher spatial resolution and real-time data collection, making it ideal for precise crop monitoring and localized field analysis. Satellite imaging provides broader coverage and frequent revisit times, useful for large-scale agricultural assessments and long-term trend observation. Combining UAV and satellite data enhances decision-making by integrating detailed site-specific information with extensive landscape-level insights.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UAV Mapping | Satellite Imaging |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | High (centimeter-level) | Medium to Low (meter-level) |
| Data Frequency | On-demand, flexible scheduling | Fixed intervals (daily to monthly) |
| Cost | Moderate - depends on scale and equipment | Lower per image, but subscription may apply |
| Coverage Area | Small to Medium fields | Large-scale agricultural zones |
| Weather Dependency | Highly sensitive (requires clear weather) | Moderate sensitivity, some cloud interference |
| Applications | Detailed crop health, plant counting, variable rate application | Crop monitoring, drought assessment, large-scale land use |
| Data Processing | Requires advanced software and manual intervention | Often pre-processed and ready to use |
Introduction to Aerial Imaging Technologies in Agriculture
UAV mapping delivers high-resolution, real-time data critical for precision agriculture, enabling detailed crop health monitoring and variable rate application. Satellite imaging provides broader spatial coverage with multispectral and temporal data ideal for large-scale agricultural trends and seasonal analysis. Combining UAV and satellite technologies enhances farm management by integrating localized insight with regional context, optimizing yield and resource use efficiency.
Fundamentals of UAV Mapping
UAV mapping utilizes unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors to capture detailed, low-altitude imagery, enabling precise geospatial data collection. This technology allows for flexible flight paths, rapid revisit times, and improved spatial resolution compared to satellite imaging, which relies on fixed orbital positions and often lower-resolution multispectral data. Key fundamentals of UAV mapping include photogrammetry, real-time kinematic (RTK) GPS integration, and advanced data processing techniques to generate accurate orthomosaic maps and 3D models.
Overview of Satellite Imaging for Agriculture
Satellite imaging for agriculture offers extensive, high-resolution data capturing vast areas consistently over time, enabling precise monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and water usage. These images utilize multispectral and hyperspectral sensors to detect variations in vegetation indices such as NDVI, allowing early detection of stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies. Satellite platforms like Sentinel-2 and Landsat provide free, frequent, and globally accessible data critical for large-scale agricultural planning and management.
Spatial Resolution: UAV vs Satellite
UAV mapping offers significantly higher spatial resolution compared to satellite imaging, with UAVs capable of capturing ground details as fine as a few centimeters per pixel, whereas typical satellite images range from 30 centimeters to several meters per pixel. This superior resolution makes UAVs ideal for detailed, localized surveying tasks such as precision agriculture, construction monitoring, and environmental assessments. Satellite imaging provides broader spatial coverage but with less granular detail, making it more suitable for large-scale regional analysis and global monitoring.
Temporal Resolution and Data Frequency
UAV mapping offers significantly higher temporal resolution and data frequency compared to satellite imaging, enabling more frequent data collection with captures possible daily or even multiple times per day. Satellite imaging often has fixed revisit intervals ranging from several days to weeks, limiting timely updates in dynamic environments. This advantage makes UAVs ideal for applications requiring rapid monitoring and real-time decision-making such as precision agriculture, disaster response, and construction site management.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
UAV mapping offers significantly lower operational costs compared to satellite imaging, especially for small to medium-sized areas, due to reduced equipment expenses and on-demand data collection. Satellite imaging incurs higher costs linked to licensing fees, less flexible revisit times, and limited resolution for detailed surveys. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors UAV mapping when precision, frequent updates, and budget constraints are critical factors in geospatial data acquisition.
Accessibility and Operational Flexibility
UAV mapping offers superior accessibility by capturing high-resolution data in hard-to-reach or restricted areas without relying on satellite availability or weather conditions. Its operational flexibility enables real-time adjustments to flight paths and data collection schedules, unlike satellite imaging which follows fixed orbital passes and predetermined intervals. This adaptability makes UAVs ideal for detailed, localized surveys requiring frequent updates and immediate data acquisition.
Data Processing and Management
UAV mapping offers high-resolution, customizable data collected at lower altitudes, enabling faster processing with specialized software tailored for photogrammetry and 3D modeling. Satellite imaging involves processing large-scale datasets with advanced geospatial tools designed for multispectral and temporal analysis, often requiring significant computational resources and cloud-based management. Efficient data management for UAV relies on localized storage and flexible export formats, whereas satellite data demands integration with global datasets and standardized formats for broad accessibility and long-term archiving.
Practical Applications in Precision Agriculture
UAV mapping offers higher-resolution and real-time data collection for precision agriculture, enabling detailed crop health monitoring, stress detection, and variable rate application of inputs. Satellite imaging provides broader coverage with frequent revisit times suitable for large-scale field analysis but often lacks the spatial resolution needed for localized decision-making. Combining UAV and satellite data enhances crop yield predictions, irrigation management, and disease detection, optimizing farm productivity and resource use.
Choosing the Right Solution: UAV or Satellite Imaging?
Choosing between UAV mapping and satellite imaging depends on project scale, resolution needs, and budget constraints. UAV mapping offers higher spatial resolution and flexibility for localized areas, enabling detailed topographic data and rapid deployment. Satellite imaging provides broad coverage and frequent revisit times, making it ideal for large-scale environmental monitoring and inaccessible regions.
Orthomosaic generation
UAV mapping produces higher-resolution orthomosaic images with greater spatial accuracy and flexibility than satellite imaging, making it ideal for detailed surface analysis and localized geographic information system (GIS) applications.
Spectral resolution
UAV mapping offers higher spectral resolution than satellite imaging by capturing fine-grained multispectral and hyperspectral data tailored for localized environmental and agricultural analysis.
Ground Sampling Distance (GSD)
UAV mapping offers superior Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) with centimeter-level resolution compared to satellite imaging's meter-level GSD, enabling more detailed and precise surface data collection.
Multispectral sensors
Multispectral sensors on UAVs provide higher spatial resolution and flexible flight paths for detailed vegetation analysis compared to satellite imaging, which offers broader coverage but lower temporal and spatial resolution.
Temporal frequency
UAV mapping offers higher temporal frequency than satellite imaging, enabling more frequent and flexible data collection for time-sensitive monitoring.
Real-time data acquisition
UAV mapping provides superior real-time data acquisition compared to satellite imaging due to its ability to capture high-resolution, on-demand images with minimal latency and flexible deployment.
Geo-referencing
UAV mapping offers higher precision geo-referencing and real-time data capture compared to satellite imaging's broader coverage but lower spatial resolution.
Crop vigor assessment
UAV mapping provides higher-resolution imagery and more frequent data collection than satellite imaging for precise crop vigor assessment, enabling timely detection of stress and optimized field management.
Canopy segmentation
UAV mapping provides higher-resolution imagery and more accurate canopy segmentation compared to satellite imaging, enabling precise vegetation analysis and better forest management.
Radiometric calibration
UAV mapping delivers superior radiometric calibration accuracy compared to satellite imaging by enabling precise, ground-level sensor adjustments and real-time reflectance measurements.
UAV mapping vs Satellite imaging Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com