Delta and Wye connections differ in their configuration and application in electrical systems, with Delta connecting three phases in a triangle, allowing higher power delivery and balanced loads without a neutral wire. Wye connections link phases to a common neutral point, enabling easier grounding and providing multiple voltage levels for different loads. The choice between Delta and Wye impacts system stability, fault tolerance, and efficiency in power distribution networks.
Table of Comparison
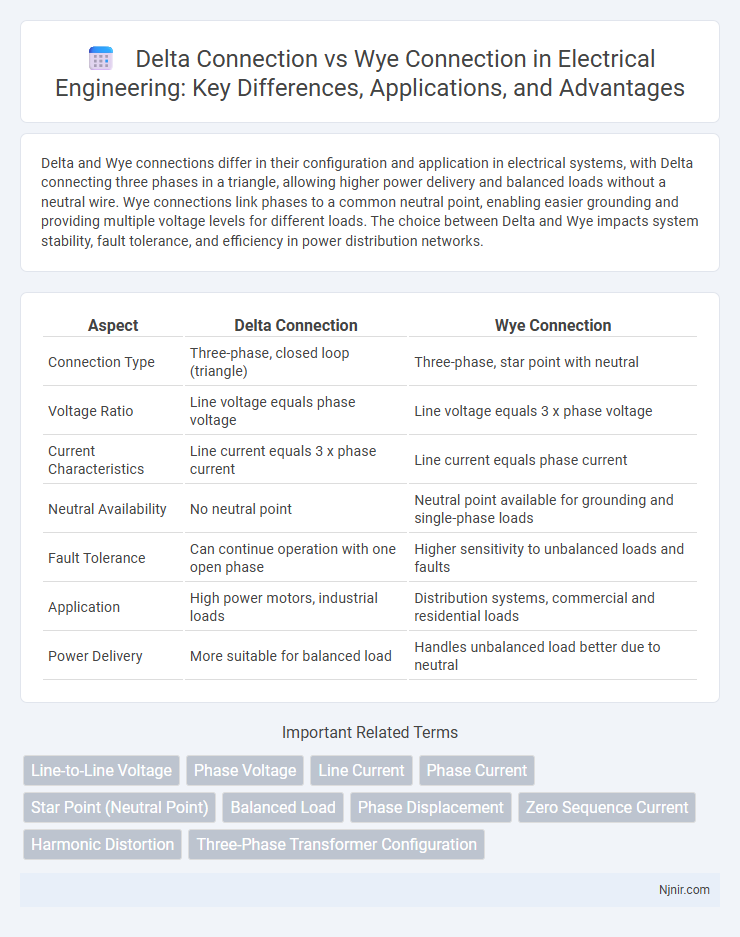
| Aspect | Delta Connection | Wye Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Three-phase, closed loop (triangle) | Three-phase, star point with neutral |
| Voltage Ratio | Line voltage equals phase voltage | Line voltage equals 3 x phase voltage |
| Current Characteristics | Line current equals 3 x phase current | Line current equals phase current |
| Neutral Availability | No neutral point | Neutral point available for grounding and single-phase loads |
| Fault Tolerance | Can continue operation with one open phase | Higher sensitivity to unbalanced loads and faults |
| Application | High power motors, industrial loads | Distribution systems, commercial and residential loads |
| Power Delivery | More suitable for balanced load | Handles unbalanced load better due to neutral |
Introduction to Delta and Wye Connections
Delta and Wye connections are fundamental configurations in three-phase electrical systems used to distribute power efficiently. The Delta connection links three windings end-to-end forming a closed loop, enabling phase voltages to equal line voltages and offering high fault tolerance. The Wye connection connects each winding to a common neutral point, producing line voltages that are 3 times the phase voltages, which provides a stable neutral for grounding and load balancing.
Fundamental Differences Between Delta and Wye
Delta connection features a triangular circuit where each phase connects end-to-end, providing line voltage equal to phase voltage and line current equal to 3 times phase current. Wye connection has all three phases connected to a common neutral point, resulting in line voltage being 3 times phase voltage and line current equal to phase current. The fundamental difference lies in voltage and current relationships as well as neutral availability, influencing their application in power distribution systems.
Construction and Wiring Diagrams
Delta connection features three windings connected end-to-end forming a closed loop, allowing current to flow through each winding in a triangular configuration, while the Wye connection has windings connected at a common neutral point, creating a star shape with each phase connected to this neutral. In wiring diagrams, Delta typically shows three terminals connected in a triangle, suitable for three-phase loads without a neutral wire, whereas Wye diagrams include a neutral terminal, allowing for both line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltage measurements. Construction differences impact phase voltage and current distribution, with Delta handling higher line currents and Wye providing a neutral for grounding and balanced load conditions.
Voltage and Current Characteristics
Delta connection features phase voltage equal to line voltage while phase current is lower by a factor of 3, optimizing for higher current loads with lower voltage drop. Wye connection has phase voltage reduced by 3 compared to line voltage, with phase current equal to line current, supporting efficient voltage distribution in balanced loads. Voltage imbalance and harmonic distortion behaviors differ significantly, impacting power quality and transformer efficiency in each configuration.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Delta connections are commonly used in high-power industrial applications due to their ability to provide a stable three-phase supply with no neutral point, making them ideal for heavy machinery and motor loads. Wye connections are preferred in distribution systems where a neutral is necessary to supply single-phase loads and ensure stable voltage levels across residential and commercial environments. Both configurations optimize electrical system performance by matching specific load requirements and enhancing fault tolerance in power transmission.
Advantages of Delta Connection
Delta connection offers advantages such as providing a higher starting torque for motors and better handling of heavy loads in industrial applications. It allows for continuous operation even if one phase is lost, enhancing system reliability and reducing downtime. The configuration also supports balanced power distribution and efficient transmission of electricity in three-phase systems.
Advantages of Wye Connection
Wye connection offers a neutral point, enabling stable voltage levels and the ability to provide both single-phase and three-phase power suitable for diverse loads. It improves safety and fault detection by allowing grounding at the neutral, reducing the risk of overvoltages during unbalanced conditions. This configuration enhances flexibility and efficiency in power distribution systems, particularly in residential and commercial applications.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Connection
Delta connection faces challenges with unbalanced load conditions that can cause circulating currents and increased losses, limiting efficiency in uneven power distribution. Wye connection struggles with neutral conductor issues under high load, risking voltage instability and harmonic distortion. Both configurations require careful management to mitigate their inherent limitations in industrial and power distribution systems.
Impact on Power Distribution and Efficiency
Delta connection provides a balanced load and allows for higher power transmission with lower line current, enhancing efficiency in three-phase systems. Wye connection offers a neutral point, enabling stable voltage levels and safer fault management, which improves reliability in power distribution. The choice between Delta and Wye impacts power quality, system protection, and overall distribution efficiency depending on load type and application.
Choosing Between Delta and Wye for Specific Applications
Choosing between Delta and Wye connections depends on the specific requirements of the electrical system. Delta connections are preferred for high starting torque applications and systems requiring a stable, balanced load, often used in industrial motors and heavy machinery. Wye connections offer better neutral grounding, safer voltage levels, and are ideal for power distribution systems requiring multiple voltage outputs and enhanced fault protection.
Line-to-Line Voltage
Delta connection provides a line-to-line voltage equal to the phase voltage, while Wye connection offers a line-to-line voltage equal to the phase voltage multiplied by 3.
Phase Voltage
In Delta connection, the phase voltage equals the line voltage, while in Wye connection, the phase voltage is the line voltage divided by the square root of three.
Line Current
In a Delta connection, the line current is 3 times the phase current, whereas in a Wye connection, the line current equals the phase current.
Phase Current
In Delta connection, the phase current is equal to the line current divided by 3, whereas in Wye connection, the phase current is equal to the line current.
Star Point (Neutral Point)
The Wye connection features a star point (neutral point) that provides a common return path and allows for stable voltage distribution, while the Delta connection lacks a star point, resulting in no neutral and typically no neutral-based voltage reference.
Balanced Load
Delta connection provides a balanced load with equal phase voltages and currents, minimizing neutral current, while Wye connection offers a neutral point allowing for easier load balancing and fault detection in three-phase systems.
Phase Displacement
Delta connection exhibits 0deg phase displacement between line and phase voltages, whereas Wye connection features a 30deg phase displacement affecting load balancing and power distribution.
Zero Sequence Current
Wye connections allow zero sequence currents to flow through the neutral, facilitating ground fault detection, whereas delta connections block zero sequence currents, limiting ground fault current paths.
Harmonic Distortion
Wye connections typically exhibit lower harmonic distortion due to neutral grounding that reduces triplen harmonics, whereas Delta connections can circulate triplen harmonics within the closed delta, potentially increasing overall harmonic distortion levels.
Three-Phase Transformer Configuration
Delta connection in three-phase transformers provides a closed loop for current flow with no neutral, offering higher phase voltages and better fault tolerance, while Wye connection offers a neutral point for grounding and enables phase voltage to be lower than line voltage, enhancing safety and versatility.
Delta connection vs Wye connection Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com