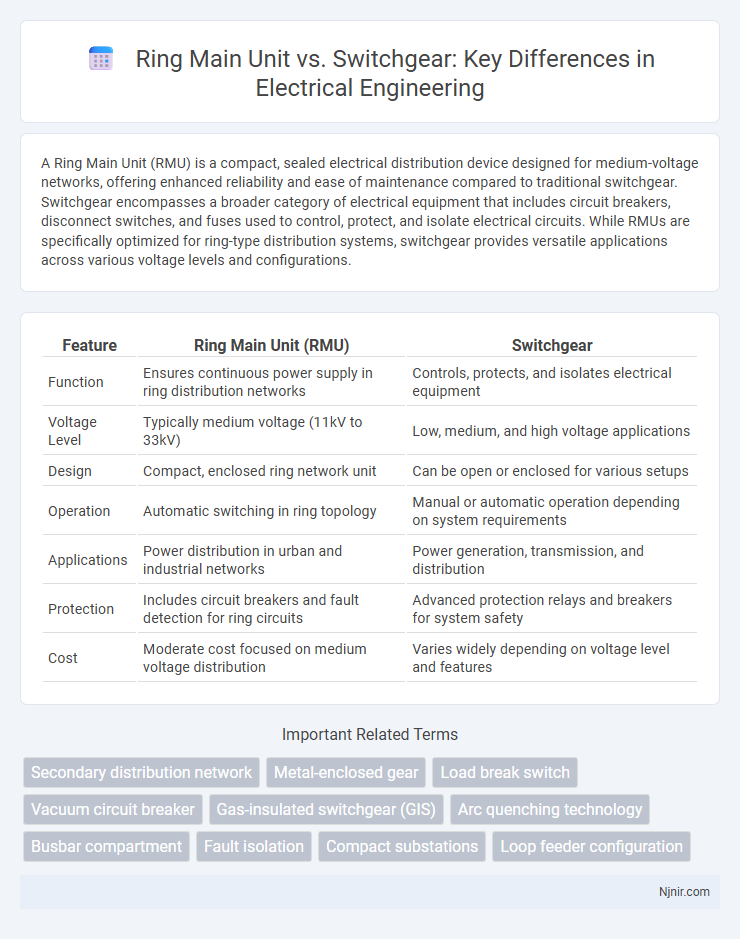
A Ring Main Unit (RMU) is a compact, sealed electrical distribution device designed for medium-voltage networks, offering enhanced reliability and ease of maintenance compared to traditional switchgear. Switchgear encompasses a broader category of electrical equipment that includes circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and fuses used to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits. While RMUs are specifically optimized for ring-type distribution systems, switchgear provides versatile applications across various voltage levels and configurations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ring Main Unit (RMU) | Switchgear |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Ensures continuous power supply in ring distribution networks | Controls, protects, and isolates electrical equipment |
| Voltage Level | Typically medium voltage (11kV to 33kV) | Low, medium, and high voltage applications |
| Design | Compact, enclosed ring network unit | Can be open or enclosed for various setups |
| Operation | Automatic switching in ring topology | Manual or automatic operation depending on system requirements |
| Applications | Power distribution in urban and industrial networks | Power generation, transmission, and distribution |
| Protection | Includes circuit breakers and fault detection for ring circuits | Advanced protection relays and breakers for system safety |
| Cost | Moderate cost focused on medium voltage distribution | Varies widely depending on voltage level and features |
Introduction to Ring Main Unit (RMU) and Switchgear
Ring Main Unit (RMU) is a compact, factory-assembled metal-enclosed switchgear designed for medium-voltage power distribution networks, ensuring reliable power supply and fault isolation. Switchgear encompasses a broad range of electrical devices, including circuit breakers, switches, and fuses, used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment in both low and high voltage systems. RMUs optimize network reliability with ring topology connections, while switchgear provides versatile solutions for managing electrical power flow and safety across various applications.
Structural Differences Between RMU and Switchgear
Ring Main Units (RMUs) are compact, ring-configured switchgear designed for medium voltage distribution networks featuring load break switches and sealed gas-insulated enclosures, optimizing space and enhancing safety. Switchgear encompasses a broader range of equipment installations, often larger and more modular, with components like circuit breakers, isolators, and relays used for both medium and high voltage applications. Structurally, RMUs are prefabricated, sealed units intended for looped systems, while switchgear setups include diverse configurations adaptable to various network demands and voltages.
Functional Comparison: RMU vs Switchgear
Ring Main Units (RMUs) provide compact, sealed, and modular solutions primarily for secondary distribution, enabling reliable load switching and fault isolation in medium-voltage networks. Switchgear, encompassing circuit breakers, fuses, and disconnectors, offers broader functionality across various voltage levels with enhanced protection, control, and switching capabilities. RMUs excel in ring network configurations for urban and industrial applications, while switchgear delivers versatile performance for complex power systems requiring detailed protection and automation.
Applications in Power Distribution Networks
Ring main units (RMUs) are compact, sealed devices primarily used for medium-voltage power distribution in urban and suburban networks, offering reliable load switching and fault isolation in confined spaces. Switchgear encompasses a broader range of electrical devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, and disconnectors, designed for protection, control, and isolation across low, medium, and high-voltage power systems. RMUs are often deployed in ring network configurations for enhanced continuity of supply, whereas switchgear installations are critical for complex industrial power systems requiring flexible operation and comprehensive fault management.
Safety Features: RMU vs Switchgear
Ring Main Units (RMUs) incorporate advanced safety features such as fully enclosed metal-clad designs and vacuum or gas-insulated interrupters that minimize arc flash hazards and ensure operator protection. Switchgear offers robust safety mechanisms including high-voltage insulation, interlocking systems, and gas or oil insulation to prevent accidental contact and electrical faults. Both RMUs and switchgear prioritize personnel safety and equipment reliability through strict compliance with international safety standards like IEC 62271.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Ring main units (RMUs) offer compact designs that simplify installation in confined spaces, reducing the need for extensive civil works compared to traditional switchgear. RMUs typically feature gas-insulated or vacuum-interruption technology, requiring less frequent maintenance and enabling safer inspections without power shutdowns. In contrast, conventional switchgear involves larger footprints with air-insulated components, leading to more complex installation and higher operational maintenance due to the need for regular cleaning, oil checks, and component replacements.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ring main units (RMUs) typically offer lower initial installation costs compared to traditional switchgear due to their compact design and modular components, making them economically favorable for urban distribution networks. Maintenance expenses of RMUs are generally reduced because of sealed, minimally exposed parts that lower downtime and servicing frequency, enhancing long-term cost efficiency. However, switchgear provides greater scalability and higher capacity options, which may justify higher capital investment in large industrial or utility-scale projects where advanced control and protection functions are required.
Advantages and Limitations of RMU
Ring Main Units (RMUs) offer compact design and high reliability for medium voltage distribution networks, providing efficient fault isolation and minimized outage times due to their ring configuration. RMUs are advantageous in urban and confined spaces where installation and maintenance space is limited, featuring sealed and gas-insulated components that reduce environmental exposure and lower maintenance requirements. However, RMUs typically have lower interrupting capacity and fewer functionality options compared to traditional switchgear, limiting their use in more complex or higher voltage systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Switchgear
Switchgear offers high reliability and safety in electrical distribution by enabling rapid fault isolation and minimizing downtime, making it crucial for managing medium to high-voltage systems. It supports complex configurations and automation, enhancing operational flexibility and protection coordination in modern power networks. Limitations include higher initial costs, larger physical footprint, and increased maintenance requirements compared to simpler devices like ring main units.
Choosing Between RMU and Switchgear: Key Considerations
Choosing between Ring Main Units (RMUs) and switchgear hinges on factors such as system voltage, load capacity, and application environment. RMUs excel in medium-voltage distribution networks with compact space requirements and offer enhanced reliability for ring-type configurations. Switchgear provides versatile protection and control for high-voltage systems and is preferred in complex industrial or utility substations requiring robust fault isolation and switching capabilities.
Secondary distribution network
Ring main units offer compact, reliable switchgear solutions optimized for secondary distribution networks, enhancing fault isolation and network flexibility.
Metal-enclosed gear
Metal-enclosed switchgear offers enhanced safety, superior insulation, and easier maintenance compared to ring main units, making it ideal for complex electrical distribution systems requiring high reliability and fault isolation.
Load break switch
A load break switch in a ring main unit enables safe load interruption and sectionalizing in medium-voltage networks, offering enhanced operational flexibility compared to conventional switchgear.
Vacuum circuit breaker
Vacuum circuit breakers in ring main units provide enhanced arc quenching and compact design compared to traditional switchgear, improving reliability and reducing maintenance in medium-voltage power distribution systems.
Gas-insulated switchgear (GIS)
Gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) offers a compact, reliable, and low-maintenance alternative to traditional ring main units by using SF6 gas for insulation, enabling higher voltage applications and enhanced safety in confined spaces.
Arc quenching technology
Ring main units predominantly use air or vacuum arc quenching technology for enhanced safety and reliability, while switchgear often employs SF6 gas or vacuum interrupters to achieve superior arc suppression and insulation performance.
Busbar compartment
The busbar compartment in Ring Main Units (RMUs) is typically more compact and modular compared to the larger, more complex busbar arrangements found in traditional switchgear, enhancing ease of installation and maintenance.
Fault isolation
Ring main units provide faster and more localized fault isolation compared to traditional switchgear by enabling sectionalizing switches to isolate faults without disrupting the entire network.
Compact substations
Compact substations integrating Ring Main Units (RMUs) offer enhanced reliability, space efficiency, and simplified maintenance compared to traditional switchgear systems.
Loop feeder configuration
Ring main units provide compact and reliable loop feeder configurations with integrated sectionalizing and protection functions, while traditional switchgear offers more extensive control and fault isolation options but requires larger installation space.
Ring main unit vs Switchgear Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com