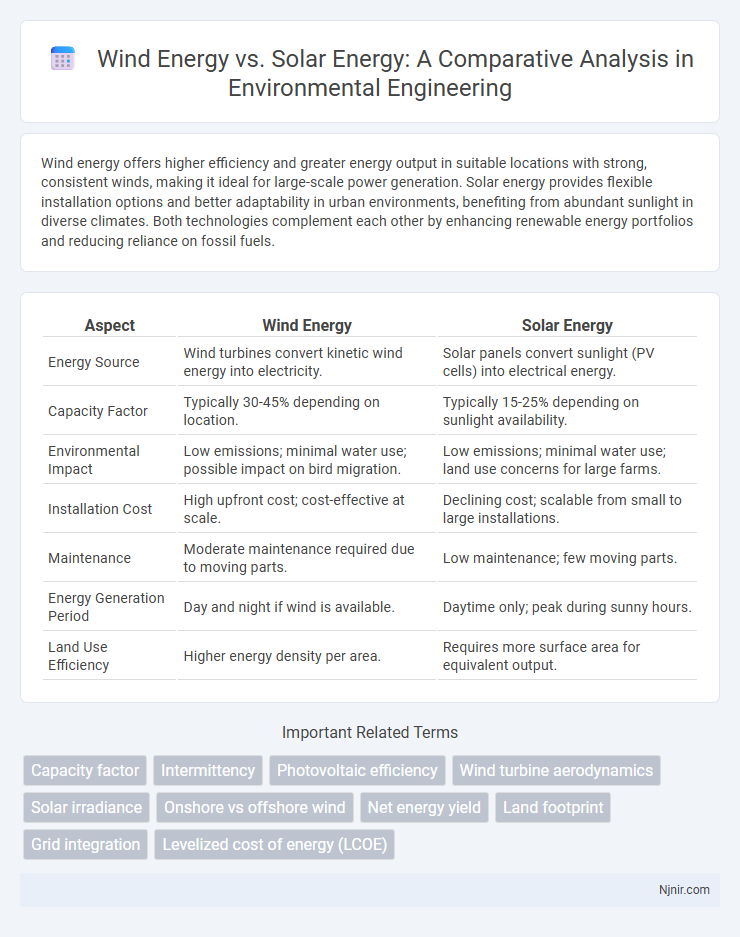
Wind energy offers higher efficiency and greater energy output in suitable locations with strong, consistent winds, making it ideal for large-scale power generation. Solar energy provides flexible installation options and better adaptability in urban environments, benefiting from abundant sunlight in diverse climates. Both technologies complement each other by enhancing renewable energy portfolios and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wind Energy | Solar Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Wind turbines convert kinetic wind energy into electricity. | Solar panels convert sunlight (PV cells) into electrical energy. |
| Capacity Factor | Typically 30-45% depending on location. | Typically 15-25% depending on sunlight availability. |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions; minimal water use; possible impact on bird migration. | Low emissions; minimal water use; land use concerns for large farms. |
| Installation Cost | High upfront cost; cost-effective at scale. | Declining cost; scalable from small to large installations. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance required due to moving parts. | Low maintenance; few moving parts. |
| Energy Generation Period | Day and night if wind is available. | Daytime only; peak during sunny hours. |
| Land Use Efficiency | Higher energy density per area. | Requires more surface area for equivalent output. |
Introduction to Renewable Energy Solutions
Wind energy and solar energy represent two of the most prominent renewable energy solutions, harnessing natural resources to generate electricity with minimal environmental impact. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from airflow into electrical power, while solar panels use photovoltaic cells to transform sunlight into usable energy. Both technologies play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting sustainable energy transitions worldwide.
Wind Energy: Technology and Applications
Wind energy harnesses aerodynamic forces generated by large rotor blades connected to turbines, converting kinetic wind power into electricity through advanced gearboxes and generators. Modern wind turbines incorporate cutting-edge materials and control systems to optimize blade pitch and yaw, maximizing energy capture even at variable wind speeds. Applications range from large-scale offshore wind farms providing substantial grid power to small-scale turbines for remote or residential use, demonstrating its versatility and growing role in sustainable energy portfolios.
Solar Energy: Technology and Applications
Solar energy harnesses sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels and concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, converting solar radiation into electricity with increasing efficiency rates above 22%. Its applications span residential rooftop installations, large-scale solar farms, and off-grid solar solutions that provide reliable power in remote areas. Advances in battery storage technology and smart grid integration further enhance solar energy's viability as a clean, sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels and complement wind energy in hybrid renewable systems.
Efficiency Comparison: Wind vs Solar
Wind energy generally achieves higher efficiency rates, often converting 35-45% of wind power into electricity, compared to solar panels which typically convert 15-22% of sunlight into electrical energy. Wind turbines can operate effectively day and night, especially in locations with consistent wind speeds above 6 meters per second, whereas solar efficiency significantly decreases during cloudy conditions and nighttime. The capacity factor for wind energy averages around 30-40%, surpassing solar's typical 15-25%, making wind power more efficient for continuous energy generation in suitable environments.
Environmental Impact of Wind and Solar Power
Wind energy generates electricity with zero greenhouse gas emissions during operation, making it highly beneficial for reducing air pollution and combating climate change. Solar power also produces clean energy with minimal emissions, but manufacturing solar panels involves resource extraction and energy-intensive processes that contribute to environmental impacts. Both technologies require land use considerations, with wind turbines potentially affecting bird and bat populations, while solar farms may lead to habitat disruption.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Wind energy installation costs average around $1,300 to $2,200 per kilowatt, while solar energy typically ranges from $1,000 to $3,000 per kilowatt, depending on system size and location. Maintenance expenses for wind turbines generally include rotor blade inspections and gearbox servicing, often costing between $0.01 and $0.02 per kilowatt-hour, whereas solar panel maintenance is minimal, primarily limited to periodic cleaning and inverter replacement, averaging about $10 to $20 per kilowatt annually. Despite higher upfront costs, wind energy offers lower operational expenses over time, while solar energy benefits from simpler maintenance and declining panel prices.
Geographic Suitability and Resource Availability
Wind energy thrives in regions with consistent, strong winds such as coastal areas, open plains, and hilltops, while solar energy excels in locations with high solar irradiance, particularly arid and semi-arid regions with minimal cloud cover. Resource availability for wind power depends on wind speed patterns that can vary significantly by season and time of day, whereas solar energy generation aligns more predictably with daily sunlight exposure. Geographic suitability also influences infrastructure costs and energy output efficiency, making wind energy favorable in offshore or rural areas and solar energy optimal in sun-rich deserts and urban rooftops.
Energy Storage and Grid Integration
Wind energy storage often relies on battery systems and pumped hydro for managing its variable output, allowing excess power to be stored during high production periods. Solar energy benefits from rapid advancements in lithium-ion batteries and grid-tied inverters, ensuring efficient storage and seamless integration during peak sunlight hours. Both renewable sources require smart grid technologies and demand response strategies to optimize grid stability and energy reliability.
Sustainability and Future Prospects
Wind energy and solar energy both offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, with wind turbines converting kinetic energy from air currents while solar panels harness sunlight through photovoltaic cells. Wind power generally provides higher energy yields and more consistent output in suitable locations, yet solar energy benefits from decreasing costs and widespread applicability, including urban environments. Future prospects for both technologies involve integration with smart grids and energy storage solutions, promoting increased efficiency and reliability in renewable energy systems.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Renewable Source
Wind energy offers higher efficiency in areas with consistent wind patterns, generating more power per installed capacity than solar energy. Solar energy provides versatility and accessibility, especially in urban and residential settings where sunlight is abundant. Selecting the optimal renewable source depends on geographic location, infrastructure feasibility, and specific energy demand profiles.
Capacity factor
Wind energy typically has a higher capacity factor, averaging 35-45%, compared to solar energy's 15-25%, making wind more efficient at converting available resources into consistent electricity generation.
Intermittency
Wind energy's intermittency varies hourly, while solar energy's intermittency is primarily limited to daylight hours and weather conditions.
Photovoltaic efficiency
Solar energy's photovoltaic efficiency typically ranges between 15-22%, offering a direct conversion of sunlight to electricity faster than wind turbines convert kinetic air energy into electrical power.
Wind turbine aerodynamics
Wind turbine aerodynamics optimize blade design to maximize lift and minimize drag, enhancing wind energy efficiency compared to solar energy's reliance on sunlight intensity and panel surface area.
Solar irradiance
Solar energy harnesses higher efficiency in regions with strong solar irradiance, outperforming wind energy in consistent power generation during daylight hours.
Onshore vs offshore wind
Onshore wind energy offers cost-effective installation and maintenance, while offshore wind delivers higher and more consistent power output due to stronger, steadier sea winds near coastal areas.
Net energy yield
Wind energy typically offers a higher net energy yield than solar energy due to its greater efficiency and capacity factor.
Land footprint
Wind energy requires significantly less land footprint per megawatt generated compared to solar energy, making it more space-efficient for large-scale renewable power production.
Grid integration
Wind energy offers higher grid integration flexibility due to its consistent generation patterns and advanced forecasting, while solar energy requires sophisticated storage solutions to manage its variability and daytime-dependent output.
Levelized cost of energy (LCOE)
Wind energy typically offers a lower Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) than solar energy, averaging around $30 to $60 per megawatt-hour compared to solar's $40 to $70 per megawatt-hour, depending on geographic location and technology.
wind energy vs solar energy Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com