Blockchain traceability in agricultural engineering offers enhanced transparency and tamper-proof documentation compared to traditional paper record-keeping. This technology enables real-time tracking of crops and livestock, facilitating efficient supply chain management and reducing fraud. By integrating blockchain systems, farmers and stakeholders ensure data accuracy, improve food safety, and streamline compliance with regulatory standards.
Table of Comparison
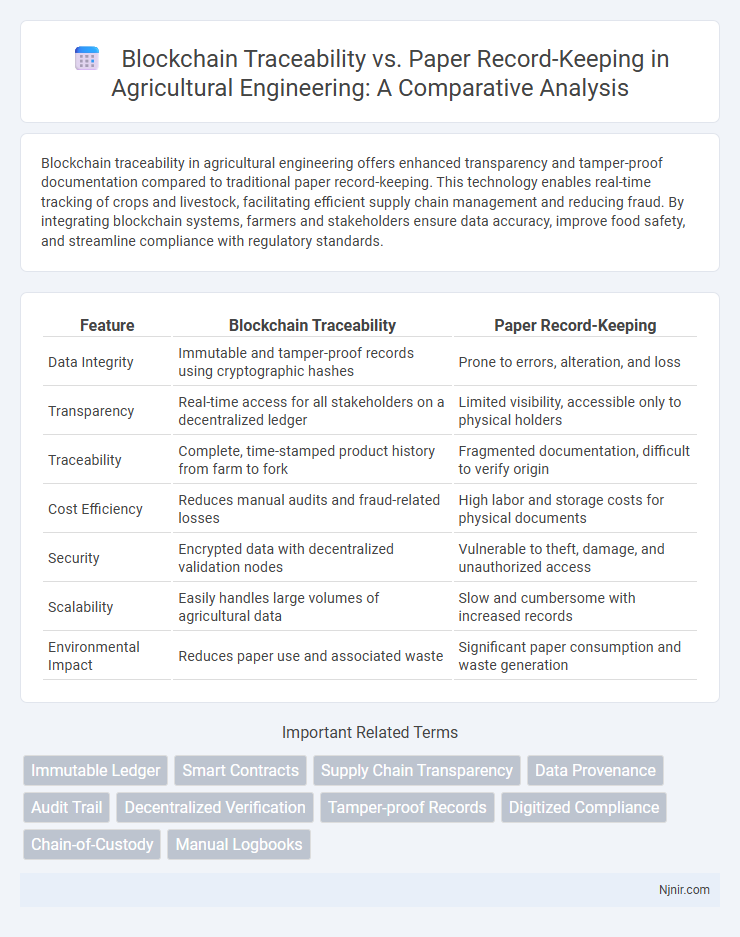
| Feature | Blockchain Traceability | Paper Record-Keeping |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Immutable and tamper-proof records using cryptographic hashes | Prone to errors, alteration, and loss |
| Transparency | Real-time access for all stakeholders on a decentralized ledger | Limited visibility, accessible only to physical holders |
| Traceability | Complete, time-stamped product history from farm to fork | Fragmented documentation, difficult to verify origin |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces manual audits and fraud-related losses | High labor and storage costs for physical documents |
| Security | Encrypted data with decentralized validation nodes | Vulnerable to theft, damage, and unauthorized access |
| Scalability | Easily handles large volumes of agricultural data | Slow and cumbersome with increased records |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces paper use and associated waste | Significant paper consumption and waste generation |
Introduction to Agricultural Traceability Systems
Agricultural traceability systems leverage blockchain technology to provide immutable and transparent records of crop origin, production processes, and distribution pathways, significantly enhancing food safety and quality assurance. Unlike traditional paper record-keeping, blockchain enables real-time data verification, reduces the risk of fraud, and streamlines regulatory compliance with tamper-proof digital ledgers. These advancements improve supply chain efficiency and consumer trust by ensuring accurate tracking of agricultural products from farm to table.
Overview of Blockchain Technology in Agriculture
Blockchain technology in agriculture enhances traceability by creating immutable, transparent digital records that replace traditional paper-based systems prone to errors and fraud. It enables real-time tracking of agricultural products from farm to consumer, improving supply chain transparency, food safety, and compliance with regulations. By integrating IoT devices and smart contracts, blockchain automates data capture and verification, reducing manual paperwork and increasing operational efficiency.
Traditional Paper-Based Record-Keeping Methods
Traditional paper-based record-keeping methods rely heavily on physical documents that are prone to loss, damage, and tampering, reducing the reliability of traceability in supply chains and transactions. These manual processes often result in slower data retrieval, limited transparency, and increased chances of human error, complicating audits and compliance verification. In contrast, blockchain traceability provides an immutable and decentralized ledger that enhances data integrity and real-time access, overcoming many inherent limitations of paper records.
Accuracy and Reliability: Blockchain vs Paper Records
Blockchain traceability ensures higher accuracy and reliability compared to traditional paper record-keeping by providing immutable, time-stamped digital entries that cannot be altered or deleted. The decentralized validation process reduces human error and fraud, enhancing data integrity across the supply chain. In contrast, paper records are prone to damage, loss, and manual inaccuracies, undermining trust and transparency in record management.
Data Security and Fraud Prevention
Blockchain traceability offers enhanced data security through cryptographic encryption and decentralized ledger technology, making records tamper-resistant and easily auditable compared to traditional paper record-keeping. Unlike paper documents vulnerable to physical damage, loss, or forgery, blockchain ensures immutable transaction histories and real-time verification, significantly reducing fraud risks. This advanced security framework empowers organizations to achieve transparent, accountable supply chain management with minimized potential for data manipulation or unauthorized access.
Real-Time Accessibility of Traceability Information
Blockchain traceability ensures real-time accessibility of supply chain data, allowing stakeholders to instantly verify product origin, status, and movement with immutable and transparent records. In contrast, paper record-keeping relies on manual updates and physical document transfers, causing delays and increasing the risk of errors or data loss. Real-time blockchain access enhances efficiency, reduces fraud, and supports faster decision-making in supply chain management.
Cost and Resource Implications
Blockchain traceability significantly reduces costs associated with manual data entry, storage, and reconciliation compared to traditional paper record-keeping, which often incurs ongoing expenses for physical storage and labor-intensive audits. Digital ledgers on blockchain enhance resource efficiency by automating verification processes and minimizing errors, leading to lower administrative overhead and faster transaction processing. While initial blockchain implementation may require upfront technology investment, long-term savings and improved accuracy outweigh the ongoing costs typical of maintaining extensive paper records.
Regulatory Compliance and Auditability
Blockchain traceability significantly enhances regulatory compliance by providing an immutable and transparent ledger that automatically records every transaction, reducing the risk of data tampering and ensuring accurate audit trails. Unlike traditional paper record-keeping, which is prone to loss, fraud, and manual errors, blockchain enables real-time verification and streamlined audits for regulators and stakeholders. This technology supports adherence to stringent regulations such as GDPR, SOX, and FDA guidelines by offering secure, decentralized data storage with easy access for compliance checks.
Adoption Challenges and Practical Considerations
Blockchain traceability faces adoption challenges such as high implementation costs, technological complexity, and the need for standardized protocols across industry stakeholders. Paper record-keeping remains prevalent due to its familiarity, low cost, and ease of use, but it suffers from risks of errors, fraud, and inefficiencies in data retrieval. Practical considerations include data privacy concerns, integration with existing systems, and the requirement for training personnel to manage blockchain platforms effectively.
Future Trends in Agricultural Traceability
Blockchain traceability offers unparalleled transparency and tamper-proof data records compared to traditional paper record-keeping in agriculture, enabling real-time tracking from farm to table. Future trends highlight the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and AI analytics with blockchain to enhance supply chain efficiency and food safety compliance. This convergence supports sustainable farming practices and consumer trust by providing immutable and verifiable provenance data throughout the agricultural value chain.
Immutable Ledger
Blockchain traceability offers an immutable ledger that enhances transparency and security far beyond traditional paper record-keeping methods.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts enhance blockchain traceability by automating and securing transaction verification, eliminating errors and fraud common in traditional paper record-keeping systems.
Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain traceability enhances supply chain transparency by providing immutable, real-time, and decentralized records compared to traditional paper record-keeping's susceptibility to errors and fraud.
Data Provenance
Blockchain traceability ensures immutable, transparent data provenance by securely recording every transaction, whereas paper record-keeping is prone to tampering and lacks verifiable audit trails.
Audit Trail
Blockchain technology enhances audit trail accuracy and transparency by providing immutable, time-stamped records compared to traditional paper record-keeping's susceptibility to tampering and loss.
Decentralized Verification
Blockchain traceability ensures decentralized verification by enabling multiple independent nodes to validate transactions, contrasting with centralized and often error-prone paper record-keeping systems.
Tamper-proof Records
Blockchain traceability ensures tamper-proof records through decentralized encryption and immutable ledgers, surpassing the vulnerability of traditional paper record-keeping to forgery and unauthorized alterations.
Digitized Compliance
Blockchain traceability enhances digitized compliance by providing immutable, transparent records that surpass the limitations of traditional paper record-keeping.
Chain-of-Custody
Blockchain traceability enhances Chain-of-Custody accuracy and transparency by providing immutable, real-time digital records compared to the error-prone, manual nature of paper record-keeping.
Manual Logbooks
Blockchain traceability surpasses manual logbooks by providing immutable, real-time digital records that enhance accuracy, security, and transparency in supply chain management.
blockchain traceability vs paper record-keeping Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com