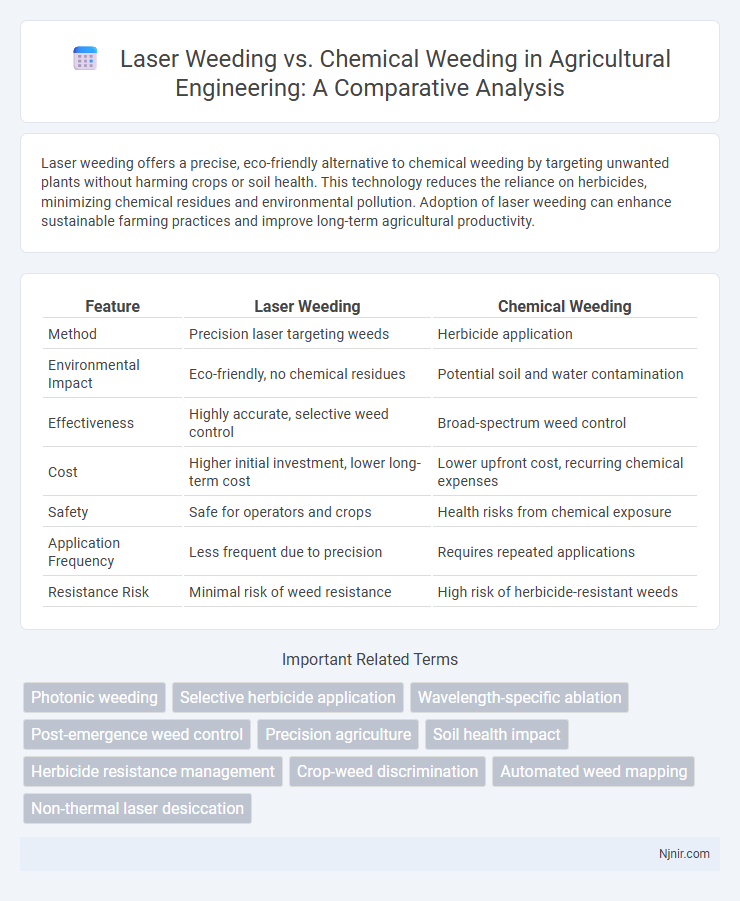
Laser weeding offers a precise, eco-friendly alternative to chemical weeding by targeting unwanted plants without harming crops or soil health. This technology reduces the reliance on herbicides, minimizing chemical residues and environmental pollution. Adoption of laser weeding can enhance sustainable farming practices and improve long-term agricultural productivity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Weeding | Chemical Weeding |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Precision laser targeting weeds | Herbicide application |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no chemical residues | Potential soil and water contamination |
| Effectiveness | Highly accurate, selective weed control | Broad-spectrum weed control |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term cost | Lower upfront cost, recurring chemical expenses |
| Safety | Safe for operators and crops | Health risks from chemical exposure |
| Application Frequency | Less frequent due to precision | Requires repeated applications |
| Resistance Risk | Minimal risk of weed resistance | High risk of herbicide-resistant weeds |
Introduction to Modern Weeding Techniques
Laser weeding utilizes focused light energy to target and eliminate weeds with precision, reducing the need for harmful chemicals and minimizing soil disturbance. Chemical weeding relies on herbicides to control unwanted vegetation but poses risks of environmental contamination and resistance buildup. Modern weeding techniques emphasize sustainable, efficient methods like laser technology to enhance crop health and promote eco-friendly agriculture.
Principles of Laser Weeding Technology
Laser weeding technology operates by using concentrated light energy to target and destroy plant cells in weeds, causing cellular damage through thermal effects, which inhibits weed growth without harming surrounding crops. This method employs precise wavelength settings and beam control to selectively affect weed species based on their pigment absorption characteristics. Laser weeding offers a sustainable alternative to chemical herbicides by minimizing chemical residues and reducing environmental impact through non-invasive, targeted weed management.
Chemical Weeding: Traditional Methods and Practices
Chemical weeding involves the application of herbicides to control unwanted vegetation, using substances such as glyphosate and atrazine that target specific plant pathways. Traditional practices rely on pre-emergent and post-emergent herbicides, often applied through spraying equipment, ensuring efficient coverage and weed suppression. Despite its effectiveness, chemical weeding poses environmental risks, including soil contamination and potential impacts on non-target species.
Efficiency and Precision: Laser vs Chemical Weeding
Laser weeding offers superior precision by targeting weeds at the cellular level, significantly reducing crop damage and minimizing chemical residues in the soil. Chemical weeding, while efficient for large-scale applications, often lacks selectivity, risking harm to nearby crops and leading to potential herbicide resistance. The efficiency of laser weeding is enhanced by real-time imaging and automation technology, enabling targeted weed destruction with lower environmental impact.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Laser weeding significantly reduces environmental harm by eliminating the use of chemical herbicides that contaminate soil and water systems. Chemical weeding often leads to pesticide runoff, harming non-target organisms and contributing to biodiversity loss and soil degradation. Adopting laser weeding promotes sustainable agriculture with lower ecological footprints and mitigates risks associated with chemical residues in ecosystems.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Laser weeding systems involve high initial capital investment but offer lower long-term operational costs due to reduced labor and chemical expenses, making them economically viable for large-scale, high-value crop production. Chemical weeding requires lower upfront costs but incurs ongoing expenses for herbicides, application, and potential environmental remediation, which can increase total costs over time. Cost analysis reveals that while chemical weeding may be more affordable for small farms, laser weeding becomes more economically advantageous as farm size and sustainability considerations grow.
Health and Safety Considerations
Laser weeding offers a chemical-free alternative that significantly reduces exposure to toxic herbicides, enhancing worker and environmental safety. Unlike chemical weeding, which can cause respiratory issues, skin irritation, and long-term health risks due to pesticide exposure, laser technology minimizes these hazards by using targeted light to eliminate weeds. Implementing laser weeding reduces contamination of soil and water sources, promoting a safer agricultural ecosystem for both farmworkers and consumers.
Effects on Crop Yield and Soil Health
Laser weeding minimizes crop damage and promotes higher yields by targeting weeds precisely without disturbing soil structure, unlike chemical weeding which can harm adjacent crops through herbicide drift. Chemical weeding often leads to residual soil toxicity and reduced microbial diversity, negatively impacting long-term soil fertility and crop productivity. Laser technology preserves soil health by maintaining beneficial microorganisms and nutrient cycles essential for sustainable crop growth.
Scalability and Applicability in Different Farming Systems
Laser weeding technology offers high scalability due to its automated precision, making it suitable for large-scale farms with diverse crop types, whereas chemical weeding is widely applicable but can face resistance issues and environmental constraints. Laser weeding systems can be integrated into both conventional and organic farming practices without chemical residues, providing a sustainable alternative for varying farm sizes and operational complexities. Chemical herbicides remain cost-effective for extensive monoculture fields but pose challenges in mixed-crop systems where selectivity and ecological impact are critical.
Future Prospects and Technological Innovations
Laser weeding technology is advancing rapidly with innovations such as AI-driven target recognition and energy-efficient lasers, promising precise and environmentally friendly weed control compared to chemical herbicides. Future prospects include integration with autonomous agricultural robots and real-time data analytics, enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing ecological impact. This shift towards laser-based solutions aligns with sustainable farming trends and stricter regulations on chemical use.
Photonic weeding
Photonic weeding, a laser-based method using precise light wavelengths, offers an eco-friendly and herbicide-free alternative to chemical weeding by effectively targeting weeds without soil contamination or chemical residues.
Selective herbicide application
Laser weeding offers precise selective herbicide application by targeting individual weeds without affecting surrounding crops, reducing chemical usage and environmental impact compared to traditional chemical weeding methods.
Wavelength-specific ablation
Wavelength-specific ablation in laser weeding enables precise targeting of weed tissues, minimizing crop damage and environmental impact compared to broad-spectrum chemical herbicides.
Post-emergence weed control
Laser weeding offers precise, chemical-free post-emergence weed control by targeting individual weeds with focused energy, reducing herbicide use and environmental impact compared to traditional chemical weeding methods.
Precision agriculture
Laser weeding in precision agriculture offers targeted plant removal that reduces herbicide use, minimizes soil disruption, and enhances sustainable crop management compared to traditional chemical weeding.
Soil health impact
Laser weeding preserves soil health by minimizing chemical residues and microbial disruption unlike chemical weeding, which often degrades soil quality through toxic buildup and microbial imbalance.
Herbicide resistance management
Laser weeding reduces herbicide resistance by eliminating weeds without chemicals, minimizing the selection pressure for herbicide-resistant weed populations compared to chemical weeding methods.
Crop-weed discrimination
Laser weeding leverages advanced optical sensors and AI algorithms for precise crop-weed discrimination, minimizing crop damage and reducing chemical usage compared to traditional chemical weeding methods.
Automated weed mapping
Automated weed mapping enhances precision in laser weeding by accurately identifying weed locations, reducing chemical herbicide use and promoting environmentally sustainable crop management.
Non-thermal laser desiccation
Non-thermal laser desiccation offers a sustainable, precise alternative to chemical weeding by targeting weed cells without heat damage, reducing herbicide use and environmental impact.
laser weeding vs chemical weeding Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com