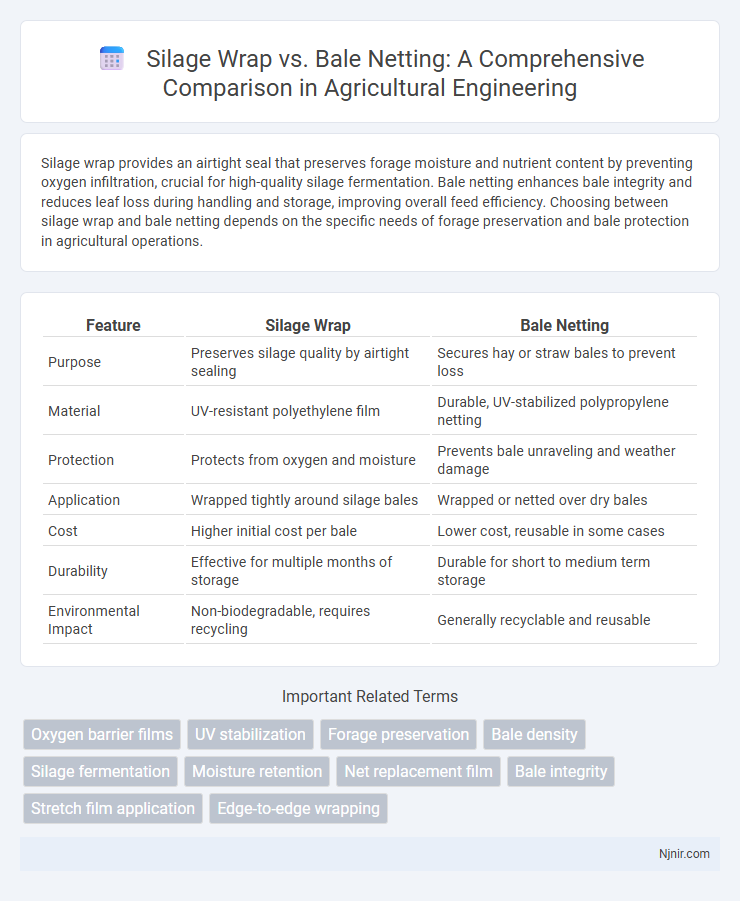
Silage wrap provides an airtight seal that preserves forage moisture and nutrient content by preventing oxygen infiltration, crucial for high-quality silage fermentation. Bale netting enhances bale integrity and reduces leaf loss during handling and storage, improving overall feed efficiency. Choosing between silage wrap and bale netting depends on the specific needs of forage preservation and bale protection in agricultural operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Silage Wrap | Bale Netting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Preserves silage quality by airtight sealing | Secures hay or straw bales to prevent loss |
| Material | UV-resistant polyethylene film | Durable, UV-stabilized polypropylene netting |
| Protection | Protects from oxygen and moisture | Prevents bale unraveling and weather damage |
| Application | Wrapped tightly around silage bales | Wrapped or netted over dry bales |
| Cost | Higher initial cost per bale | Lower cost, reusable in some cases |
| Durability | Effective for multiple months of storage | Durable for short to medium term storage |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, requires recycling | Generally recyclable and reusable |
Introduction to Forage Preservation Methods
Silage wrap and bale netting are essential materials in forage preservation, designed to protect harvested crops and maintain nutritional quality. Silage wrap creates an airtight seal that promotes anaerobic fermentation, preserving moisture and nutrient content in silage bales. Bale netting, on the other hand, secures dry hay bales by reducing spoilage from weather exposure while allowing airflow to prevent mold growth.
Understanding Silage Wrap: Features and Benefits
Silage wrap is a highly stretchable polyethylene film designed to create an airtight seal around silage bales, preserving forage quality by minimizing oxygen exposure and promoting anaerobic fermentation. Its UV resistance and puncture strength protect against environmental damage, ensuring longer storage life and reducing feed spoilage. Compared to bale netting, silage wrap offers superior moisture retention and helps maintain higher nutritional value through better ensiling conditions.
Overview of Bale Netting: Purpose and Applications
Bale netting is designed to secure hay and silage bales, improving handling and storage efficiency by providing a tight and durable wrap. Commonly used in agriculture, it reduces crop loss and protects bales from weather damage and pests. This material enhances bale density and reduces waste compared to traditional twine, promoting better feed quality and operational productivity.
Comparative Analysis: Silage Wrap vs Bale Netting
Silage wrap provides an airtight seal that preserves forage quality by minimizing oxygen exposure, making it ideal for long-term storage of silage bales. Bale netting, on the other hand, offers robust protection against physical damage and reduces dry matter loss by holding the bale tightly, but it lacks the airtight properties necessary for fermentation. Overall, silage wrap excels in fermentation preservation, while bale netting is more effective for protecting hay and straw bales from weather and handling damage.
Forage Quality and Nutrient Retention
Silage wrap creates an airtight seal that significantly reduces oxygen exposure, preserving forage quality by minimizing spoilage and nutrient loss during storage. Bale netting, while effective for securing bales, does not prevent oxygen infiltration, leading to higher risks of mold and fermentation that degrade nutrient retention. Using silage wrap enhances the preservation of moisture and essential nutrients, ensuring optimal feed quality for livestock.
Cost-Effectiveness in Forage Storage
Silage wrap typically offers superior cost-effectiveness for forage storage by providing airtight protection that extends forage preservation and reduces spoilage losses. Bale netting, while often less expensive upfront, may result in higher forage wastage due to limited protection against moisture and oxygen exposure. Choosing silage wrap can optimize long-term savings by enhancing forage quality and minimizing feed waste.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Silage wrap, typically made from polyethylene, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential to contribute to plastic pollution if not properly recycled. Bale netting, often composed of polypropylene, offers improved durability and requires less material per bale, reducing overall plastic use and waste generation. Sustainable farm practices increasingly favor bale netting for its recyclability and lower environmental footprint compared to traditional silage wrap.
Practical Usage and Handling Considerations
Silage wrap offers airtight protection by sealing bales to preserve forage quality, making it ideal for high-moisture crops but requires careful handling to avoid punctures during application. Bale netting provides structural support and reduces bale damage during transport, enhancing efficiency in handling dry hay but does not protect against weather exposure. Selecting between silage wrap and bale netting depends on forage moisture levels and storage conditions, with silage wrap prioritized for anaerobic preservation and netting for mechanical durability.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Silage wrap often faces challenges such as punctures and UV degradation, which can compromise airtight seals and lead to silage spoilage, while bale netting struggles with high initial costs and environmental concerns due to plastic waste. Silage wrap requires careful handling and disposal to minimize environmental impact, whereas bale netting can cause feeding issues if not removed properly, potentially leading to animal health risks. Both methods demand labor-intensive application and present limitations in durability under extreme weather conditions, affecting overall efficiency and crop preservation.
Choosing the Best Solution for Your Operation
Silage wrap provides airtight protection to preserve forage quality by minimizing oxygen exposure, while bale netting offers superior durability and efficient handling for dry hay bales. Farmers should evaluate moisture content, storage duration, and forage type to determine the ideal option, with silage wrap excelling in anaerobic fermentation and bale netting enhancing bale integrity during transport. Selecting the best solution maximizes feed value and operational efficiency based on specific farm conditions and equipment compatibility.
Oxygen barrier films
Oxygen barrier films in silage wrap prevent aerobic spoilage by limiting oxygen ingress, whereas bale netting lacks this barrier, allowing more oxygen exposure and reduced preservation quality.
UV stabilization
Silage wrap offers superior UV stabilization compared to bale netting, protecting forage quality by preventing UV degradation and extending storage life.
Forage preservation
Silage wrap creates an airtight seal that preserves forage quality by preventing oxygen exposure, while bale netting provides structural support but allows limited airflow, making silage wrap superior for long-term forage preservation.
Bale density
Bale netting enhances bale density by providing tighter, more uniform compression compared to silage wrap, which primarily protects rather than compresses the bale.
Silage fermentation
Silage wrap provides an airtight seal crucial for optimal silage fermentation by minimizing oxygen exposure, whereas bale netting offers less protection against air infiltration, potentially compromising fermentation quality.
Moisture retention
Silage wrap provides superior moisture retention for preserving forage quality compared to bale netting, which primarily offers structural support without preventing moisture loss.
Net replacement film
Net replacement film offers superior silage wrap durability and UV resistance compared to traditional bale netting, enhancing feed preservation and reducing material waste.
Bale integrity
Bale netting enhances bale integrity by providing superior compression and protection against weather damage compared to silage wrap.
Stretch film application
Silage wrap offers superior stretch film application by providing airtight sealing and flexibility, whereas bale netting prioritizes structural support without stretchability.
Edge-to-edge wrapping
Edge-to-edge silage wrap provides airtight sealing crucial for fermentation, whereas bale netting offers structural support but lacks complete coverage, affecting silage preservation quality.
Silage wrap vs Bale netting Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com