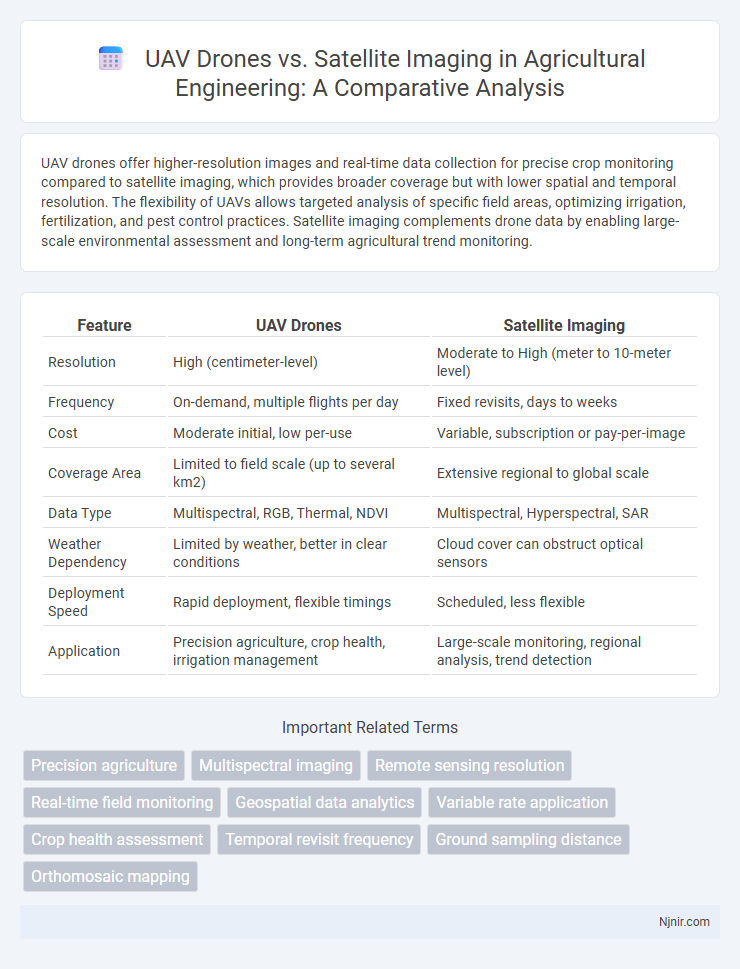
UAV drones offer higher-resolution images and real-time data collection for precise crop monitoring compared to satellite imaging, which provides broader coverage but with lower spatial and temporal resolution. The flexibility of UAVs allows targeted analysis of specific field areas, optimizing irrigation, fertilization, and pest control practices. Satellite imaging complements drone data by enabling large-scale environmental assessment and long-term agricultural trend monitoring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UAV Drones | Satellite Imaging |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | High (centimeter-level) | Moderate to High (meter to 10-meter level) |
| Frequency | On-demand, multiple flights per day | Fixed revisits, days to weeks |
| Cost | Moderate initial, low per-use | Variable, subscription or pay-per-image |
| Coverage Area | Limited to field scale (up to several km2) | Extensive regional to global scale |
| Data Type | Multispectral, RGB, Thermal, NDVI | Multispectral, Hyperspectral, SAR |
| Weather Dependency | Limited by weather, better in clear conditions | Cloud cover can obstruct optical sensors |
| Deployment Speed | Rapid deployment, flexible timings | Scheduled, less flexible |
| Application | Precision agriculture, crop health, irrigation management | Large-scale monitoring, regional analysis, trend detection |
Introduction: UAV Drones and Satellite Imaging in Agriculture
UAV drones and satellite imaging represent two pivotal technologies transforming agricultural monitoring and management. UAV drones offer high-resolution, real-time data collection with flexibility in deployment, enabling precise crop health assessments and targeted interventions. Satellite imaging provides extensive spatial coverage and continuous monitoring, essential for large-scale agricultural analysis and long-term environmental trend identification.
Overview of UAV Drone Technology
UAV drone technology offers high-resolution, real-time imaging capabilities at lower costs and greater operational flexibility compared to satellite imaging. Equipped with advanced sensors like LiDAR, multispectral, and thermal cameras, drones provide precise data collection for localized areas, enabling rapid deployment and targeted monitoring. Their ability to fly at low altitudes allows UAVs to capture detailed imagery unaffected by atmospheric distortion, making them ideal for agriculture, infrastructure inspection, and environmental monitoring.
Satellite Imaging: How It Works
Satellite imaging operates by capturing high-resolution images of the Earth's surface using sensors mounted on satellites orbiting the planet. These sensors utilize various imaging techniques such as multispectral, hyperspectral, and radar to collect data across different wavelengths, enabling detailed analysis of land, vegetation, water bodies, and atmospheric conditions. The continuous and wide-area coverage provided by satellites facilitates large-scale monitoring and environmental assessment that complements the more localized and flexible data collection capabilities of UAV drones.
Spatial Resolution: Drones vs Satellites
UAV drones provide higher spatial resolution imaging compared to most satellite systems, offering details up to a few centimeters per pixel. Satellites typically capture images with spatial resolutions ranging from 30 centimeters to several meters per pixel, limited by orbit altitude and sensor technology. This makes drones ideal for applications requiring fine-scale monitoring such as precision agriculture, infrastructure inspection, and environmental surveys.
Temporal Frequency: Data Collection Efficiency
UAV drones offer superior temporal frequency by enabling flexible, on-demand data collection multiple times per day, outperforming satellites limited by fixed orbital passes. This increased revisit rate allows UAVs to capture rapidly changing environments with high responsiveness and precision. Satellite imaging, while comprehensive in coverage, typically provides lower temporal resolution due to predetermined orbital schedules and atmospheric interference.
Cost Comparison: Investment and Operational Expenses
UAV drones offer significantly lower initial investment costs compared to satellite imaging systems, which require expensive manufacturing and launch expenses. Operational expenses for drones remain minimal due to easy maintenance, rapid deployment, and no reliance on orbital infrastructure, whereas satellites involve costly ground control and data transmission networks. The flexibility of UAVs in targeted data collection also reduces recurring survey costs, providing a cost-effective alternative for localized monitoring tasks.
Data Accuracy and Detail in Crop Monitoring
UAV drones provide higher data accuracy and finer detail compared to satellite imaging in crop monitoring, capturing high-resolution images at lower altitudes. Their ability to fly below cloud cover ensures consistent data collection, enhancing the detection of crop stress, disease, and nutrient deficiencies. Satellite imaging offers broader coverage but often at lower spatial resolution, which can limit precision in identifying small-scale variations within fields.
Scalability: Suitability for Different Farm Sizes
UAV drones offer exceptional scalability for farm surveillance, providing high-resolution, real-time data suitable for small to medium-sized farms. Satellite imaging covers vast agricultural areas efficiently, making it ideal for large-scale operations but with lower spatial resolution. Combining UAV drones with satellite imagery enables scalable monitoring tailored to varying farm sizes, optimizing precision agriculture practices.
Applications: Use Cases in Precision Agriculture
UAV drones provide high-resolution, real-time imaging for precision agriculture, enabling targeted crop monitoring, disease detection, and variable rate application of fertilizers and pesticides. Satellite imaging covers larger areas with multispectral data useful for yield prediction, drought assessment, and long-term field health analysis. Combining UAV drones with satellite data optimizes decision-making by delivering both detailed local insights and broad regional trends.
Future Trends in Agricultural Remote Sensing
Advancements in UAV drones and satellite imaging are revolutionizing agricultural remote sensing by enabling higher-resolution data collection and real-time monitoring. UAVs offer customizable flight paths and immediate access to crop health metrics, while satellite systems provide extensive area coverage with increasing revisit frequencies due to mega-constellations like Starlink and OneWeb. Emerging trends emphasize the integration of AI-powered analytics and multispectral sensors to enhance precision agriculture and optimize yield predictions.
Precision agriculture
UAV drones provide higher-resolution, real-time imaging and targeted crop monitoring for precision agriculture compared to broader, less frequent satellite imaging.
Multispectral imaging
UAV drones provide higher-resolution multispectral imaging with greater flexibility and lower cost compared to satellite imaging, enabling more precise agricultural and environmental monitoring.
Remote sensing resolution
UAV drones provide higher spatial resolution remote sensing images compared to satellite imaging, enabling detailed, low-altitude data collection for precise environmental monitoring.
Real-time field monitoring
UAV drones provide real-time field monitoring with high-resolution, low-latency imaging, outperforming satellite imaging's delayed data refresh and lower spatial resolution.
Geospatial data analytics
UAV drones provide high-resolution, real-time geospatial data analytics with greater flexibility and lower operational costs compared to satellite imaging, which offers broader coverage but lower temporal resolution.
Variable rate application
UAV drones enable precise variable rate application by capturing high-resolution, real-time data for targeted treatments, surpassing the spatial and temporal limitations of satellite imaging.
Crop health assessment
UAV drones provide higher-resolution, real-time crop health data with greater flexibility and lower operational costs compared to satellite imaging, making them ideal for precise, localized agricultural monitoring.
Temporal revisit frequency
UAV drones offer higher temporal revisit frequency than satellite imaging by providing on-demand, real-time data collection multiple times per day.
Ground sampling distance
UAV drones achieve superior ground sampling distance (GSD) of a few centimeters compared to satellites, enabling higher-resolution imaging for detailed localized analysis.
Orthomosaic mapping
UAV drones provide high-resolution, cost-effective orthomosaic mapping with greater flexibility and faster turnaround times compared to satellite imaging, which offers broader coverage but lower spatial resolution.
UAV drones vs satellite imaging Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com