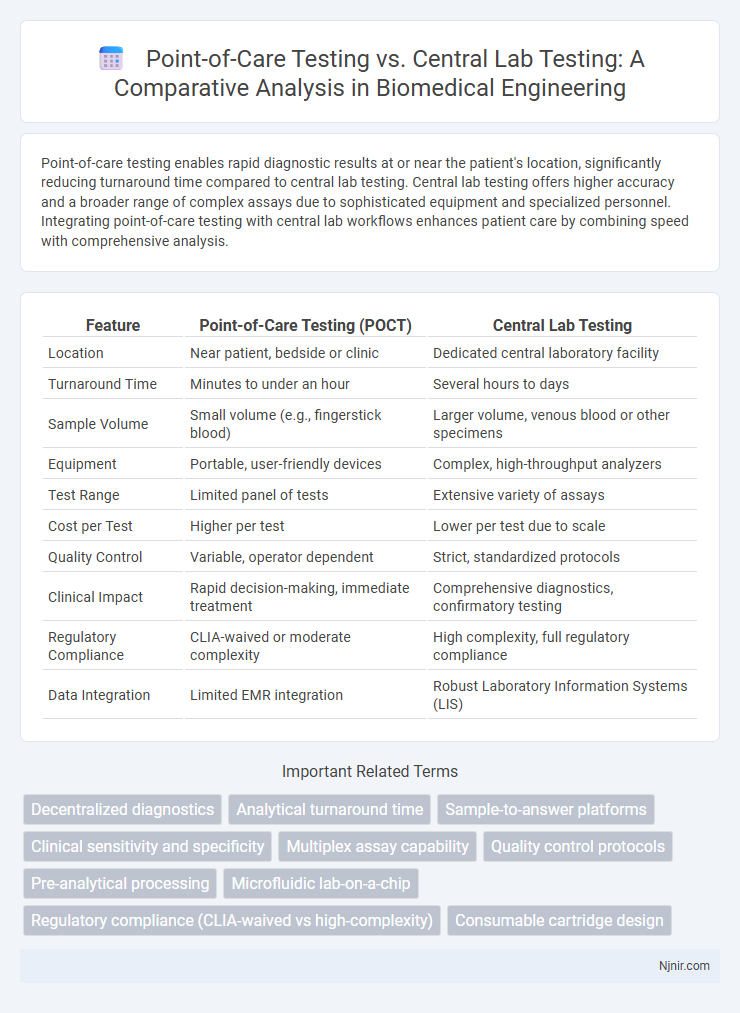
Point-of-care testing enables rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient's location, significantly reducing turnaround time compared to central lab testing. Central lab testing offers higher accuracy and a broader range of complex assays due to sophisticated equipment and specialized personnel. Integrating point-of-care testing with central lab workflows enhances patient care by combining speed with comprehensive analysis.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) | Central Lab Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Near patient, bedside or clinic | Dedicated central laboratory facility |
| Turnaround Time | Minutes to under an hour | Several hours to days |
| Sample Volume | Small volume (e.g., fingerstick blood) | Larger volume, venous blood or other specimens |
| Equipment | Portable, user-friendly devices | Complex, high-throughput analyzers |
| Test Range | Limited panel of tests | Extensive variety of assays |
| Cost per Test | Higher per test | Lower per test due to scale |
| Quality Control | Variable, operator dependent | Strict, standardized protocols |
| Clinical Impact | Rapid decision-making, immediate treatment | Comprehensive diagnostics, confirmatory testing |
| Regulatory Compliance | CLIA-waived or moderate complexity | High complexity, full regulatory compliance |
| Data Integration | Limited EMR integration | Robust Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) |
Introduction to Point-of-Care Testing and Central Lab Testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT) delivers rapid diagnostic results at or near the patient's location, facilitating immediate clinical decisions and improved patient outcomes. Central lab testing involves transporting samples to specialized facilities equipped with advanced instruments, ensuring high accuracy and comprehensive analysis. The choice between POCT and central lab testing depends on clinical needs, turnaround time, accuracy requirements, and resource availability.
Technological Innovations in Point-of-Care Devices
Technological innovations in point-of-care (POC) testing devices have revolutionized diagnostics by integrating microfluidics, biosensors, and wireless connectivity, enabling rapid, accurate results outside central laboratories. Advanced POC devices utilize nanotechnology and artificial intelligence algorithms for enhanced sensitivity and real-time data analysis, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to traditional central lab testing. These innovations support decentralized healthcare by facilitating immediate clinical decisions and improving patient outcomes, particularly in remote or resource-limited settings.
Workflow and Turnaround Time: A Comparative Analysis
Point-of-care testing (POCT) significantly streamlines workflow by enabling immediate sample analysis near the patient, reducing pre-analytical errors and bypassing sample transport delays inherent in central lab testing. Central lab testing offers high-throughput processing with advanced automation but typically involves longer turnaround times due to batch processing and centralized sample handling. Faster turnaround times in POCT enhance clinical decision-making at the bedside, whereas central labs deliver comprehensive test panels with high accuracy and quality control, suitable for complex diagnostic needs.
Accuracy and Reliability in Diagnostic Testing
Point-of-care testing offers rapid results but may exhibit variability in accuracy and reliability compared to centralized lab testing, which utilizes advanced instrumentation and strict quality controls to ensure consistent diagnostic precision. Central labs benefit from standardized protocols and experienced personnel, reducing errors and enhancing the reproducibility of test outcomes. While point-of-care devices improve accessibility, critical diagnostic decisions often require confirmation from high-sensitivity assays performed in central laboratories.
Cost Implications and Resource Allocation
Point-of-care testing (POCT) reduces costs associated with specimen transport and turnaround time, enabling faster clinical decisions and potentially lowering hospitalization duration. Central lab testing, while typically requiring higher infrastructure investment and skilled personnel, benefits from economies of scale and standardized quality control, which can reduce per-test cost in high-volume settings. Allocating resources between POCT and central labs involves balancing immediate diagnostic needs and long-term operational efficiency to optimize overall healthcare expenditure.
Integration with Electronic Medical Records
Point-of-care testing (POCT) offers rapid diagnostic results directly at the patient site, facilitating immediate clinical decisions, while central lab testing involves comprehensive analysis with higher accuracy but longer turnaround times. Integration of POCT with Electronic Medical Records (EMR) enhances real-time data capture, improves clinical workflow efficiency, and reduces manual entry errors, supporting timely patient management. Central lab testing systems often feature robust EMR interoperability through standardized interfaces like HL7 and FHIR, enabling seamless data exchange and longitudinal patient record accuracy.
Regulatory and Quality Control Challenges
Point-of-care testing (POCT) faces stringent regulatory challenges due to the need for rapid, accurate results outside traditional laboratory settings, requiring compliance with agency standards such as CLIA and FDA guidelines. Quality control in POCT must address variability in operator skill and environmental conditions, demanding robust training and frequent validation to maintain test reliability. Central lab testing benefits from standardized protocols and controlled environments, minimizing variability while adhering to established regulatory frameworks that oversee equipment calibration and quality management systems.
Impact on Patient Outcomes and Clinical Decision Making
Point-of-care testing (POCT) enables rapid diagnostic results at the bedside, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to central lab testing, which enhances timely clinical decision-making and immediate patient management. Studies show POCT improves patient outcomes by facilitating early intervention, particularly in emergency and critical care settings where delays in central lab results can adversely affect prognosis. However, central lab testing offers higher analytical accuracy and comprehensive test panels, which remain essential for confirmatory diagnostics and complex cases requiring detailed clinical evaluation.
Practical Considerations in Implementation
Point-of-care testing (POCT) offers rapid results directly at the patient site, reducing turnaround time and enabling immediate clinical decisions, while central lab testing provides higher analytical accuracy and supports complex assays with standardized quality controls. Implementation of POCT requires rigorous staff training, quality assurance protocols, and integration with electronic health records to maintain data accuracy and regulatory compliance. Central lab testing demands substantial infrastructure investment, skilled personnel, and efficient sample logistics to ensure reliable and reproducible diagnostic outcomes.
Future Trends in Biomedical Testing Platforms
Point-of-care testing (POCT) is advancing with innovations in microfluidics, biosensors, and portable devices, enabling rapid, accurate diagnostics outside traditional laboratory settings. Central lab testing is evolving through automation, high-throughput sequencing, and AI-driven data analysis to enhance precision and efficiency in biomarker detection. The convergence of decentralized POCT and centralized laboratory data integration promises a hybrid model that optimizes real-time patient monitoring and large-scale epidemiological surveillance.
Decentralized diagnostics
Point-of-care testing enables decentralized diagnostics by providing rapid, on-site results, enhancing timely clinical decisions compared to traditional central lab testing.
Analytical turnaround time
Point-of-care testing delivers analytical results within minutes at the patient's location, significantly reducing turnaround time compared to central lab testing, which typically requires hours due to sample transportation and batch processing.
Sample-to-answer platforms
Sample-to-answer point-of-care testing platforms deliver rapid, accurate results at the patient site by integrating sample processing and analysis, whereas central lab testing offers higher throughput and broader test menus but with longer turnaround times due to sample transport and batch processing.
Clinical sensitivity and specificity
Point-of-care testing offers rapid results with variable clinical sensitivity and specificity often lower than centralized lab testing, which provides higher accuracy through advanced technology and quality control processes.
Multiplex assay capability
Point-of-care testing offers rapid, on-site multiplex assay capability for simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers, while central lab testing provides higher throughput and greater analytical sensitivity for complex multiplex assays.
Quality control protocols
Point-of-care testing requires rigorous, standardized quality control protocols tailored for decentralized environments, while central lab testing implements comprehensive, automated quality assurance systems with continuous monitoring to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Pre-analytical processing
Point-of-care testing minimizes pre-analytical processing by allowing immediate sample analysis at the collection site, while central lab testing requires extensive sample transport, handling, and preparation, increasing the risk of pre-analytical errors.
Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip
Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technology enables rapid, accurate point-of-care testing by miniaturizing central lab testing processes into portable devices that reduce sample volume and turnaround time.
Regulatory compliance (CLIA-waived vs high-complexity)
Point-of-care testing typically operates under CLIA-waived regulations allowing simpler oversight, whereas central lab testing adheres to stringent high-complexity regulatory compliance standards to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Consumable cartridge design
Point-of-care testing consumable cartridges prioritize compact, user-friendly designs with integrated reagents for rapid results, while central lab testing cartridges emphasize high-throughput capacity and precise material formulations for accuracy.
Point-of-care testing vs Central lab testing Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com