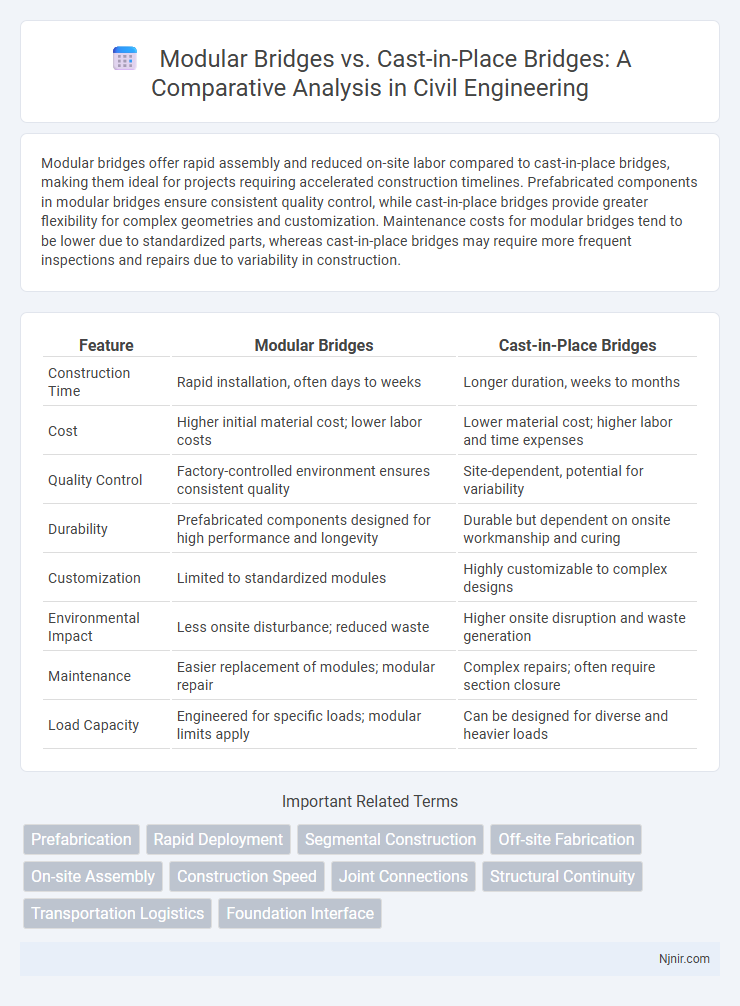
Modular bridges offer rapid assembly and reduced on-site labor compared to cast-in-place bridges, making them ideal for projects requiring accelerated construction timelines. Prefabricated components in modular bridges ensure consistent quality control, while cast-in-place bridges provide greater flexibility for complex geometries and customization. Maintenance costs for modular bridges tend to be lower due to standardized parts, whereas cast-in-place bridges may require more frequent inspections and repairs due to variability in construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modular Bridges | Cast-in-Place Bridges |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | Rapid installation, often days to weeks | Longer duration, weeks to months |
| Cost | Higher initial material cost; lower labor costs | Lower material cost; higher labor and time expenses |
| Quality Control | Factory-controlled environment ensures consistent quality | Site-dependent, potential for variability |
| Durability | Prefabricated components designed for high performance and longevity | Durable but dependent on onsite workmanship and curing |
| Customization | Limited to standardized modules | Highly customizable to complex designs |
| Environmental Impact | Less onsite disturbance; reduced waste | Higher onsite disruption and waste generation |
| Maintenance | Easier replacement of modules; modular repair | Complex repairs; often require section closure |
| Load Capacity | Engineered for specific loads; modular limits apply | Can be designed for diverse and heavier loads |
Introduction to Modular and Cast-in-place Bridges
Modular bridges consist of prefabricated components that are manufactured off-site and quickly assembled on location, significantly reducing construction time and minimizing traffic disruption. Cast-in-place bridges are constructed directly at the site using poured concrete molds, offering superior adaptability to complex designs and site-specific conditions. Both construction methods influence project timelines, costs, and durability based on the bridge's structural requirements and environmental factors.
Key Differences in Construction Methods
Modular bridges utilize prefabricated components manufactured off-site, allowing rapid assembly and reduced on-site labor, whereas cast-in-place bridges require concrete to be poured and cured directly at the construction location, often resulting in longer project timelines. The modular method enhances precision and quality control due to factory conditions, while cast-in-place bridges offer greater flexibility in shape and customization tailored to complex site requirements. Modular construction minimizes traffic disruption and environmental impact through faster installation, contrasted by the prolonged construction phases associated with cast-in-place techniques.
Materials Used in Modular vs Cast-in-place Bridges
Modular bridges primarily use prefabricated concrete or steel components manufactured under controlled conditions, ensuring high-quality materials with enhanced durability and reduced curing time compared to cast-in-place structures. Cast-in-place bridges rely on onsite poured concrete, which requires formwork and curing time, potentially leading to variability in material strength due to environmental factors during installation. The choice of materials affects the construction timeline, structural performance, and maintenance requirements, with modular designs often incorporating advanced corrosion-resistant steel and high-performance concrete mixes for longevity.
Speed of Construction and Installation
Modular bridges significantly reduce construction and installation time, often cutting project schedules by up to 50% compared to cast-in-place bridges due to prefabricated components assembled onsite with minimal disruption. Cast-in-place bridges require extensive formwork, curing periods, and onsite labor, leading to longer construction timelines and increased traffic interruptions. The accelerated assembly of modular bridges enhances project efficiency, making them ideal for locations demanding rapid deployment and limited downtime.
Cost Comparison: Modular vs Cast-in-place
Modular bridges typically offer lower initial construction costs compared to cast-in-place bridges due to prefabrication efficiencies and reduced labor requirements on-site. Cast-in-place bridges often incur higher expenses related to extensive formwork, concrete pouring, and longer curing times, leading to increased project durations and associated costs. Over the long term, modular bridges may also reduce maintenance costs because of standardized components and improved quality control during factory production.
Site Constraints and Accessibility
Modular bridges offer significant advantages in site-constrained locations due to their prefabricated components, which reduce on-site construction time and minimize the need for heavy equipment and extensive staging areas. Cast-in-place bridges require larger work zones and longer construction periods, making them less feasible in areas with limited accessibility or strict environmental regulations. The modular approach enhances flexibility in challenging terrains and urban settings by enabling rapid installation with minimal disruption to surrounding infrastructure and traffic flow.
Structural Performance and Durability
Modular bridges offer enhanced structural performance through precision-fabricated components that ensure consistent quality and reduced onsite construction errors, leading to improved load distribution and resistance to dynamic forces. Cast-in-place bridges, while adaptable to complex site conditions, often face challenges with curing variability that can affect concrete strength and durability. Modular construction materials are typically engineered for superior corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance, resulting in longer service life compared to traditional cast-in-place bridges.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
Modular bridges offer reduced maintenance costs and faster repairs due to their prefabricated components that can be easily replaced or upgraded, minimizing downtime and lifecycle disruptions. Cast-in-place bridges often require more frequent inspections and extensive maintenance efforts because they are susceptible to environmental wear and cracking over time. Lifecycle considerations favor modular bridges for their durability and adaptability, while cast-in-place bridges typically involve higher long-term maintenance expenses and longer repair durations.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Modular bridges significantly reduce construction waste and minimize site disturbance by enabling off-site prefabrication, leading to lower carbon emissions compared to cast-in-place bridges that require extensive on-site concrete pouring and formwork. The reuse potential of modular components supports circular economy principles, while cast-in-place methods often involve higher resource consumption and longer construction timelines, increasing environmental impact. Furthermore, modular bridges enhance sustainability through faster installation, reducing traffic disruptions and associated pollution.
Future Trends in Bridge Construction Technology
Modular bridges offer rapid assembly, reduced construction time, and enhanced quality control through prefabrication, making them a preferred choice for future infrastructure projects. Cast-in-place bridges provide adaptability to complex site conditions and designs but face challenges with longer construction durations and higher labor costs. Emerging trends emphasize integrating smart sensors and advanced materials in modular bridge systems to improve monitoring, durability, and sustainability in bridge construction technology.
Prefabrication
Modular bridges utilize prefabricated components manufactured off-site for faster assembly and reduced onsite labor, while cast-in-place bridges require on-site concrete pouring and curing, leading to longer construction times and increased traffic disruption.
Rapid Deployment
Modular bridges enable rapid deployment through prefabricated components that minimize on-site construction time compared to the longer curing periods required for cast-in-place bridges.
Segmental Construction
Segmental construction in modular bridges enables faster assembly and reduced onsite labor compared to cast-in-place bridges, enhancing durability and minimizing traffic disruption.
Off-site Fabrication
Modular bridges offer accelerated construction and improved quality control through off-site fabrication, reducing on-site labor and minimizing traffic disruptions compared to cast-in-place bridges.
On-site Assembly
Modular bridges enable faster on-site assembly with pre-fabricated components, significantly reducing construction time and site disruption compared to the longer, more labor-intensive on-site processes required for cast-in-place bridges.
Construction Speed
Modular bridges significantly reduce construction time by enabling prefabricated components to be quickly assembled onsite, while cast-in-place bridges require longer curing periods and extensive onsite labor, resulting in slower overall construction speed.
Joint Connections
Modular bridges feature prefabricated joint connections that allow for faster assembly and increased durability compared to the labor-intensive, on-site cast joint connections of cast-in-place bridges.
Structural Continuity
Modular bridges offer enhanced structural continuity by using prefabricated components that minimize construction joints compared to cast-in-place bridges, which typically have more joints that can affect long-term durability and load transfer efficiency.
Transportation Logistics
Modular bridges reduce transportation logistics challenges by enabling prefabricated sections to be transported and assembled quickly on-site, whereas cast-in-place bridges require extensive on-site material delivery and staging, increasing transportation complexity and time.
Foundation Interface
Modular bridges feature prefabricated components that enable faster installation on standardized foundation interfaces, while cast-in-place bridges require customized foundation work tailored to site-specific conditions, impacting construction time and adaptability.
Modular Bridges vs Cast-in-place Bridges Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com