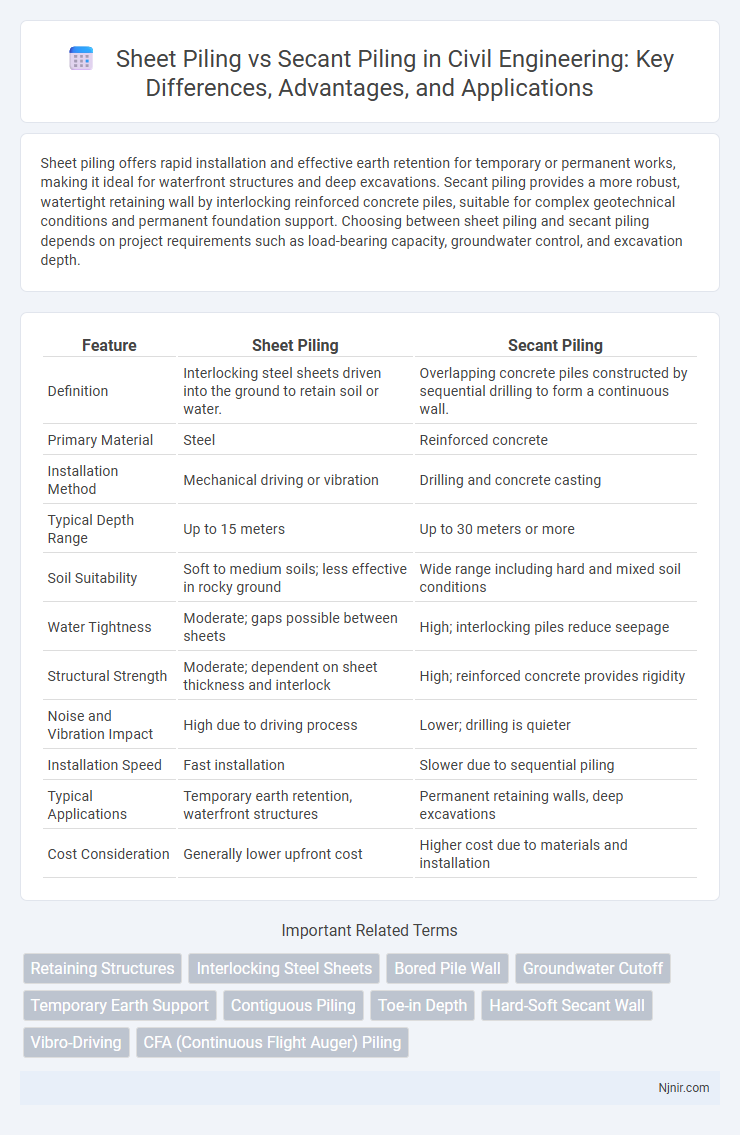
Sheet piling offers rapid installation and effective earth retention for temporary or permanent works, making it ideal for waterfront structures and deep excavations. Secant piling provides a more robust, watertight retaining wall by interlocking reinforced concrete piles, suitable for complex geotechnical conditions and permanent foundation support. Choosing between sheet piling and secant piling depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, groundwater control, and excavation depth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sheet Piling | Secant Piling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interlocking steel sheets driven into the ground to retain soil or water. | Overlapping concrete piles constructed by sequential drilling to form a continuous wall. |
| Primary Material | Steel | Reinforced concrete |
| Installation Method | Mechanical driving or vibration | Drilling and concrete casting |
| Typical Depth Range | Up to 15 meters | Up to 30 meters or more |
| Soil Suitability | Soft to medium soils; less effective in rocky ground | Wide range including hard and mixed soil conditions |
| Water Tightness | Moderate; gaps possible between sheets | High; interlocking piles reduce seepage |
| Structural Strength | Moderate; dependent on sheet thickness and interlock | High; reinforced concrete provides rigidity |
| Noise and Vibration Impact | High due to driving process | Lower; drilling is quieter |
| Installation Speed | Fast installation | Slower due to sequential piling |
| Typical Applications | Temporary earth retention, waterfront structures | Permanent retaining walls, deep excavations |
| Cost Consideration | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher cost due to materials and installation |
Introduction to Sheet Piling and Secant Piling
Sheet piling involves driving interlocking steel sheets into the ground to form a continuous barrier for earth retention and water control, frequently used in waterfront structures and excavation support. Secant piling consists of overlapping reinforced concrete piles that create a solid wall, ideal for retaining soil in deep excavations and areas with complex ground conditions. Both methods provide structural support but differ in material, installation techniques, and suitability depending on site-specific geotechnical requirements.
Fundamental Differences Between Sheet and Secant Piling
Sheet piling involves interlocking steel sheets driven vertically into the ground to create a continuous wall, providing temporary or permanent earth retention. Secant piling consists of overlapping reinforced concrete piles drilled in sequence to form a watertight, rigid wall, typically used for deep excavations and heavy load support. The fundamental difference lies in material composition and installation method: sheet piling relies on steel interlocks and driving force, while secant piling uses cast-in-place concrete piles with structural interpenetration.
Common Applications in Civil Engineering Projects
Sheet piling is commonly used for temporary and permanent retaining walls, cofferdams, and waterfront structures due to its quick installation and cost-effectiveness in soil retention and excavation support. Secant piling is preferred in deep excavation projects requiring water-tight barriers and high structural strength, such as basement construction, diaphragm walls, and bridge abutments, especially in challenging ground conditions with high groundwater levels. Both techniques are integral to foundation stabilization, earth retention, and dewatering in urban infrastructure and large-scale civil engineering developments.
Material Types Used for Sheet and Secant Piles
Sheet piling commonly utilizes steel, vinyl, or composite materials, with steel being the most prevalent due to its high strength and durability in retaining soil and water. Secant piling involves reinforced concrete piles, combining primary unreinforced piles with secondary reinforced piles to create a continuous wall that offers superior structural integrity and water tightness. Material selection depends on project requirements, soil conditions, and load-bearing needs, with secant piles providing enhanced resistance in complex subsurface environments compared to conventional steel sheet piles.
Installation Methods and Equipment Required
Sheet piling installation involves driving prefabricated steel sheets into the ground using impact hammers, vibratory drivers, or pressing equipment, enabling quick and efficient soil retention for temporary or permanent structures. Secant piling requires drilling overlapping concrete piles formed by alternating primary and secondary piles, using rotary drilling rigs equipped with Kelly bars and bentonite slurry for stability, offering enhanced groundwater control and structural support. Equipment for sheet piling focuses on pile driving machinery, while secant piling depends heavily on rotary drilling rigs and concrete tremie systems for precise installation and interlocking pile formation.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Sheet piling provides effective lateral support and is ideal for temporary or lightweight load-bearing applications, utilizing interlocking steel sheets to resist soil and water pressures. Secant piling offers superior structural performance and higher load-bearing capacity through the overlapping cast-in-place concrete piles, creating a continuous, reinforced wall suitable for deep excavation and permanent structures. The enhanced rigidity and strength of secant piles make them preferable for complex projects requiring robust groundwater cutoff and high stability under heavy loads.
Waterproofing Capabilities and Groundwater Control
Sheet piling offers effective groundwater control by creating a continuous barrier, preventing water seepage and soil erosion, ideal for temporary and permanent cofferdams. Secant piling provides superior waterproofing capabilities through interlocking reinforced concrete piles, forming a rigid, impermeable wall that excels in controlling groundwater flow in deep excavations. This method is preferred for structures requiring high water tightness, such as basements and tunnels, due to its durability and resistance to hydrostatic pressure.
Environmental and Site Considerations
Sheet piling offers a faster installation process with less noise and vibration, minimizing disturbance to nearby ecosystems and urban environments, making it suitable for projects with strict environmental constraints. Secant piling, while more time-consuming and resource-intensive, provides superior groundwater control and structural stability, essential for sites with complex soil conditions or high water tables. Choosing between the two depends on specific site characteristics, such as soil composition, groundwater presence, and proximity to sensitive habitats or urban infrastructure.
Cost Comparison: Sheet Piling vs Secant Piling
Sheet piling typically offers a more cost-effective solution for temporary or less complex retaining walls due to its faster installation and reusable steel sections. Secant piling involves higher upfront costs caused by the intricate drilling and concrete work required, making it suitable for permanent structures and challenging soil conditions. The choice impacts overall budget, where sheet piling reduces labor and material expenses, while secant piling demands greater investment but provides superior structural integrity.
Selection Criteria for Construction Projects
Selection criteria for sheet piling versus secant piling in construction projects emphasize soil conditions, project depth, and load requirements. Sheet piling is preferred for temporary earth retention in soft to medium soils with shallow excavation, offering rapid installation and cost efficiency. Secant piling suits deeper excavations in mixed or unstable ground, providing superior water tightness and structural support despite higher complexity and cost.
Retaining Structures
Sheet piling offers quick installation and cost-effectiveness for temporary retaining structures, while secant piling provides superior load-bearing capacity and groundwater cutoff for permanent retaining walls in complex soil conditions.
Interlocking Steel Sheets
Interlocking steel sheets in sheet piling provide faster installation and enhanced water tightness compared to secant piling's overlapping concrete segments.
Bored Pile Wall
Secant piling forms watertight bored pile walls by interlocking primary and secondary piles, offering superior groundwater control compared to traditional sheet piling methods.
Groundwater Cutoff
Secant piling provides a more effective groundwater cutoff compared to sheet piling due to its interlocking concrete wall design that minimizes seepage.
Temporary Earth Support
Sheet piling offers rapid installation and cost-effective temporary earth support, while secant piling provides superior structural stability and minimal ground movement for complex site conditions.
Contiguous Piling
Contiguous piling offers a cost-effective and faster alternative to secant piling by using continuous interlocking steel sheet piles to create a watertight retaining wall ideal for moderate groundwater and load conditions.
Toe-in Depth
Sheet piling typically features a shallow toe-in depth suitable for temporary support, whereas secant piling offers a significantly deeper toe-in depth providing enhanced stability for permanent retaining structures.
Hard-Soft Secant Wall
Hard-soft secant piling combines hardened primary piles with softer secondary piles to create a watertight and structurally stable retaining wall, offering better adaptability and cost efficiency compared to traditional sheet piling in challenging soil conditions.
Vibro-Driving
Vibro-driving is highly effective for sheet piling installation due to its ability to minimize soil displacement and noise compared to secant piling, which typically requires rotary drilling and concrete casting for structural integrity.
CFA (Continuous Flight Auger) Piling
CFA piling offers faster installation and less noise compared to sheet piling and secant piling, making it ideal for urban construction sites requiring efficient deep foundation solutions.
sheet piling vs secant piling Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com