ESL (Electronic System Level) design enables higher abstraction by modeling systems using functional blocks and hardware-software co-design early in the development process, significantly accelerating system validation and architecture exploration. In contrast, RTL (Register Transfer Level) focuses on detailed hardware description using registers and logic gates, providing precise control over hardware implementation and timing but often leading to longer development cycles. Utilizing ESL allows engineers to optimize design performance and verify system behavior before committing to the detailed RTL coding stage.
Table of Comparison
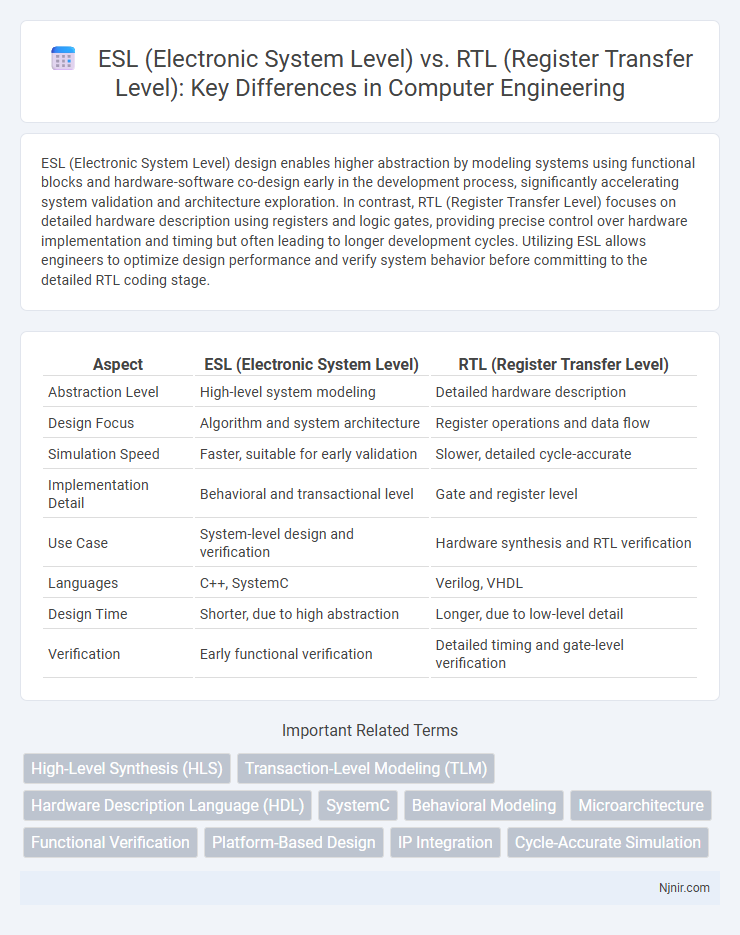
| Aspect | ESL (Electronic System Level) | RTL (Register Transfer Level) |
|---|---|---|
| Abstraction Level | High-level system modeling | Detailed hardware description |
| Design Focus | Algorithm and system architecture | Register operations and data flow |
| Simulation Speed | Faster, suitable for early validation | Slower, detailed cycle-accurate |
| Implementation Detail | Behavioral and transactional level | Gate and register level |
| Use Case | System-level design and verification | Hardware synthesis and RTL verification |
| Languages | C++, SystemC | Verilog, VHDL |
| Design Time | Shorter, due to high abstraction | Longer, due to low-level detail |
| Verification | Early functional verification | Detailed timing and gate-level verification |
Introduction to ESL and RTL Design Paradigms
Electronic System Level (ESL) design focuses on high-level abstraction for system modeling, enabling early software development and system verification through transaction-level modeling (TLM). Register Transfer Level (RTL) design deals with detailed hardware description using registers and logic gates to specify data flow and control between registers accurately. ESL accelerates design space exploration and functional verification, while RTL ensures precise hardware synthesis and timing implementation.
Defining Electronic System Level (ESL)
Electronic System Level (ESL) is an abstraction for designing complex integrated circuits, focusing on system-wide functionality and architecture rather than individual register transfers. ESL enables high-level modeling using languages like SystemC, facilitating early software development and architectural exploration before detailed Register Transfer Level (RTL) implementation. This approach significantly reduces time-to-market by allowing concurrent hardware-software co-design and system validation at an early stage.
Overview of Register Transfer Level (RTL)
Register Transfer Level (RTL) is a hardware description abstraction used to model digital circuits by specifying the flow of data between registers and the logical operations performed on that data. RTL designs describe how data moves through registers and how combinational logic transforms the data during clock cycles, serving as a crucial stage in the digital design process. This level enables precise control over timing, concurrency, and resource allocation, forming the foundation for synthesis into gate-level implementations and ultimately physical hardware.
Design Abstraction: ESL vs RTL
Electronic System Level (ESL) design abstracts hardware and software components at a high level, allowing system architects to model, simulate, and validate entire systems early in the development cycle. Register Transfer Level (RTL) design operates at a lower abstraction, describing data flow between hardware registers and the detailed logic behavior, which is essential for synthesis and implementation. ESL enables faster design space exploration and system integration, while RTL provides precise control required for hardware realization and timing optimization.
Modeling and Simulation Capabilities
ESL (Electronic System Level) offers higher abstraction modeling, enabling faster and more efficient simulation of complex system architectures compared to RTL (Register Transfer Level), which focuses on detailed hardware description at the register-transfer level. ESL supports system-wide validation, algorithm development, and early software integration, while RTL excels in cycle-accurate timing and hardware-specific verification. Simulation capabilities in ESL leverage transaction-level modeling for faster performance, whereas RTL simulation provides precise control over hardware behavior for final design verification.
Productivity and Design Cycle Time
ESL (Electronic System Level) design significantly enhances productivity by enabling early software development, system validation, and architectural exploration through high-level abstractions and virtual prototypes. RTL (Register Transfer Level) focuses on detailed hardware description, which requires longer design cycle times due to intricate coding, simulation, and synthesis processes. Utilizing ESL methodologies reduces overall design cycle time by allowing concurrent hardware/software development and early detection of design flaws.
Hardware/Software Co-Design in ESL and RTL
Hardware/software co-design in ESL (Electronic System Level) enables early exploration and validation of system architecture through high-level modeling and simulation, improving design efficiency and reducing time-to-market. In contrast, RTL (Register Transfer Level) focuses on detailed hardware design, specifying exact data flow and timing at the register level, which limits software integration but ensures precise hardware implementation. ESL's abstraction facilitates concurrent hardware and software development, making it ideal for complex SoC designs, whereas RTL remains essential for final hardware verification and synthesis.
Verification Techniques: ESL vs RTL
ESL verification techniques leverage high-level models and transaction-level abstractions, enabling early error detection and faster simulation speeds compared to RTL, which focuses on cycle-accurate, clock-driven design verification. ESL uses formal methods, model checking, and software-driven testbenches to verify system functionality before detailed hardware descriptions are available, whereas RTL verification relies heavily on stimulus generation, assertion-based verification, and coverage analysis at the register transfer granularity. This distinction allows ESL to identify architectural flaws early, while RTL verification ensures precise timing, signal integrity, and logic correctness in synthesized hardware.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
ESL (Electronic System Level) modeling enables early software and hardware co-design, making it ideal for complex system integration and multimedia applications in automotive and consumer electronics industries. RTL (Register Transfer Level) focuses on detailed hardware design and verification, crucial for microprocessor development, ASICs, and FPGA implementations in telecommunications and semiconductor sectors. ESL accelerates time-to-market by exploring architectural trade-offs, while RTL ensures precise logic functionality and timing accuracy in final chip production.
Choosing the Right Level: ESL or RTL?
Choosing between ESL (Electronic System Level) and RTL (Register Transfer Level) depends on project scope, design complexity, and verification needs. ESL offers higher abstraction, enabling quicker system modeling, early software development, and faster architectural exploration, essential for complex SoC designs. RTL provides detailed hardware implementation and precise timing control, making it ideal for cycle-accurate verification and synthesis-ready designs.
High-Level Synthesis (HLS)
High-Level Synthesis (HLS) automates the translation of ESL designs, described in C/C++ or SystemC, into RTL code, significantly accelerating the hardware development process compared to traditional manual RTL design.
Transaction-Level Modeling (TLM)
Transaction-Level Modeling (TLM) in ESL enables higher abstraction and faster simulation compared to RTL by focusing on data transactions rather than detailed register transfers.
Hardware Description Language (HDL)
ESL (Electronic System Level) uses high-level languages like SystemC for system modeling and early design verification, while RTL (Register Transfer Level) relies on detailed Hardware Description Languages (HDLs) such as VHDL and Verilog to describe hardware circuits for synthesis and implementation.
SystemC
SystemC, as a key ESL modeling language, enables higher abstraction and faster simulation compared to RTL, facilitating early hardware/software co-design and verification in complex system development.
Behavioral Modeling
Behavioral modeling in ESL emphasizes high-level system abstraction and faster simulation speed, while RTL focuses on detailed cycle-accurate hardware description for precise synthesis and implementation.
Microarchitecture
ESL (Electronic System Level) enables high-level microarchitecture exploration and validation through system-level modeling and simulation, while RTL (Register Transfer Level) provides detailed hardware description for precise microarchitecture implementation and synthesis.
Functional Verification
Functional verification at the ESL (Electronic System Level) offers higher abstraction, faster simulation speeds, and earlier bug detection compared to the more detailed, cycle-accurate but slower RTL (Register Transfer Level) verification.
Platform-Based Design
Platform-Based Design leverages ESL to enable high-level system modeling and faster design space exploration, whereas RTL focuses on low-level hardware description for precise digital circuit implementation.
IP Integration
ESL enables faster and more efficient IP integration by modeling systems at a higher abstraction level compared to RTL, which requires detailed hardware description and results in longer design cycles.
Cycle-Accurate Simulation
Cycle-accurate simulation in ESL offers higher abstraction and faster execution compared to RTL, which provides detailed hardware timing and precise control at the register transfer level for accurate hardware verification.
ESL (Electronic System Level) vs RTL (Register Transfer Level) Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com