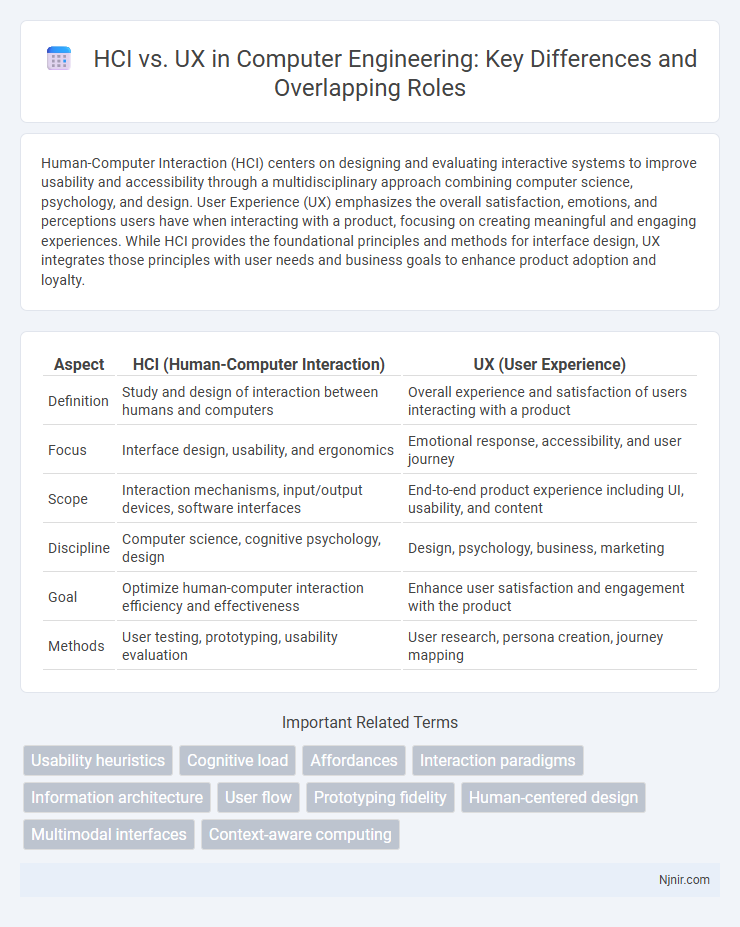
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) centers on designing and evaluating interactive systems to improve usability and accessibility through a multidisciplinary approach combining computer science, psychology, and design. User Experience (UX) emphasizes the overall satisfaction, emotions, and perceptions users have when interacting with a product, focusing on creating meaningful and engaging experiences. While HCI provides the foundational principles and methods for interface design, UX integrates those principles with user needs and business goals to enhance product adoption and loyalty.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | HCI (Human-Computer Interaction) | UX (User Experience) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study and design of interaction between humans and computers | Overall experience and satisfaction of users interacting with a product |
| Focus | Interface design, usability, and ergonomics | Emotional response, accessibility, and user journey |
| Scope | Interaction mechanisms, input/output devices, software interfaces | End-to-end product experience including UI, usability, and content |
| Discipline | Computer science, cognitive psychology, design | Design, psychology, business, marketing |
| Goal | Optimize human-computer interaction efficiency and effectiveness | Enhance user satisfaction and engagement with the product |
| Methods | User testing, prototyping, usability evaluation | User research, persona creation, journey mapping |
Introduction to HCI and UX
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) explores the design and use of computer technology, emphasizing the interfaces between people and computers. User Experience (UX) focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product. Both fields prioritize understanding user behavior and designing systems that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
Defining Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is the interdisciplinary study focused on the design and use of computer technology, emphasizing the interfaces between people and computers. HCI explores how users interact with software and hardware, aiming to improve usability, accessibility, and user experience through user-centered design principles. Distinct from UX, which concentrates broadly on overall user satisfaction and emotional connection, HCI specifically analyzes the technical and cognitive aspects of human interaction with digital systems.
Understanding User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) centers on understanding users' emotions, behaviors, and preferences during interaction with a product or service, aiming to enhance satisfaction and usability. It encompasses factors such as accessibility, intuitive design, and overall user journey, ensuring a seamless and engaging experience. Unlike Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), which broadly studies interfaces and system usability, UX prioritizes emotional impact and user-centered design principles in product development.
Core Principles of HCI
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) centers on core principles such as usability, accessibility, and user-centered design to optimize the interface between people and computer systems. It emphasizes learnability, efficiency, memorability, error prevention, and satisfaction to create intuitive and effective digital experiences. While UX encompasses broader emotional and experiential aspects, HCI's foundational focus is on measurable interactions and interface functionality.
Fundamental Elements of UX
Fundamental elements of UX encompass usability, interaction design, and user behavior, ensuring that digital products meet user needs efficiently and intuitively. Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) delves deeper into the scientific study of how users engage with technology, emphasizing cognitive processes and ergonomic factors. UX prioritizes the emotional and experiential aspects of user engagement, while HCI provides the foundational research and principles that inform effective UX design strategies.
Key Differences Between HCI and UX
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) primarily focuses on the study and design of computer technology and the interaction between users and computers, emphasizing usability, interface design, and user behavior analysis. User Experience (UX) encompasses a broader scope, including emotional, psychological, and experiential aspects of user interaction with products or services, aiming to enhance overall satisfaction and engagement. While HCI is centered on optimizing interface functionality and interaction models, UX integrates HCI principles with design, content, and branding to create holistic and meaningful user experiences.
Overlapping Areas in HCI and UX
The overlapping areas in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and User Experience (UX) primarily include usability, interaction design, and user-centered design principles that ensure effective communication between users and digital systems. Both fields emphasize understanding user needs and behaviors through research methods like usability testing, cognitive modeling, and iterative prototyping to enhance product functionality and satisfaction. Integration of visual design, accessibility standards, and information architecture further bridges HCI and UX in creating intuitive and engaging digital experiences.
Role of Computer Engineering in HCI and UX
Computer engineering plays a critical role in both Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and User Experience (UX) by designing and developing the hardware and software systems that facilitate seamless, intuitive user interfaces. It enables the integration of advanced sensors, processors, and input devices that improve interaction capabilities, directly impacting usability and user satisfaction. Effective collaboration between computer engineers and UX designers ensures the creation of optimized systems that align with user needs and technical constraints.
Real-World Applications: HCI vs UX
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) emphasizes the design and evaluation of interactive systems for usability and accessibility in real-world contexts such as workplace software, medical devices, and automotive interfaces. User Experience (UX) focuses on optimizing the overall emotional and functional satisfaction of users in practical applications like mobile apps, e-commerce platforms, and customer service systems. Real-world implementation of HCI principles ensures system efficiency and error reduction, while UX drives brand loyalty and user engagement through personalized and intuitive design.
Future Trends in HCI and UX within Computer Engineering
Future trends in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and User Experience (UX) within computer engineering emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to create adaptive, context-aware interfaces. Advances in natural language processing and augmented reality are driving the development of immersive and intuitive user environments that enhance accessibility and personalization. The convergence of biometric sensors and emotion recognition technologies is poised to revolutionize UX design by enabling systems to respond dynamically to users' cognitive and emotional states.
Usability heuristics
Usability heuristics in HCI focus on evaluating interface design principles for effectiveness and efficiency, while UX encompasses broader user satisfaction and emotional impact beyond these heuristic guidelines.
Cognitive load
HCI minimizes cognitive load by designing intuitive interfaces, while UX emphasizes reducing mental effort through user-centered experiences and seamless interactions.
Affordances
Affordances in HCI emphasize the design elements that suggest user actions, while in UX they enhance overall user satisfaction by ensuring intuitive interaction and seamless usability.
Interaction paradigms
HCI interaction paradigms encompass traditional models like command-line and direct manipulation, while UX interaction paradigms prioritize user-centered design through immersive, adaptive, and intuitive experiences.
Information architecture
Information architecture in HCI organizes interface structure for usability, while in UX it enhances user experience by optimizing content discoverability and navigation.
User flow
User flow in HCI emphasizes optimizing interface interactions for efficiency, while UX focuses on crafting seamless, satisfying end-to-end user journeys.
Prototyping fidelity
High-fidelity prototypes in UX provide realistic user interactions and detailed design elements, while HCI often utilizes varying fidelity prototypes to study user behavior and interface functionality.
Human-centered design
Human-centered design integrates HCI principles to create user experiences that prioritize usability, accessibility, and emotional engagement.
Multimodal interfaces
Multimodal interfaces in HCI integrate multiple sensory inputs to enhance user experience (UX) by enabling more natural and efficient interactions across voice, touch, and gesture modalities.
Context-aware computing
Context-aware computing enhances Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) by dynamically adapting interfaces based on user context, while User Experience (UX) design leverages these adaptations to create personalized, intuitive, and seamless interactions.
HCI vs UX Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com