Ferrules provide a secure, insulated connection for stranded wires, preventing fraying and ensuring reliable electrical contact. Lugs offer a robust connection by mechanically fastening wires to terminals or bus bars, often used for higher current applications. Choosing between ferrules and lugs depends on factors like conductor size, installation environment, and current requirements.
Table of Comparison
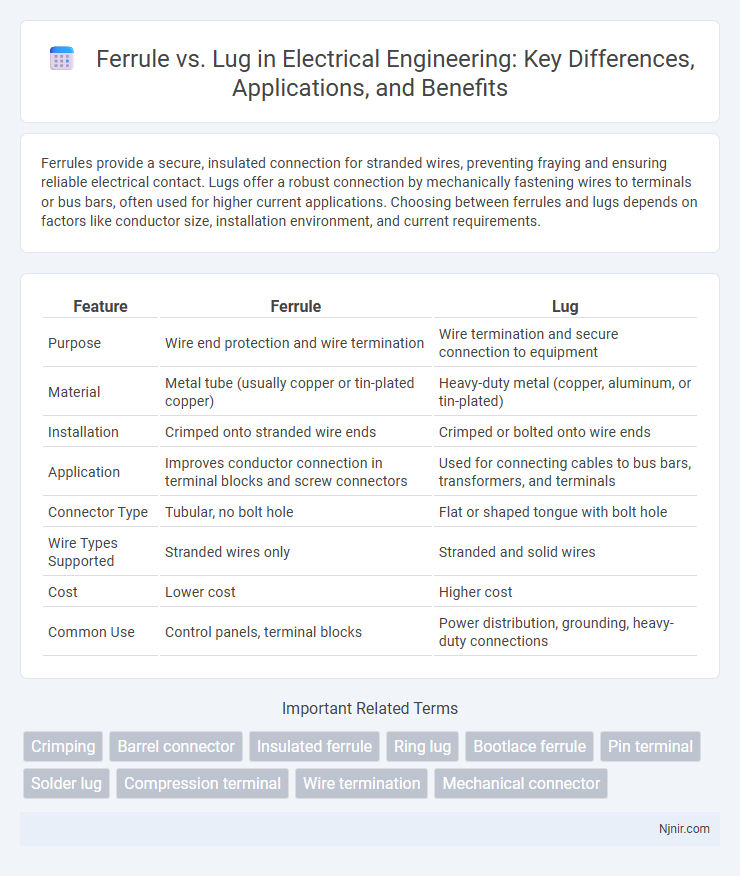
| Feature | Ferrule | Lug |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Wire end protection and wire termination | Wire termination and secure connection to equipment |
| Material | Metal tube (usually copper or tin-plated copper) | Heavy-duty metal (copper, aluminum, or tin-plated) |
| Installation | Crimped onto stranded wire ends | Crimped or bolted onto wire ends |
| Application | Improves conductor connection in terminal blocks and screw connectors | Used for connecting cables to bus bars, transformers, and terminals |
| Connector Type | Tubular, no bolt hole | Flat or shaped tongue with bolt hole |
| Wire Types Supported | Stranded wires only | Stranded and solid wires |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Use | Control panels, terminal blocks | Power distribution, grounding, heavy-duty connections |
Introduction to Ferrules and Lugs in Electrical Engineering
Ferrules and lugs are essential components in electrical engineering used to ensure secure and reliable connections of wires to terminals. Ferrules are metal sleeves crimped over stranded wire ends to prevent fraying and improve conductivity, especially in control panels and circuit breakers. Lugs, typically made from copper or aluminum, are designed for direct attachment to cable ends and provide robust mechanical and electrical connections in power distribution and grounding applications.
Defining Ferrules: Structure and Function
Ferrules are small cylindrical metal sleeves designed to reinforce or join two objects, commonly used to secure stranded wire ends in electrical installations. Their structure typically consists of a hollow tube made from materials like copper or aluminum, which is crimped onto the wire to prevent fraying and improve conductivity. Unlike lugs, ferrules do not feature holes or flanges for bolting but provide a compact, reliable termination that enhances connection quality in electrical circuits.
Understanding Lugs: Types and Applications
Lugs are essential electrical connectors designed to securely join cables to devices or terminals, available in various types such as compression, mechanical, and insulated lugs to suit different applications. Compression lugs require crimping tools for a permanent connection, ideal for high-current circuits, while mechanical lugs use screws or bolts, allowing easy installation and maintenance. Insulated lugs provide added safety by preventing accidental contact and short circuits, commonly used in automotive and industrial electrical systems.
Material Differences: Ferrules vs Lugs
Ferrules are typically made from copper or aluminum with a tin plating to enhance conductivity and corrosion resistance, ideal for securing stranded wires in electrical circuits. Lugs, on the other hand, often use heavier-duty copper or aluminum alloys and may include insulating sleeves to provide robust mechanical and electrical connections in high-current applications. Material differences impact their durability, conductivity, and suitability for specific wiring needs, with ferrules favoring finer wire integrity and lugs supporting stronger terminal connections.
Installation Techniques for Ferrules and Lugs
Ferrule installation techniques involve stripping the wire to the correct length, inserting it fully into the metal tube, and using a crimping tool designed specifically for ferrules to ensure a secure electrical connection and prevent wire strand unraveling. Lug installation requires selecting the appropriate lug size, stripping the wire insulation to expose the correct conductor length, inserting the wire into the lug barrel, and utilizing a hydraulic or mechanical crimping tool to create a tight, durable mechanical bond that can withstand high current loads and environmental conditions. Both techniques emphasize proper tool selection, precise wire preparation, and quality control measures to guarantee safety and conductivity in electrical systems.
Electrical Conductivity and Performance Comparison
Ferrules provide enhanced electrical conductivity by ensuring a secure connection between stranded wires and terminal blocks, reducing resistance and preventing wire strand fraying. Lugs, typically made from copper or aluminum, offer superior performance in high-current applications due to their robust mechanical strength and larger contact surface area that facilitates efficient current flow. Comparing both, ferrules excel in maintaining reliable circuit integrity in control panels, while lugs are preferable for heavy-duty power distribution systems requiring maximum conductivity and durability.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Ferrules enhance safety by providing a secure, insulated termination for stranded wires, preventing fraying and ensuring consistent electrical contact under vibration or stress. Lugs offer superior mechanical strength and reliability for high-current applications by firmly crimping or soldering cables to terminals, reducing the risk of loose connections and electrical faults. Selecting ferrules or lugs based on wire size, current load, and environmental conditions maximizes connection durability and operational safety.
Use Cases: When to Choose Ferrules over Lugs
Ferrules are ideal for use in applications requiring neat conductor ends for insertion into terminal blocks or screw-type connectors, particularly in control panels and industrial equipment wiring. They provide excellent strain relief and prevent wire strand fraying in fine or multi-stranded wires, making them the preferred choice for precision electronic assemblies and automation systems. In contrast, lugs are better suited for heavy-duty electrical connections in power distribution and grounding where high current capacity and mechanical robustness are required.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Ferrules and lugs differ significantly in industry standards and compliance requirements, with ferrules typically adhering to IEC 61210 standards for ensuring secure wire connections in electrical installations. Lugs comply with UL 486A-486B standards, which govern the performance and safety of wire connectors in industrial and commercial applications. Both components must meet strict certification criteria such as RoHS and REACH to ensure environmental safety and reliability within global supply chains.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Terminal Connector
Choosing between ferrules and lugs depends primarily on the application requirements and electrical parameters. Ferrules excel in providing secure, corrosion-resistant wire terminations for fine stranded wires in terminal blocks, ensuring reliable connections and easy maintenance. Lugs are better suited for heavy-duty applications involving larger cables and higher current loads, offering robust mechanical and electrical performance for industrial and power distribution systems.
Crimping
Crimping ferrules provides reliable wire end protection and improved conductivity, while crimping lugs ensures a secure connection with terminal equipment for high-current applications.
Barrel connector
Barrel connector ferrules provide secure wire termination by preventing strand fraying, while lugs offer durable mechanical connections ideal for high-current applications.
Insulated ferrule
Insulated ferrules provide enhanced electrical insulation and protection compared to lugs by securely terminating stranded wires and preventing wire strand fraying in electrical connections.
Ring lug
Ring lugs provide secure wire termination by encircling a screw or bolt, offering greater mechanical stability compared to ferrules, which primarily protect wire strands and improve insertion.
Bootlace ferrule
Bootlace ferrules provide secure wire termination by preventing strand fraying and ensuring consistent electrical contacts, distinguishing them from lugs which primarily offer mechanical and bolted connections.
Pin terminal
Ferrules provide a secure, insulated sleeve for stranded wire pin terminals, enhancing electrical contact and preventing wire strand fraying, while lugs offer robust mechanical connection with stronger mounting options but bulkier profiles.
Solder lug
Solder lugs provide a secure permanent connection by allowing wires to be soldered directly to terminals, offering superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength compared to ferrules.
Compression terminal
Compression terminals such as ferrules provide enhanced wire strand integrity and reliable electrical contact compared to lugs, which offer a solid connection but require larger installation space and often more complex crimping tools.
Wire termination
Ferrules ensure secure, corrosion-resistant wire termination by neatly bundling stranded wires, while lugs provide robust mechanical and electrical connections for larger gauge wires in high-current applications.
Mechanical connector
Ferrules provide enhanced wire strand containment and easier insertion in mechanical connectors, while lugs offer stronger, more durable termination ideal for high-current or heavy-duty applications.
Ferrule vs Lug Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com