RCDs (Residual Current Devices) are designed to protect against earth faults by detecting leakage currents, providing essential safety against electric shock. RCBOs (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) combine the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker, offering protection against both leakage currents and overloads or short circuits in a single device. Choosing between RCD and RCBO depends on the specific requirement for comprehensive protection at the circuit level or selective earth fault monitoring.
Table of Comparison
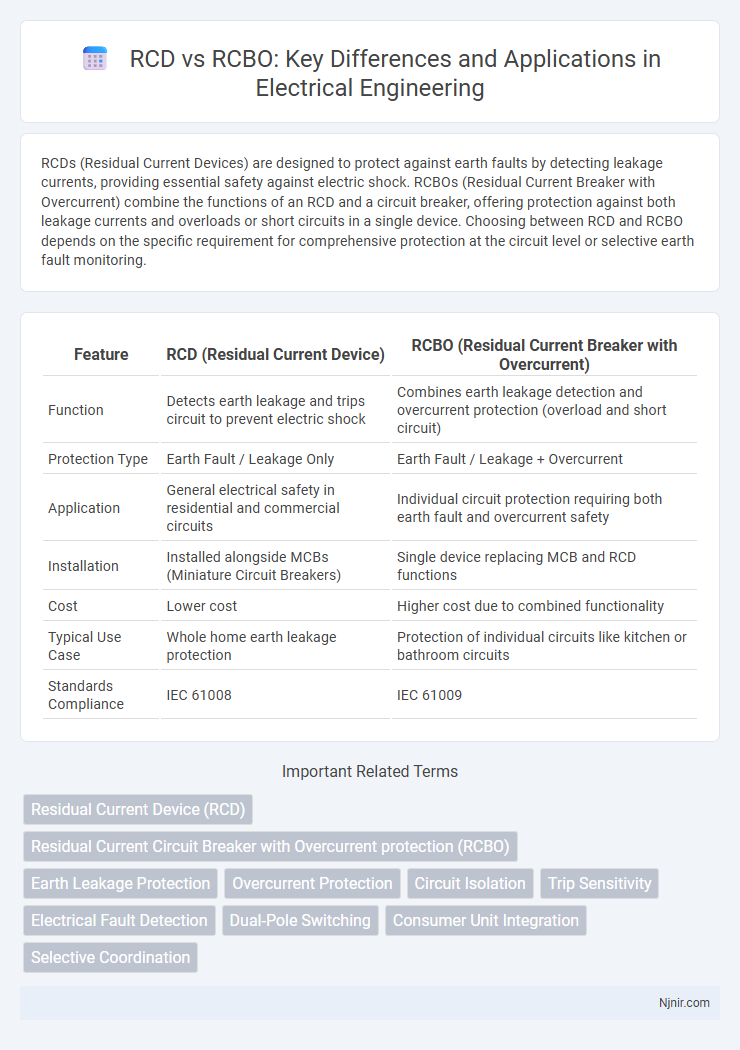
| Feature | RCD (Residual Current Device) | RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects earth leakage and trips circuit to prevent electric shock | Combines earth leakage detection and overcurrent protection (overload and short circuit) |
| Protection Type | Earth Fault / Leakage Only | Earth Fault / Leakage + Overcurrent |
| Application | General electrical safety in residential and commercial circuits | Individual circuit protection requiring both earth fault and overcurrent safety |
| Installation | Installed alongside MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) | Single device replacing MCB and RCD functions |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to combined functionality |
| Typical Use Case | Whole home earth leakage protection | Protection of individual circuits like kitchen or bathroom circuits |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 61008 | IEC 61009 |
Introduction to RCD and RCBO
RCD (Residual Current Device) detects earth leakage currents to prevent electric shocks by quickly disconnecting the power supply. RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) combines RCD's earth fault protection with overcurrent protection, safeguarding against both leakage currents and circuit overloads or short circuits. Both devices play crucial roles in enhancing electrical safety in residential and commercial installations.
Key Functions of RCDs
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) primarily detect earth leakage currents to prevent electric shock and fire hazards by disconnecting power when imbalance occurs between live and neutral conductors. Their key function is to provide life-saving protection against electrocution caused by current leakage, typically at a sensitivity of 30mA. Unlike RCBOs, RCDs do not provide overcurrent protection such as short circuit or overload, focusing solely on residual current monitoring for safety.
Key Functions of RCBOs
RCBOs integrate the functions of both Residual Current Devices (RCD) and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB), providing combined protection against earth faults and overcurrent conditions. They detect and interrupt leakage currents to prevent electric shocks, while also safeguarding circuits from overloads and short circuits. This dual functionality enhances electrical safety by consolidating protection mechanisms into a single device, making RCBOs essential for residential and commercial electrical installations.
Main Differences Between RCD and RCBO
RCD (Residual Current Device) primarily detects earth leakage currents to protect against electric shock, whereas RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent protection) combines earth fault detection with overcurrent and short circuit protection in a single device. RCDs are typically used solely for life safety by detecting residual currents above a set threshold, while RCBOs provide comprehensive protection by interrupting circuits during overload or fault conditions. The key difference lies in RCBOs offering dual functionality, enhancing circuit safety and reducing the need for separate protective devices.
Applications and Use Cases
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) are primarily used for general electrical safety to prevent electric shock by disconnecting power when a leakage current is detected, making them ideal for residential and light commercial applications. RCBOs (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) combine the functions of an RCD and a circuit breaker, protecting against earth faults, overloads, and short circuits, which suits industrial settings and critical circuits requiring both leakage and overcurrent protection. RCBOs are preferred in distribution boards where individual circuit protection and fault isolation enhance system reliability and minimize downtime.
Advantages of Using RCDs
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) offer superior protection against earth faults by detecting leakage currents as low as 30mA, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock and fire hazards in residential and commercial installations. They provide continuous monitoring of current flow, enabling rapid disconnection in fault conditions to enhance electrical safety. RCDs are simpler and more cost-effective compared to RCBOs, making them ideal for safeguarding circuits without overcurrent protection needs.
Advantages of Using RCBOs
RCBOs combine the functions of Residual Current Devices (RCDs) and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) to provide both earth fault protection and overload protection in a single unit, enhancing electrical safety and reducing wiring complexity. They enable precise fault isolation by protecting individual circuits, minimizing power disruption compared to RCDs that protect multiple circuits together. RCBOs improve system reliability and reduce downtime by preventing unnecessary tripping and allowing faster fault identification and resolution.
Installation Guidelines
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) should be installed in electrical circuits requiring protection from earth faults, ensuring they are correctly rated for the circuit's current and sensitivity, typically 30mA for personal protection. RCBOs (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) combine RCD and MCB functions, requiring careful selection based on load current, fault current, and application to provide both earth fault and overload protection in a single device. Installation guidelines emphasize proper wiring, adherence to manufacturer specifications, correct polarity, and testing post-installation to verify functionality and ensure electrical safety compliance.
Maintenance and Testing Procedures
RCDs require regular monthly testing using their built-in test button to ensure the device trips correctly under fault conditions, preventing earth leakage hazards. RCBOs combine residual current detection and overcurrent protection, necessitating both functionality tests for earth fault trips and periodic verification of overcurrent trip settings according to manufacturer guidelines. Maintenance procedures for RCBOs often involve infrared thermography and insulation resistance tests to detect potential degradation, ensuring reliability in both leakage and circuit protection.
Choosing Between RCD and RCBO
Choosing between an RCD (Residual Current Device) and an RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent) hinges on the specific protection needs of an electrical installation. An RCD primarily protects against earth faults and electric shocks by detecting leakage currents, while an RCBO combines this function with overload and short-circuit protection, offering comprehensive circuit safety. Opting for an RCBO is ideal for individual circuit protection in residential or commercial settings where precise fault isolation and enhanced safety are priorities.
Residual Current Device (RCD)
A Residual Current Device (RCD) is a safety device designed to quickly disconnect electrical circuits to prevent electric shocks caused by earth faults and leakage currents, offering essential protection that differs from the combined overload and earth fault protection provided by an RCBO.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection (RCBO)
RCBOs combine Residual Current Device (RCD) functionality with overcurrent protection, offering enhanced safety by detecting earth leakage currents and preventing overload or short circuits in electrical circuits.
Earth Leakage Protection
An RCD detects earth leakage currents exceeding 30mA to prevent electric shocks, while an RCBO combines earth leakage protection with overcurrent and short circuit protection in a single device for comprehensive safety.
Overcurrent Protection
RCBO combines RCD's earth fault detection with overcurrent protection, while RCD alone only provides residual current detection without safeguarding against overcurrents.
Circuit Isolation
RCD provides basic earth fault protection by detecting residual current, whereas RCBO offers combined earth fault and overcurrent protection with precise circuit isolation for improved safety and fault management.
Trip Sensitivity
RCBOs offer higher trip sensitivity by combining residual current detection with overcurrent protection, whereas RCDs detect only earth leakage currents without overcurrent trip functionality.
Electrical Fault Detection
RCBO combines residual current detection of RCD with overcurrent protection of MCB, enabling comprehensive electrical fault detection including earth faults and overloads.
Dual-Pole Switching
RCDs provide single-pole switching for residual current protection, while RCBOs offer dual-pole switching, enabling simultaneous disconnection of both live and neutral conductors for enhanced safety and compliance with electrical standards.
Consumer Unit Integration
RCBOs integrate both overload and residual current protection in a single device, enhancing Consumer Unit efficiency and safety compared to using separate RCDs and MCBs.
Selective Coordination
Selective coordination between RCD and RCBO devices ensures that only the faulted circuit is disconnected, maintaining power supply continuity and minimizing system downtime.
RCD vs RCBO Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com