Solder mask protects printed circuit boards by preventing solder bridges during assembly, enhancing electrical insulation and reducing corrosion risk. Conformal coating provides a protective barrier over the entire PCB assembly, guarding against moisture, dust, chemicals, and mechanical wear. Both are essential for increasing reliability, but solder mask is primarily focused on manufacturing precision while conformal coating ensures long-term environmental protection.
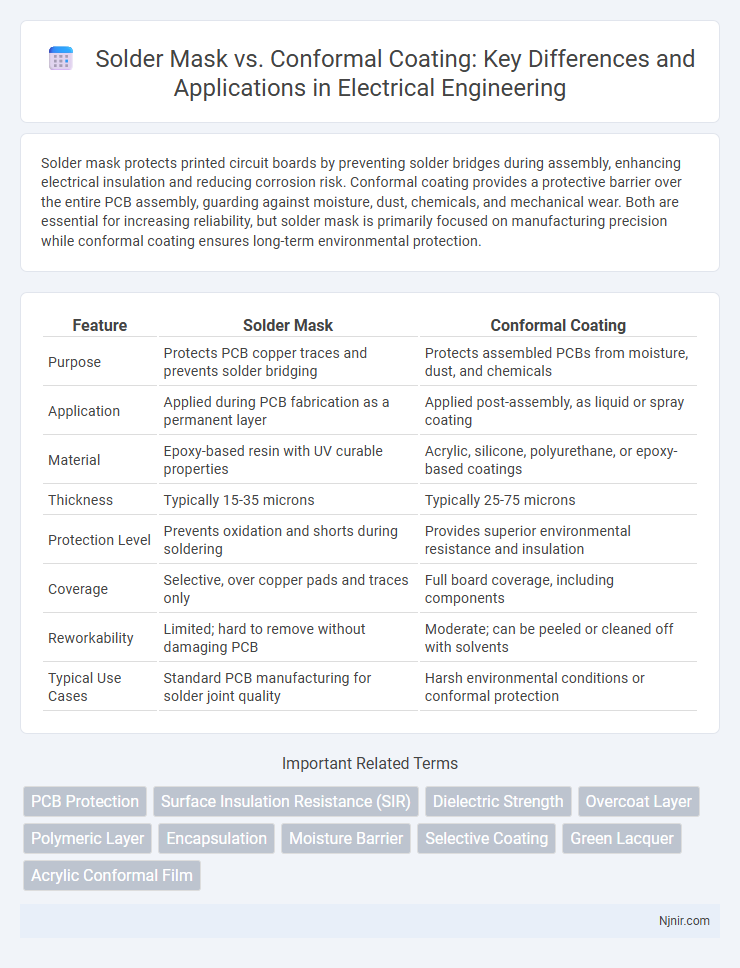
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Solder Mask | Conformal Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects PCB copper traces and prevents solder bridging | Protects assembled PCBs from moisture, dust, and chemicals |
| Application | Applied during PCB fabrication as a permanent layer | Applied post-assembly, as liquid or spray coating |
| Material | Epoxy-based resin with UV curable properties | Acrylic, silicone, polyurethane, or epoxy-based coatings |
| Thickness | Typically 15-35 microns | Typically 25-75 microns |
| Protection Level | Prevents oxidation and shorts during soldering | Provides superior environmental resistance and insulation |
| Coverage | Selective, over copper pads and traces only | Full board coverage, including components |
| Reworkability | Limited; hard to remove without damaging PCB | Moderate; can be peeled or cleaned off with solvents |
| Typical Use Cases | Standard PCB manufacturing for solder joint quality | Harsh environmental conditions or conformal protection |
Introduction to PCB Protection Methods
Solder mask and conformal coating are essential PCB protection methods safeguarding circuit boards from environmental damage, corrosion, and electrical shorts. Solder mask, a polymer layer applied during PCB fabrication, prevents solder bridging and shields copper traces, enhancing durability and reliability. Conformal coating, a thin protective film applied after assembly, offers additional protection against moisture, dust, and chemicals, ensuring long-term performance in harsh operating conditions.
What is Solder Mask?
Solder mask is a protective polymer layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) to prevent solder bridges during assembly and protect against environmental damage like moisture and contaminants. It enhances the electrical insulation between conductive areas, ensuring reliable circuitry and reducing short circuits. Commonly green, solder mask is essential for maintaining PCB integrity and improving manufacturing yield.
Overview of Conformal Coating
Conformal coating is a protective chemical layer applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) to shield components from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature variations. Unlike solder mask, which primarily insulates copper traces and prevents solder bridging during assembly, conformal coatings provide environmental protection and enhance the reliability of electronic devices in harsh conditions. Common materials for conformal coating include acrylics, silicones, polyurethanes, and epoxies, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific application requirements.
Material Composition and Properties
Solder mask is typically composed of epoxy or polymer materials designed to insulate and protect PCB copper traces from oxidation and solder bridges, featuring high thermal and chemical resistance suitable for soldering processes. Conformal coating consists of thin dielectric materials such as acrylic, polyurethane, silicone, or epoxy, providing moisture, dust, and chemical protection with flexibility and dielectric strength to withstand environmental stress. The distinct compositions influence their physical properties: solder masks offer robust mechanical protection and solder resistivity, while conformal coatings deliver adaptability and comprehensive surface protection across diverse PCB geometries.
Application Processes Compared
Solder mask is applied using screen printing or photolithography techniques, ensuring precise coverage on PCB surfaces to prevent solder bridging during assembly. Conformal coating is typically applied via spray, dip, or selective coating, forming a protective layer against moisture, dust, and chemicals on fully assembled boards. The solder mask process is integrated early in PCB fabrication, while conformal coating is a post-assembly step focused on environmental protection.
Functionality and Protective Roles
Solder mask serves as a protective layer on printed circuit boards (PCBs) that prevents solder bridges and short circuits by insulating copper traces during soldering processes. Conformal coating provides a thin, protective film that shields electronic assemblies from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature variations, enhancing durability and reliability. Both materials play critical roles in safeguarding electronic components, with solder mask primarily focusing on electrical isolation during manufacturing, while conformal coating offers long-term environmental protection.
Pros and Cons of Solder Mask
Solder mask provides excellent protection against solder bridges, oxidation, and short circuits on printed circuit boards (PCBs), promoting reliable electrical performance and ease of assembly. Its limitations include reduced flexibility and potential damage under mechanical stress or thermal cycling, which can lead to cracks and compromised protection. Compared to conformal coatings, solder mask offers robust masking during soldering but lacks the comprehensive environmental sealing provided by conformal coatings.
Advantages and Limitations of Conformal Coating
Conformal coating offers superior protection for printed circuit boards (PCBs) against moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature variations, enhancing circuit reliability and lifespan. Its flexibility allows application on complex geometries and detailed components, which solder mask cannot cover effectively. However, conformal coatings can be more expensive, require precise application techniques, and may complicate rework or inspection processes compared to solder masks.
Typical Use Cases and Industry Standards
Solder mask is primarily used in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing to protect copper traces from oxidation and prevent solder bridges during assembly, adhering to IPC-4552 standards. Conformal coating provides environmental protection for assembled PCBs against moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants, conforming to IPC-CC-830 industry standards. Typical applications for solder mask include high-density PCB designs in consumer electronics, while conformal coating is favored in automotive, aerospace, and industrial electronics requiring harsh environmental resistance.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your PCB
Choosing the right solution for your PCB involves understanding the distinct protective roles of solder mask and conformal coating. Solder mask provides essential insulation and prevents solder bridges during assembly, making it ideal for standard manufacturing processes, while conformal coating offers superior environmental protection against moisture, dust, and chemicals, suitable for harsh operational conditions. Evaluating factors such as exposure risks, electrical insulation needs, and application complexity ensures optimal PCB reliability and longevity.
PCB Protection
Solder mask provides essential PCB protection by preventing solder bridges and corrosion during assembly, while conformal coating offers superior environmental shielding against moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants for long-term durability.
Surface Insulation Resistance (SIR)
Solder mask provides higher Surface Insulation Resistance (SIR) than conformal coating, enhancing PCB protection against electrical leakage and corrosion.
Dielectric Strength
Solder mask typically offers a dielectric strength of 20-40 kV/mm, while conformal coatings provide higher dielectric strength ranging from 50-100 kV/mm, making conformal coatings more effective for electrical insulation in high-voltage applications.
Overcoat Layer
The overcoat layer in solder mask provides precise circuit protection and solder resistance, while conformal coating offers broader environmental sealing and moisture resistance on PCB assemblies.
Polymeric Layer
Solder mask and conformal coating are both polymeric layers applied to PCBs, with solder mask primarily protecting copper traces during soldering and conformal coating providing comprehensive environmental protection against moisture, dust, and chemicals.
Encapsulation
Solder mask provides basic PCB protection by preventing solder bridges and corrosion, while conformal coating offers comprehensive encapsulation that shields electronic circuits from moisture, dust, chemicals, and thermal stress.
Moisture Barrier
Solder mask provides basic moisture barrier protection on PCB surfaces, while conformal coating offers superior, comprehensive moisture resistance for enhanced environmental protection.
Selective Coating
Selective coating techniques in PCB manufacturing prioritize solder mask application over conformal coating for precise protection and improved electrical performance on exposed areas.
Green Lacquer
Green lacquer solder mask provides precise circuit insulation and protection, whereas conformal coating offers flexible environmental resistance but lacks the defined application precision of solder mask.
Acrylic Conformal Film
Acrylic conformal film offers superior moisture protection and flexibility compared to traditional solder mask, enhancing PCB durability in harsh environments.
Solder Mask vs Conformal Coating Infographic
 njnir.com
njnir.com